Table of contents
- What are phishing scams?
- Top of biggest phishing scams
- 1. Facebook and Google
- 2. FACC
- 3. Crelan Bank
- 4. Sony Pictures
- 5. Upsher-Smith Laboratories
- 6. Colonial Pipeline
- 7. Ubiquiti Networks
- Popular phishing scams
- 1. Email phishing
- 2. Voice phishing (vishing)
- 3. Spear phishing
- 4. HTTPS phishing
- 5. Smishing
- 6. Evil twin phishing
- 7. Man-in-the-middle
- 8. Website spoofing
- 9. Angler phishing
- 10. Search engine phishing
- 11. Watering hole phishing
- 12. Deceptive phishing
- Conclusion
The largest phishing attacks include:
- Email phishing
- Voice phishing (vishing)
- Spear phishing
- HTTPS phishing
- Smishing
- Evil twin phishing
- Man-in-the-middle
- Website spoofing
- Angler phishing
- Search engine phishing
- Watering hole phishing
- Deceptive phishing
- Amazon scams
- Temu scams
- iCloud scams
- Social engineering
- CEO fraud
- Clone phishing
- Check fraud
- DNS spoofing
- Blackmail scams
- Romance scams
- Fake websites
- Charity scams
- Pharming scams
- Topical scams
- Tech support scams
What are phishing scams?
Phishing scam definition
A phishing scam occurs when an attacker uses deceptive tactics to convince or trick a victim into providing their sensitive information over the phone or the Internet. Email phishing is currently one of the most common phishing scams, although attackers use various types of online scams to deceive victims, some of which we’ll explore below.
What's really dangerous about phishing is that hackers can send fraudulent emails to you pretending to be someone you know. These emails often contain malicious links, which, when clicked on, may install malware on your device. The outcome of such attacks can be identity theft, financial losses, data breaches, reputational harm, and other worrisome issues.
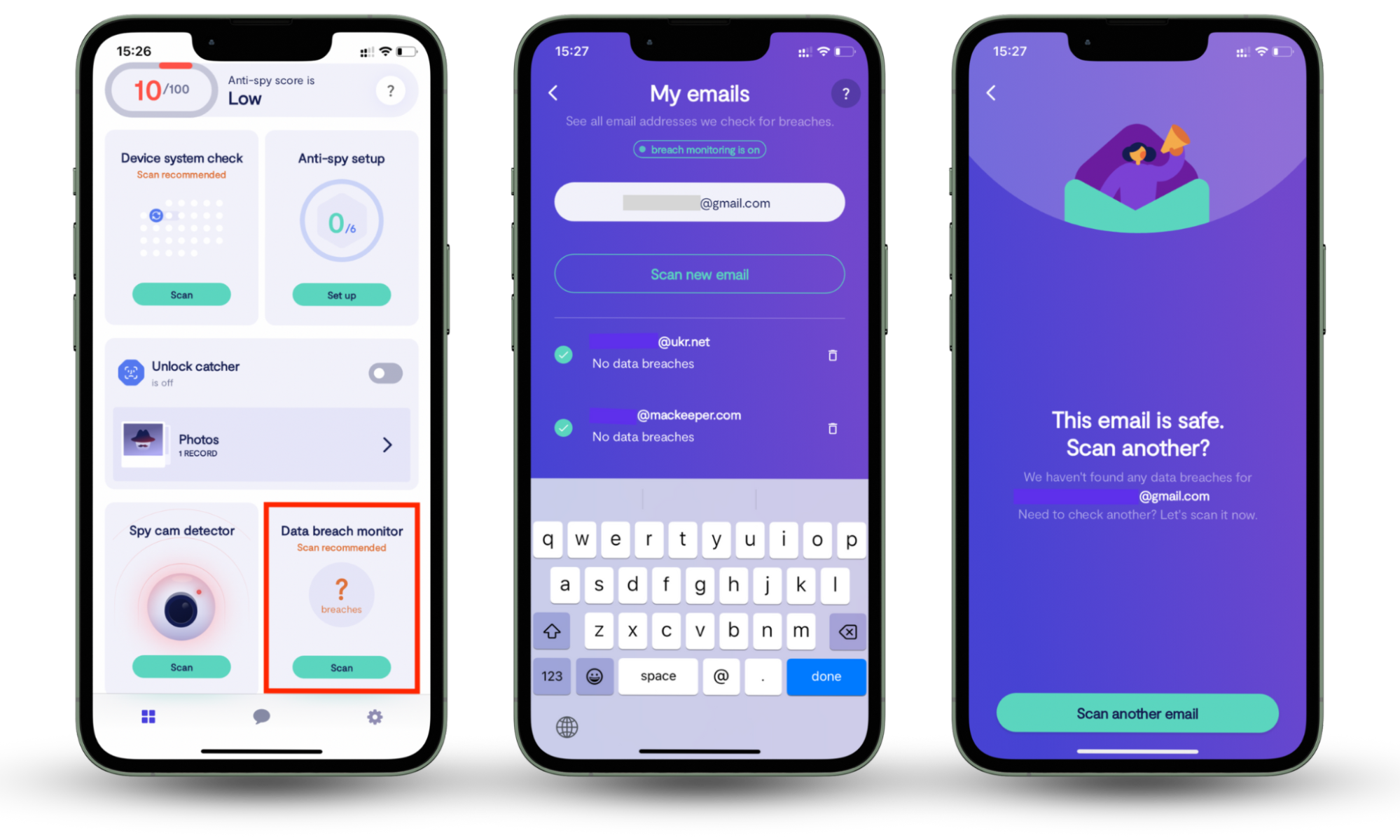
To protect yourself from phishing scams, especially email phishing, you need to first check whether your email has been compromised. This is important because when your email ends up in a database of stolen emails, it immediately puts you at risk of phishing attacks. Clario Anti Spy can help you check if your email was compromised. Our mobile app has a unique, powerful tool called Data breach monitor that scans your email and shows the list of found breaches (if there are any). It checks which of your online accounts are accessible to spies, allowing you to fix leaks asap. It also stays on guard 24/7, continuously monitoring your data safety.
Here’s how to start with Clario Anti Spy’s Data breach monitor:
- Install Clario Anti Spy and set up an account.
- Open the app and go to the Data breach monitor feature.
- Tap Scan and enter your email.
- Wait for the results.
Cybercriminals don’t have to know their targets. They leverage the data they have to steal your information or money. This data includes your:
- Email address
- Cell phone number
- Social media profile or handle.
In addition, they include whatever sensitive information they’ve obtained about you or assume about you to try to convince you that they are legitimate.
For example, let’s say an attacker obtained your email address from a data breach. Assuming you use online baking systems like most people, they would contact you via your leaked email address to “update” your bank account details. However, obliging would result in a loss of funds.
Top of biggest phishing scams
Businesses are not immune to phishing. Here are the largest organizations tainted by phishing scam scandals resulting in millions of dollars in losses in recent years:
- Facebook and Google
- FACC
- Crelan Bank
- Sony Pictures
- Upsher-Smith Laboratories
- Colonial Pipeline
- Ubiquiti Networks
In the sections below, we will detail seven notable phishing attacks in which attackers scammed large businesses out of millions of dollars. Each case demonstrates the methods scammers use to deceive and, ultimately, con even their victims.
1. Facebook and Google
Between 2013 and 2015, Lithuanian attacker Evaldas Rimasauskas defrauded tech giants Facebook and Google out of more than $100 million in an elaborate fake invoice scam.
Rimasauskas and his co-conspirators achieved this by posing as employees representing Quanta, a Taiwan-based vendor shared by the two companies. Together, they sent fake invoices from bogus email accounts. Facebook and Google paid the invoices into several bank accounts opened and controlled by Rimasauskas.
As detailed in a press release from the US Attorney's Office of the Southern District of New York, Rimasauskas pled guilty and forfeited half of the funds stolen.
2. FACC
In 2016, aerospace and defense company FACC lost millions of dollars to a phishing scam. Attackers succeeded by posing as the company’s CEO, Walter Stephan, and requesting an employee transfer $61 million to a specified bank account for a fake project. The employee obliged, costing the company millions of dollars in losses.
The request was later revealed to have been a scam. While limited details were disclosed about it, FACC partially blamed and fired the CEO after launching an internal investigation. FACC failed in Austrian courts to sue its executives for $11 million.
3. Crelan Bank
About a month after the FACC scam, Belgium’s Crelan bank lost approximately $75.8 million in a CEO fraud or business email compromise scam, according to The Brussels Times. In this attack, scammers spoofed the CEO’s email account, requesting employees to transfer funds to their bank account. Crelan uncovered the fraudulent scheme through internal audits and claims none of its clients were affected.
4. Sony Pictures
In 2014, a hacking incident linked to a state-sponsored North Korean group cost Sony Pictures approximately $100 million. The hacking group, Guardians of Peace, compromised Sony Pictures by sending its senior executives fake Apple emails asking them for ID verification emails and directing them to a site to obtain their login details.
As a result, Sony Pictures’ scammers stole and leaked 100 terabytes of data relating to Sony's private correspondence, unreleased films, and details about its employees and their relatives. Furthermore, attackers leveraged malware to erase Sony Pictures’ computer infrastructure.
The hacking group’s true motives appeared to be retaliation against Sony Pictures’ upcoming release of the film The Interview, which ridicules North Korean leader Kim Jong-un. According to Deadline, Sony Pictures’ momentous breach involved the US’ top government officials and entities, including the:
- US President
- Congress
- State Department
- CIA
- FBI
- Department of Homeland Security
5. Upsher-Smith Laboratories
In 2014, drug company Upsher-Smith Laboratories was compromised in a business email compromise scam. During the phishing scam, attackers posing as the CEO requested the accounts payable coordinator to follow his lawyer’s instruction and transfer $50 million.
The accounts payable coordinator responded by initiating wire transfers through the company’s bank, Fifth Third Bank. However, after discovering the scam, Upsher-Smith Laboratories recalled a $39 million wire transfer and, according to Fox 9, sued the bank for damages.
6. Colonial Pipeline
In May 2021, American fuel supplier Colonial Pipeline fell victim to a ransomware attack at the hands of the hacking group DarkSide, compromising its billing system and billing network and crippling its operations. DarkSide attackers accessed an employee’s password, likely through a phishing attack, and infected the company’s system with malicious software. Colonial Pipeline paid the attackers $4.4 million in exchange for the decryption key. However, the cost of the attack reached far beyond finances.
As a result of the ransomware attack, Colonial Pipeline systems went offline for a week, failing to deliver approximately 20 billion gallons of oil and spreading panic throughout the US East Coast—a consequence that DarkSide claimed it did not intend to achieve.
7. Ubiquiti Networks
In 2015, wireless products maker Ubiquiti Networks fell victim to a business email compromise scam costing it $46.7 million. Forbes reports that fraudsters impersonated Ubiquiti Networks lawyer and CEO Robert Pera in a series of emails, instructing the chief accounting officer to make several wire transactions relating to a confidential acquisition. Scammers reached out from email addresses ending with @consultant.com and another email account appearing as a corporate email.
Over the course of 14 days, Ubiquiti Networks’ chief accounting officer made 14 wire transfers to accounts in China, Poland, Hungary, and Russia. The company halted future transfers when the FBI alerted it about its Hong Kong bank account being compromised.
Popular phishing scams
Knowing what types of phishing attacks exist is the first step toward protecting yourself. The most popular phishing scams include:
- Email phishing
- Voice phishing or vishing
- Spear phishing
- HTTPS phishing
- Smishing or SMS phishing
- Evil twin phishing
- Man-in-the-middle
- Website spoofing
- Angler phishing
- Search engine phishing
- Watering hole phishing
- Deceptive phishing
The phishing attacks described above underscore companies’ failure to identify and halt attacks, even though some involve minimal sophistication. While you can’t completely avoid phishing emails or spam, you can certainly empower yourself to identify them. In the section below, we will describe the 12 popular phishing attacks to help you identify them and avoid becoming a victim.
1. Email phishing
Phishing emails are scams in which attackers send you bogus emails asking for your personal details. In many cases, attackers pose as representatives from a legitimate company, such as Apple, to gain your trust. In the email, they require you to respond with sensitive information or click on a link redirecting you to a malicious website to steal your data. Check whether your data has been compromised using to protect yourself from email phishing.
2. Voice phishing (vishing)
Voice phishing or vishing entails a scammer calling you to ask for your personal details or money. Fraudsters take advantage of the latest technology that allows them to spoof caller IDs to appear as a legitimate caller. Typically, they create a sense of urgency to appear authoritative and prevent you from thinking clearly. A popular scenario involves a scammer calling an elderly victim posing as their grandchild and asking them for thousands of dollars for an emergency.
3. Spear phishing
Spear phishing attacks are more sophisticated. Criminals use publicly available information to target specific individuals in organizations. During such attacks, fraudsters contact employees with an unusual request, pretending to be someone else, like a company executive.
4. HTTPS phishing
Hypertext transfer protocol secure (HTTPS) phishing occurs when an attacker tricks you into clicking a link to a fake or malicious site. Attackers steal your information when you enter it into the site. In the past, HTTPS was enabled to protect users from cybercrime. Nowadays, cybercriminals trick unsuspecting victims by obtaining HTTPS certificates for free and adding them to their sites.
5. Smishing
SMS phishing or smishing is a form of phishing whereby fraudsters send you an unsolicited SMS with links or attachments aimed at stealing your personal information. Like vishing, hackers pose as an authentic source, presenting a fake scenario to convince you to take action. For example, they can announce that you’ve won a prize and prompt you to click the link provided to claim it.
6. Evil twin phishing
Evil twin attacks take advantage of unsuspecting Wi-Fi users. Attackers set up a fake, unsecured Wi-Fi network and steal the information of anyone who logs in to it and enters their information, including financial information.
7. Man-in-the-middle
Man-in-the-middle attacks occur when attackers intercept communication between two individuals. Posing as the middleman, the scammer controls the correspondence and tricks the two parties into believing they are communicating with each other. Doing so allows the attacker to gain and exploit sensitive information from both parties.
8. Website spoofing
In website spoofing attacks, cybercriminals create fake websites resembling real ones, including similar elements such as brand colors, graphics, texts, and more. Attackers steal your information when you use it to log in to a site. Website spoofing works because users typically don’t check the authenticity of the websites they visit or check various website elements, which usually include some discrepancies. That’s where anti-spying protection proves helpful.
9. Angler phishing
Angler phishing attacks exploit your vulnerability. Attackers typically find you through comments or complaints you’ve posted on a company’s social media page or comments section. They approach you by posing as customer service agents, offering to help resolve the issue. During the interaction, the attackers request that you confirm your details and provide a link to click on. However, clicking on the link results in your device getting infected with malicious software, compromising your privacy.
10. Search engine phishing
Scammers involved in search engine phishing attacks lure victims using search engine optimization (SEO) tactics. They create pages loaded with high-value keywords to rank high on popular search engines, increasing the likelihood that you’ll see and click on them. When you do, you’re prompted to enter your sensitive information, such as your banking details, compromising them. Search engine phishing scams are characterized by hard-to-miss offers that are known to catch people’s attention, such as giveaways.
11. Watering hole phishing
In watering hole phishing attacks, scammers target individuals or organizations by exploiting vulnerabilities in the third-party websites they frequent. After infecting the website with malware, cybercriminals send victims emails luring them to it, compromising them, and gaining access to their system and network.
12. Deceptive phishing
Deceptive phishing attackers use deceptive technology to target victims. They trick you into clicking on a link by posing as a legitimate company reporting a cyberattack. However, clicking on the link infects your device with malware.
Conclusion
Phishing scams are deceptive attacks designed to steal your information and defraud you out of your money. Knowing the tricks and tactics used by cybercriminals is the first step toward phishing detection and prevention.
The second step is staying alert, looking out for signs of phishing, and using cybersecurity measures to safeguard yourself. The best approach includes using anti-spying tools to protect your data. Use Clario Anti Spy’s Data breach monitor to scan for email leaks and fix breaches before more damage is done.


