Table of contents
- What is personal information сompromise
- How online activity reveals your personal information
- What is most frequently exposed type of personal information
- Why you should be concerned if your information is compromised
- Signs that your personal information may be compromised
- 1. Unauthorized financial activity
- 2. Login attempts from unknown location
- 3. Password reset emails you didn’t request
- 4. Emails or messages about new account registrations
- 5. Sudden increase in spam calls or phishing emails
- 6. Unexplained changes to security settings
- How to check if your personal data has been breached
- 1. Review your digital footprint at a glance
- 2. Check your data breach history
- 3. Find out if your email leaked
- 4. Check your account info
- 5. Check if your password was exposed
- 6. Find out if your Email is on the Dark Web
- 7. Check if someone is impersonating you on social media
- What to do if your personal information is compromised
- 1. Change your passwords immediately
- 2. Confirm if your info was exposed in a data breach
- 3. Determine what information was stolen
- 4. Notify affected organizations
- 5. Enable two-factor authentication
- 6. Place fraud alert or credit freeze
- 7. Monitor suspicious activity and transactions
- 8. Report the attack
- 9. Check your account closely
- 10. Secure online identity
- 11. Use identity theft and data breach protection
- Conclusion
What is personal information сompromise
If your personal information has been compromised, it means that someone has unauthorized access to some of your data. That might mean passwords, email addresses, social security numbers, banking info, or other sensitive details.
Hackers might gain data by running phishing scams, using spying tools, or getting into a company’s database. Unfortunately, even big organizations can be at risk—the Equifax data breach exposed around 147 million people’s details in November 2024.
Sometimes, criminals take your data for their own use and publish it online or share it with others.
Some types of data harvesting are legal, like using tracking cookies or browser fingerprinting, but stealing and using private information such as banking details or social security numbers isn’t.
How online activity reveals your personal information
Here's how your online activities might lead to personal information leakage:
- Online shopping: payment details, delivery address, purchasing habits.
- Social media: photos, location tags, and contacts.
- Search engines: searches, interests, and auto-saved passwords.
- Apps and devices: dating, delivery, transportation apps, and smart home devices all store sensitive data and might be used for cyberattacks.
What is most frequently exposed type of personal information
Certain types of personal information are especially valuable to cybercriminals. These include:
- Email addresses: for spam or phishing attacks.
- Passwords: to access your accounts.
- Credit card numbers: to commit financial fraud.
- Social Security Numbers (SSN): used in identity theft schemes.
- Phone numbers: used for scams, phishing, or identity validation hacks.
- Social media details: photos, posts, and followers can be used in social engineering attacks.
Why you should be concerned if your information is compromised
So, what can hackers do with your personal information? If your information is compromised, hackers can use it for the following malicious purposes:
- Identity theft: impersonate you to open fake bank accounts.
- Financial fraud: drain your accounts.
- Credit history damage: illegally opened accounts can damage your credit profile.
- Social engineering attacks: manipulate your contacts to make money transfers, etc.
Signs that your personal information may be compromised
So, how do you know if your data was breached? Fortunately, there are sometimes signs of a data leak.
How to tell if your personal info has been compromised:
- Unauthorized financial activity—perhaps unexpected charges on your credit card or bank transactions.
- Unusual activity on your online accounts—perhaps from locations you’ve never visited or at times when you weren’t online. This could also include suspicious login attempts.
- Password reset emails you didn’t request—or changed passwords.
- New accounts set up in your name—you might receive activation emails or letters
- about new credit cards, for example.
- An increase in spam calls or phishing emails—your contact details may have been leaked.
- Changed security settings—perhaps you no longer need to use multi-factor authentication, or you don’t need to enter your password every time you access an online account.
I’ll explain a little more about some of these signs of a data breach in a moment.
But first, if you notice any of these signs, you should check if your personal information has been compromised.
There are a few ways you can do this, but I like to use a data breach monitoring service. Clario Anti Spy’s Data breach monitor lets you scan for data breaches involving your email addresses with just a few taps. It checks databases of leaks constantly, and alerts you as soon as it finds your information.
How to check whether your information is compromised:
- Download Clario Anti Spy and subscribe.
- Open the app, and, under Data breach monitor, tap Scan.
- Enter your email address.
- When the scan is complete, follow the on-screen guidance to review any data breaches.
- Repeat the process for any other email addresses.
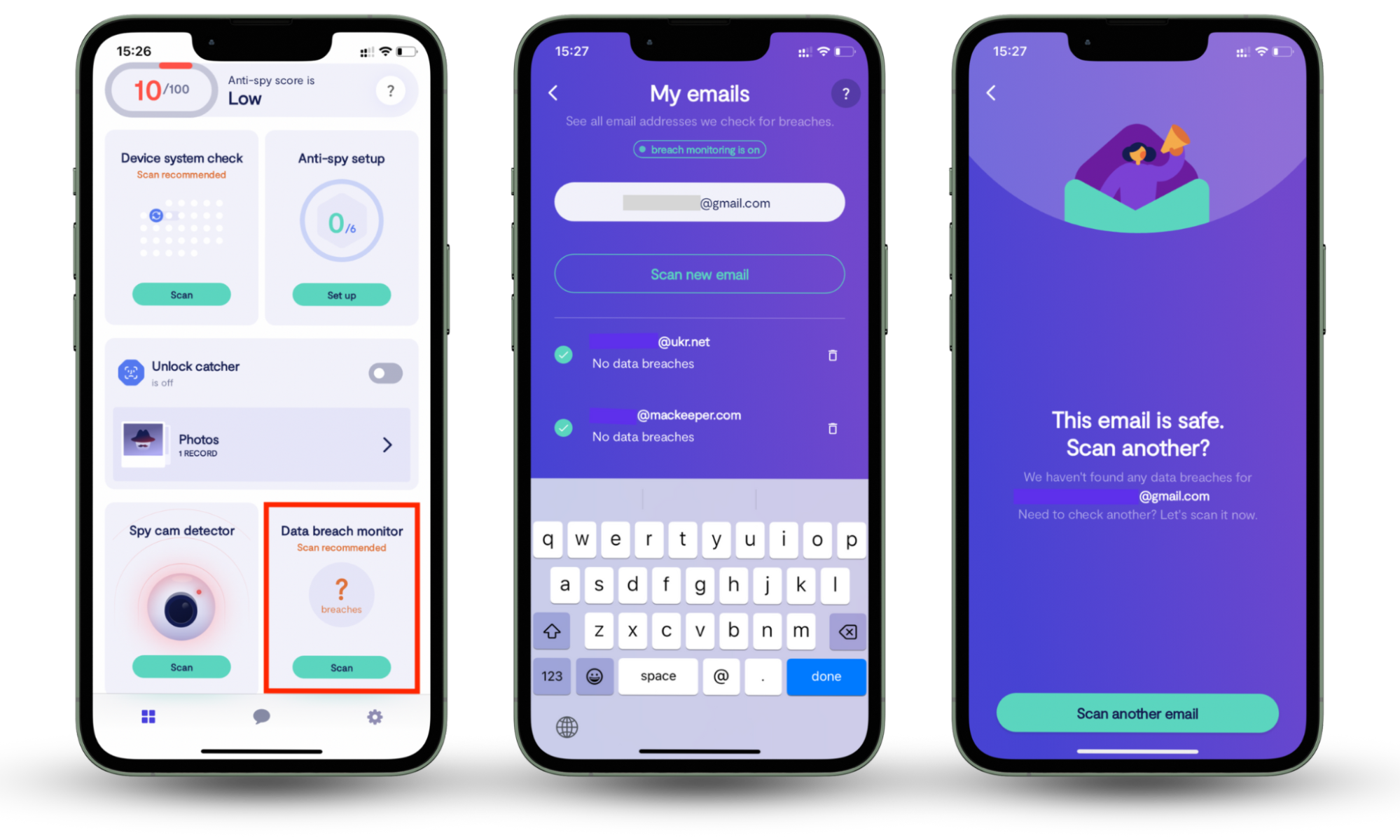
Now, let’s talk about some of the ways to know if your information has been leaked.
1. Unauthorized financial activity
Have you noticed unexpected charges, withdrawals, or other transactions? This could be a sign that your bank details are compromised.
Check your bank transactions regularly, and alert your bank immediately if you see anything unexpected.
Maybe someone has your card information, and they’re spending your money—or applying for credit in your name.
2. Login attempts from unknown location
Have you received emails or text alerts saying someone has tried to log in to one of your online accounts? Or maybe you’re locked out of an account because of too many unsuccessful login attempts.
If you haven’t tried to log in recently, this could be a sign that someone’s trying to get unauthorized access.
Alternatively, check when your account was last accessed. Look at the time and location—if it’s somewhere you’ve never been, or when you weren’t online, it could be a sign that someone has unauthorized access.
3. Password reset emails you didn’t request
Have you received an email saying that you’ve requested a password reset? This can be a way to check if your personal information has been compromised.
If you didn’t request a password reset but you’ve received an email, there are two possibilities:
- Someone genuinely made a password reset request but mistyped their own email address.
- Someone knows your email address and is trying to reset your password.
The email may explain what to do if you didn’t request a password reset.
If you didn’t request a password reset, don’t click on any links in the email. It could be a phishing scam rather than a genuine password reset email.
If you’re worried about the security of your email account, find out how to check if your email was hacked.
4. Emails or messages about new account registrations
Have you received emails or letters about your new accounts? Maybe they’re online accounts—or even new credit cards or bank accounts.
If you haven’t signed up for anything new and you’ve received one of these emails, it could be a way to know if your information has been leaked.
You might even receive debt collection letters. Perhaps someone has taken out a line of credit in your name, and payments are due.
5. Sudden increase in spam calls or phishing emails
Are you getting more spam calls or emails than usual?
Whether this unwanted contact is coming to your cell, landline, email, or even home address, it could be a sign that your personal details have been leaked or sold online.
6. Unexplained changes to security settings
To keep your online accounts safe, it’s a good idea to use multi-factor authentication (sometimes also called two-factor authentication) where possible. If you used to have these security protocols set up and they’ve been removed from your account, this could be a sign that someone has unauthorized access.
You might also notice that someone has changed your recovery phone number or email address.
How to check if your personal data has been breached
There are methods and even tools that can help you check if your personal information has been stolen. Below, we listed several steps to identify breaches and strengthen your cybersecurity measures.
1. Review your digital footprint at a glance
Look through the platforms, websites, and services where you shared your data. If you have accounts you don't use anymore, consider deleting them.
2. Check your data breach history
Clario Anti Spy's Data breach monitor lets you scan for data leaks related to your email addresses. It checks databases for personal information leaks and notifies you as soon as it finds your information.
3. Find out if your email leaked
Email leaks often lead to phishing attacks. Say alert for any unfamiliar subscriptions or a sudden surge in spam emails.
4. Check your account info
Check for suspicious login attempts by reviewing your account activity log. Google and Facebook, for instance, allow users to see active sessions and all devices connected to their accounts.
5. Check if your password was exposed
LastPass or Dashlane tools automatically scan the web for data breaches involving your stored passwords. In case a personal information leakage happens, they will alert you so you'll have the chance to update those credentials immediately.
6. Find out if your Email is on the Dark Web
If stolen, your information can be traded somewhere in the hidden corners of the internet. Fortunately, services like Norton 360 or Identity Guard include dark web scanning features.
7. Check if someone is impersonating you on social media
Is your personal information compromised? Type in your name or use Google Photo search to check if anyone is mimicking your identity. In case you find such, report it to the platform immediately.
What to do if your personal information is compromised
So now you know how to check if your personal information has been compromised. But what are the next steps you should think about?
After you’ve followed these tips, I’d recommend that you check the security of your computer and other devices, too. After all, they could have been compromised as well. Find out how to use a code to check if your phone is hacked.
1. Change your passwords immediately
If you suspect that scammers know your passwords, change them immediately.
You’ll probably need to do this on multiple websites, and it can be time-consuming—but it’s crucial to protect your identity.
Tips for choosing a safe new password:
- Don’t repeat passwords.
- Avoid using a word or number that’s easy for someone to guess, like your birthday or child’s name.
- Use letters, numbers, and special characters to make your password more secure.
- Don’t write your passwords down and leave them somewhere they could be found.
Enable multi-factor authentication where possible as well. This ensures that even if someone guesses your password, they can’t easily access your account.
2. Confirm if your info was exposed in a data breach
Start by checking whether your data was indeed leaked and what type of information was exposed (use the tools we discussed above). Check your emails and spam folder for breach alerts.
3. Determine what information was stolen
Understanding what was compromised is necessary for quick risk mitigation. For instance, if your financial data is leaked, you should report this to your bank as soon as possible so that there's time to protect your funds.
4. Notify affected organizations
If you suspect that the leak came from one account, you should contact them. When a company is involved in a data breach, it should contact affected users and explain what they should do next.
If your accounts at specific organizations have been compromised or hacked, you may also need to contact them. If you have been a victim of your personal information breach, you may be eligible to sue the company for financial loss or emotional distress.
This might include:
- Asking online retailers to cancel orders or close an account
- Contacting your bank to recover stolen money or freeze a card
- Telling your employer or clients that their data may also be compromised
Find out what to do if someone has your Social Security Number.
5. Enable two-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication can help prevent your accounts from exposing personal information when attacked via ransomware or other type of malware. So, even if your login credentials were compromised, hackers will not be able to access your accounts without the second verification step.
6. Place fraud alert or credit freeze
If you’re in the US, you can place a fraud alert or freeze your credit with the three major credit bureaus: Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion.
This means there are some extra identity verification steps if anyone tries to take out a line of credit in your name, stopping criminals from ruining your finances.
If you live elsewhere, there may be similar processes available. Contact your bank, building society, or credit union for advice.
7. Monitor suspicious activity and transactions
Keep a close eye on your credit card statements and account activity. Look for the following red flags:
- Unknown charges on your credit card
- Unauthorized withdrawals from your bank accounts
- Login attempts from unrecognized locations or devices
- Services bills you didn't authorize.
8. Report the attack
If your personal information has been exposed, you can file a report at IdentityTheft.gov. In case of financial fraud, inform your bank and file a dispute for fraudulent transactions.
9. Check your account closely
Once the data has been leaked, it can be sold on the dark web and used for further attacks. So, continue to closely monitor your account's activity even after you have regained control over them.
10. Secure online identity
Follow these simple yet powerful online security practices to avoid exposing personal information:
- Regularly update your OS, browser, and antivirus software.
- Revoke permissions for apps and websites you no longer use.
- Avoid storing passwords or payment data in browsers.
11. Use identity theft and data breach protection
Use dedicated services that monitor the dark web and alert you of breaches involving your personal details.
Conclusion
Everyone should know how to check if their personal information has been compromised. Whether criminals are trying to steal money, commit identity theft or fraud, or publish your personal details online, being the victim of a data breach can be awful.
Clario Anti Spy makes it easy to know if your information has been leaked. The app’s Data breach monitor helps you check for stolen details with just a few taps, and reports back if there are any threats to your privacy.


