Table of contents
- What is a zero-day attack?
- What are the most infamous zero-day attack examples?
- Why are zero-day attacks so dangerous?
- Zero-day attacks in 2025
- How to stay safe from zero-day attacks?
- Use a firewall
- Always update operating systems
- Limit application privileges on mobile devices
- Stay informed of the latest cybersecurity news
- Only utilise essential applications
- Conclusion
Zero-day attacks exploit vulnerabilities in software or hardware discovered before developers have had a chance to create a fix. Users are potentially put at risk as there is limited protection against any quick-witted cybercriminals looking to exploit this security flaw for their own ends.
Recently, thousands of companies were caught up in the zero-day attacks on the Microsoft Exchange server, prompting the tech giant customers to issue recommendations and guidance for users to help them avoid the online commotion.
Elsewhere, Apple has been forced to rush out an update to macOS Big Sur 11.3 to provide a patch for a recently uncovered vulnerability.
While macOS Big Sur 11.3 was relevant at the time, zero-day vulnerabilities continue to affect modern systems today, including recent versions of macOS, iOS, Android, and Microsoft cloud services. This shows that even fully supported and regularly updated platforms remain exposed to zero-day risks.
It sounds worrying but don’t panic as zero-day attack prevention can be enhanced by following some simple steps. Here we will explore:
- What is a zero-day attack?
- What are the most famous zero-day attack examples?
- Why are zero-day attacks dangerous?
- How to prevent zero-day attacks
Pro tip
While zero-day attacks target unknown vulnerabilities in your software and devices, an all-round cybersecurity solution like Clario can cover most of the known gaps. Test it out now by downloading Clario Anti Spy. And read on to know how to avoid getting harmed by a zero-day attack.
What is a zero-day attack?
A zero-day exploit is a cyberattack that occurs on the same day a vulnerability is discovered in a software.
This attack targets this lack of defense before a fix is made available by a service’s company.
Users will often report a bug or vulnerability to a developer, then an update will be developed as a patch and applied. It’s during the development time spent creating this patch that zero-day attacks are often launched.
Zero-day attacks are so-called as developers often have ‘zero days’ to create a security fix. They therefore need to design one as fast as possible to help keep users secure from any malware or zero-day viruses.
Explainer: how zero-day attacks actually spread
Modern zero-day attacks rarely rely on obvious malware downloads. Instead, they often exploit memory corruption, privilege escalation, or sandbox escape vulnerabilities triggered by everyday actions such as opening documents, previewing emails, or visiting compromised websites. Because these exploits target unknown flaws, traditional signature-based antivirus tools may not detect them during the early stages of an attack.
What are the most infamous zero-day attack examples?
Operation Aurora is one of the most infamous zero-day attacks. It was carried out in 2010 by Beijing's Elderwood Group that reportedly had ties to the Chinese military.
This attack (actually, a series of attacks) hit dozens of American companies — Adobe, Yahoo, and Symantec, among others — but the primary aim was Google.
The attack was, presumably, a retaliation for Google.cn notifying users when some of the results were censored out of their searches, and meant to make Google more compliant.
Why it mattered?
This attack demonstrated how zero-day exploits could be used in large-scale, targeted campaigns and changed how companies approach vulnerability disclosure and threat intelligence.
We’ve all come to love and loathe video conferencing platform Zoom in equal measure during the last 12 months. But in 2020, a zero-day vulnerability was discovered in the service for Zoom users utilising Windows 7 or earlier versions of the operating system. It allowed cybercriminals to gain remote access to devices and files or information stored on them.
Why it mattered?
The exploit showed how quickly widely adopted consumer software can become a zero-day target, especially during periods of rapid user growth.
Back in 2011, security firm RSA was attacked by hackers exploiting an Adobe Flash Player vulnerability. Its network was breached by attackers sending employees emails with Excel spreadsheets. A member of staff opened a file with an embedded Flash file which allowed the cybercriminals to take control of their machine and infiltrate their IT systems.
Why it mattered?
This incident highlighted how zero-day attacks are often delivered through trusted internal channels such as employee emails rather than direct external attacks.
Such is the potential risk presented by zero-day attacks, Google established its own Project Zero team of security experts in 2014, tasked with finding any zero-day vulnerabilities.
Why are zero-day attacks so dangerous?
A zero-day vulnerability can pose a real threat to computer users of all kinds regardless of how tech-savvy you are.
Malware could potentially infect your device through usually harmless activity such as opening emails, downloading attachments or browsing websites.
As the name suggests, developers are often under great pressure to come up with a fix quickly once details of a zero-day vulnerability enter the public domain. Despite this, sometimes developers may be unable to come up with a fix before this security issue is exploited. It can take days, weeks or even months for fixes to be released.
The compromised software or service may need to be used during this time, leaving their personal information at risk.
Zero-day attacks in 2025
Zero-day exploits are no longer limited to government or espionage operations. Today, they are increasingly sold through private exploit brokers and used by ransomware groups. Many zero-day vulnerabilities are now weaponized within days of discovery, reducing the time users have to react. This makes early detection and layered security controls more important than ever.
How to stay safe from zero-day attacks?
While zero-day attacks often put you at risk, you can follow best practice to keep your cybersecurity defenses up to date and give yourself a better chance of protecting your personal information.
Use a firewall
Setting up a firewall can be an effective way of maintaining your security. You can configure your firewall to scan for certain threats to keep your data safe.
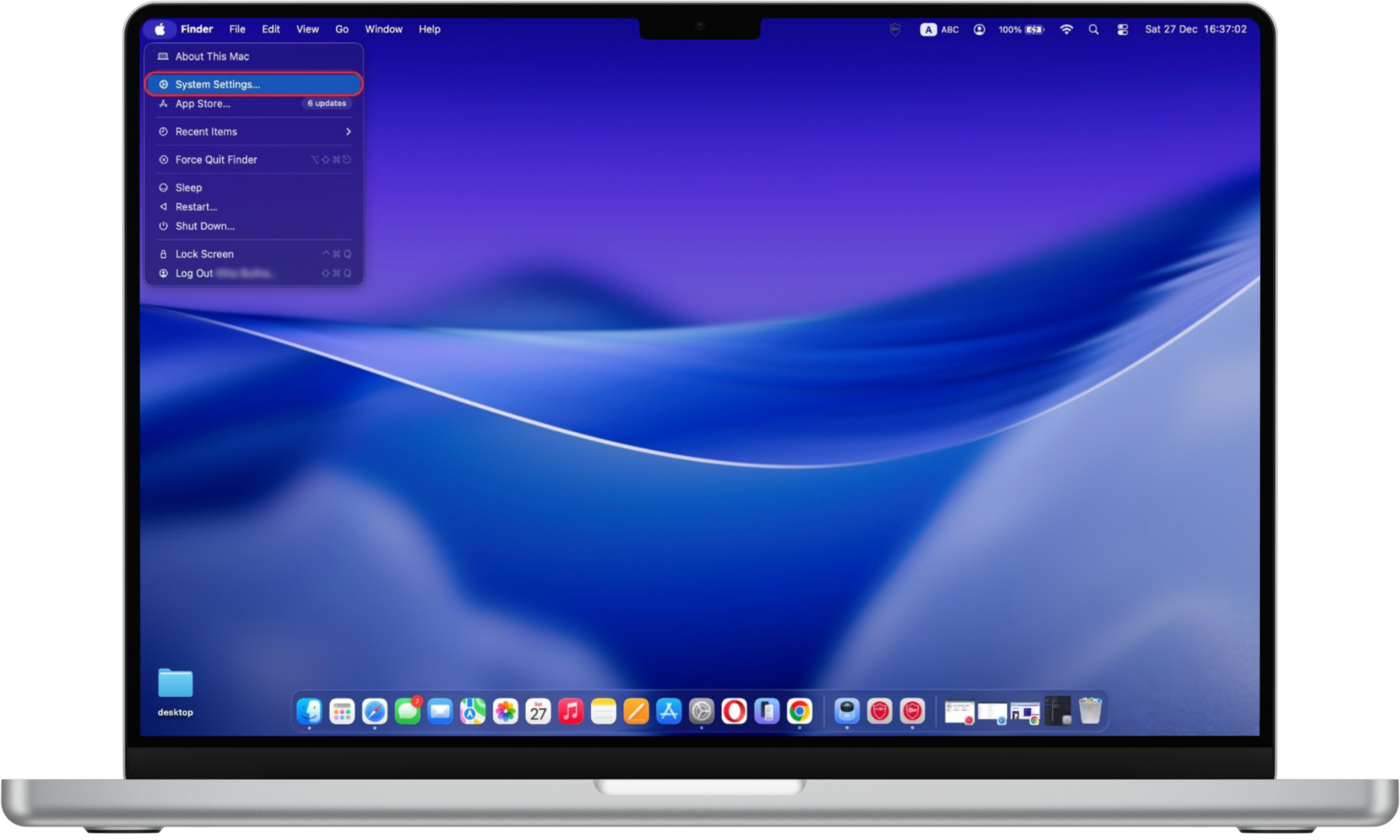
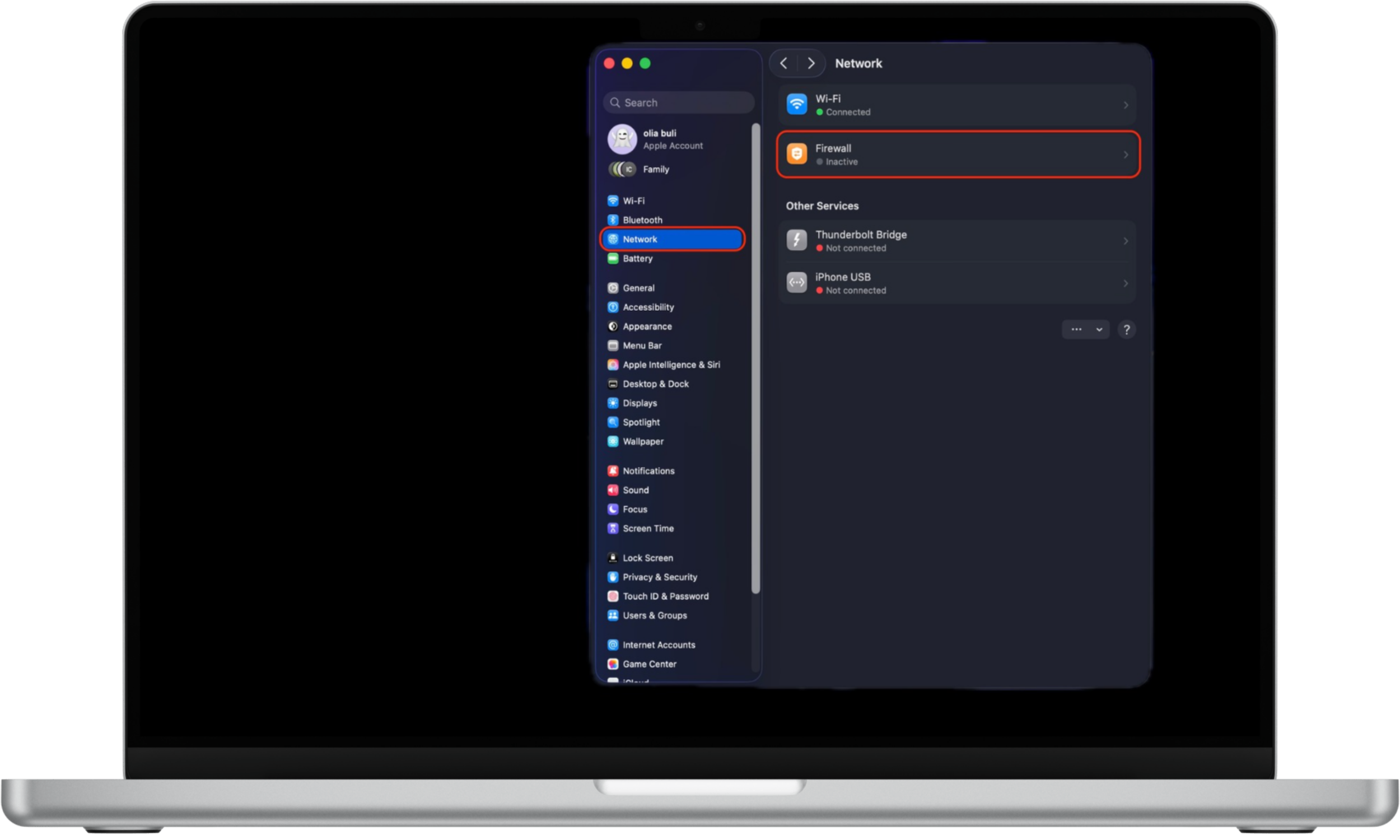
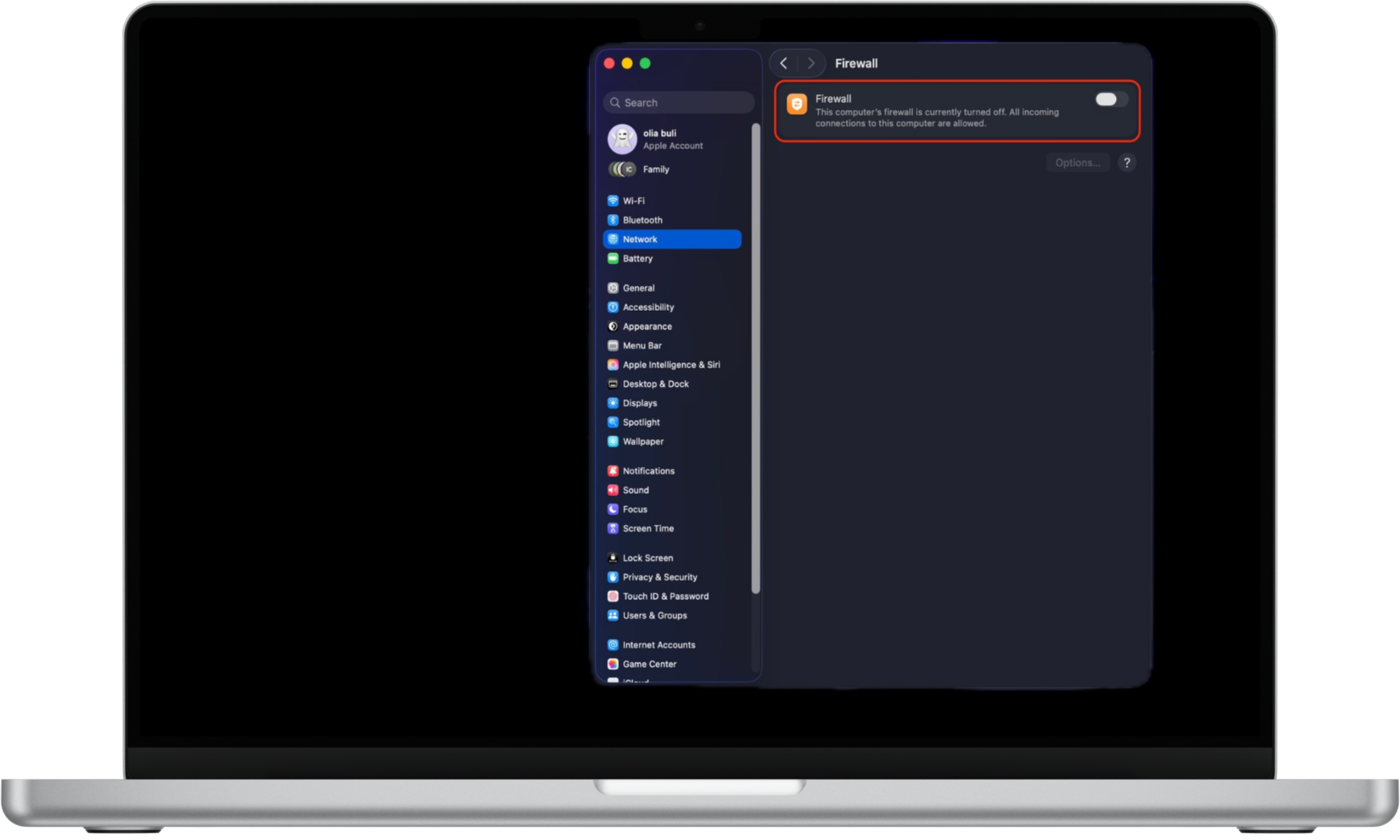
To enable the firewall on Mac:
- Open the Apple menu and go to System Settings.
- Select Network from the sidebar.
- Click Firewall.
- Turn the firewall On.
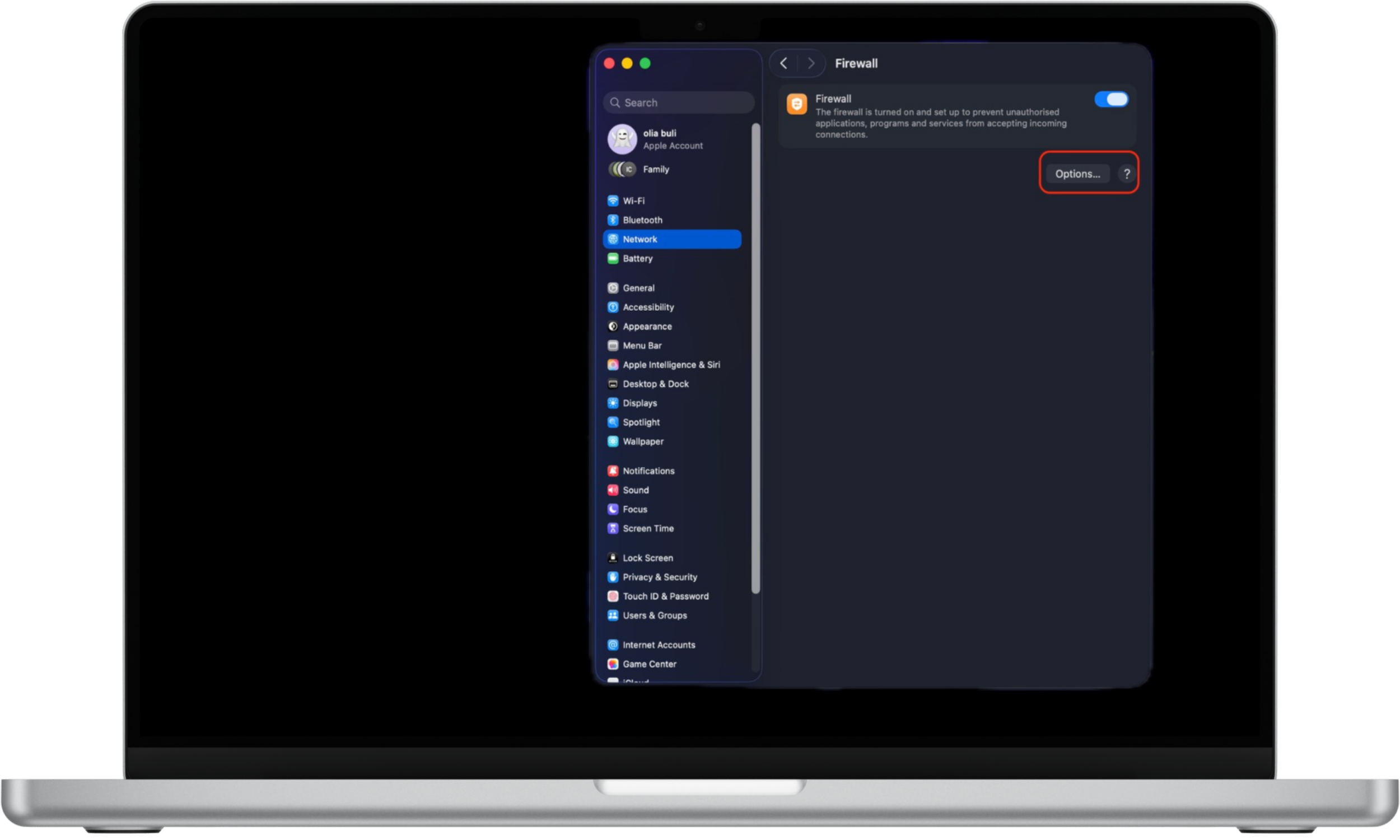
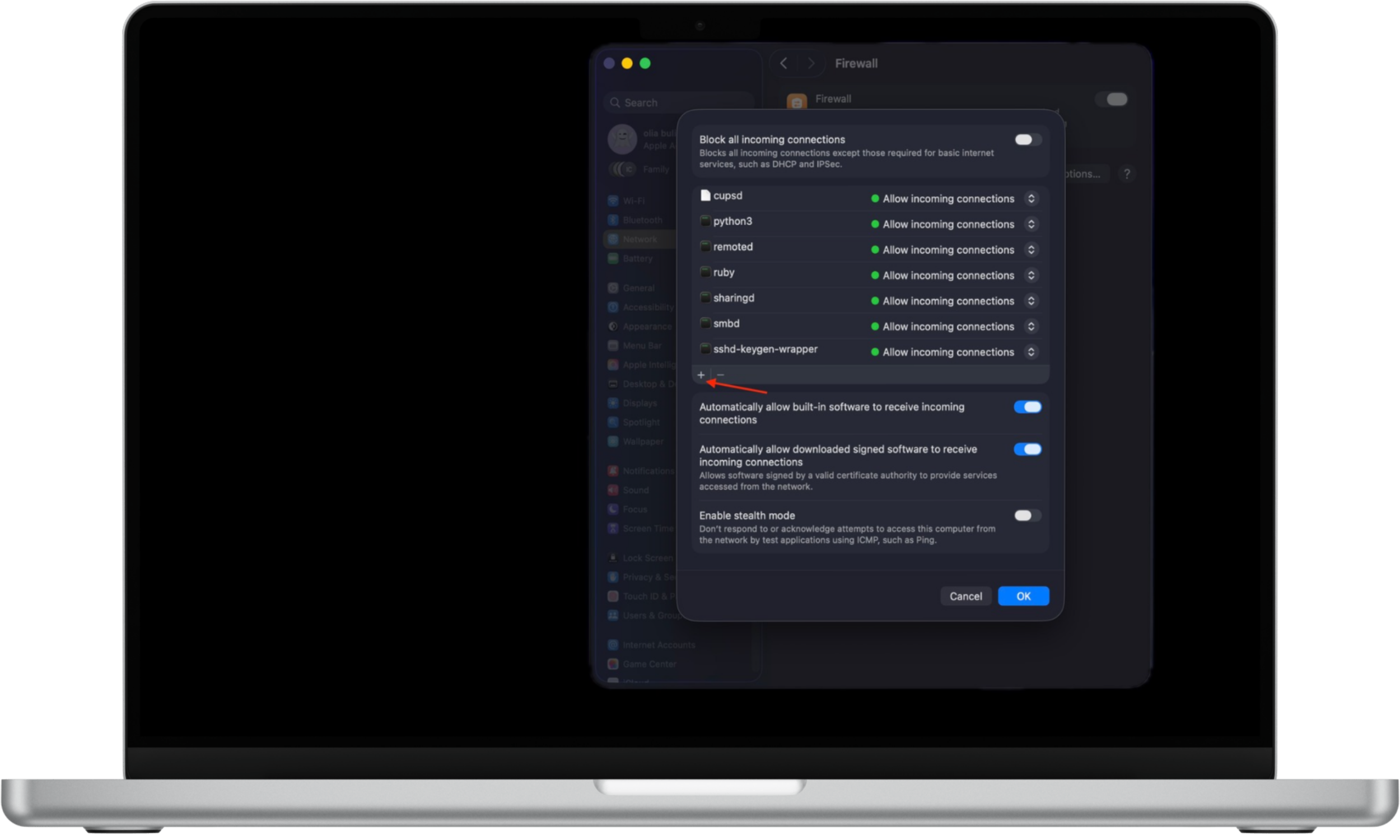
Here's how to manage firewall options on Mac:
- In System Settings → Network → Firewall, click Options.
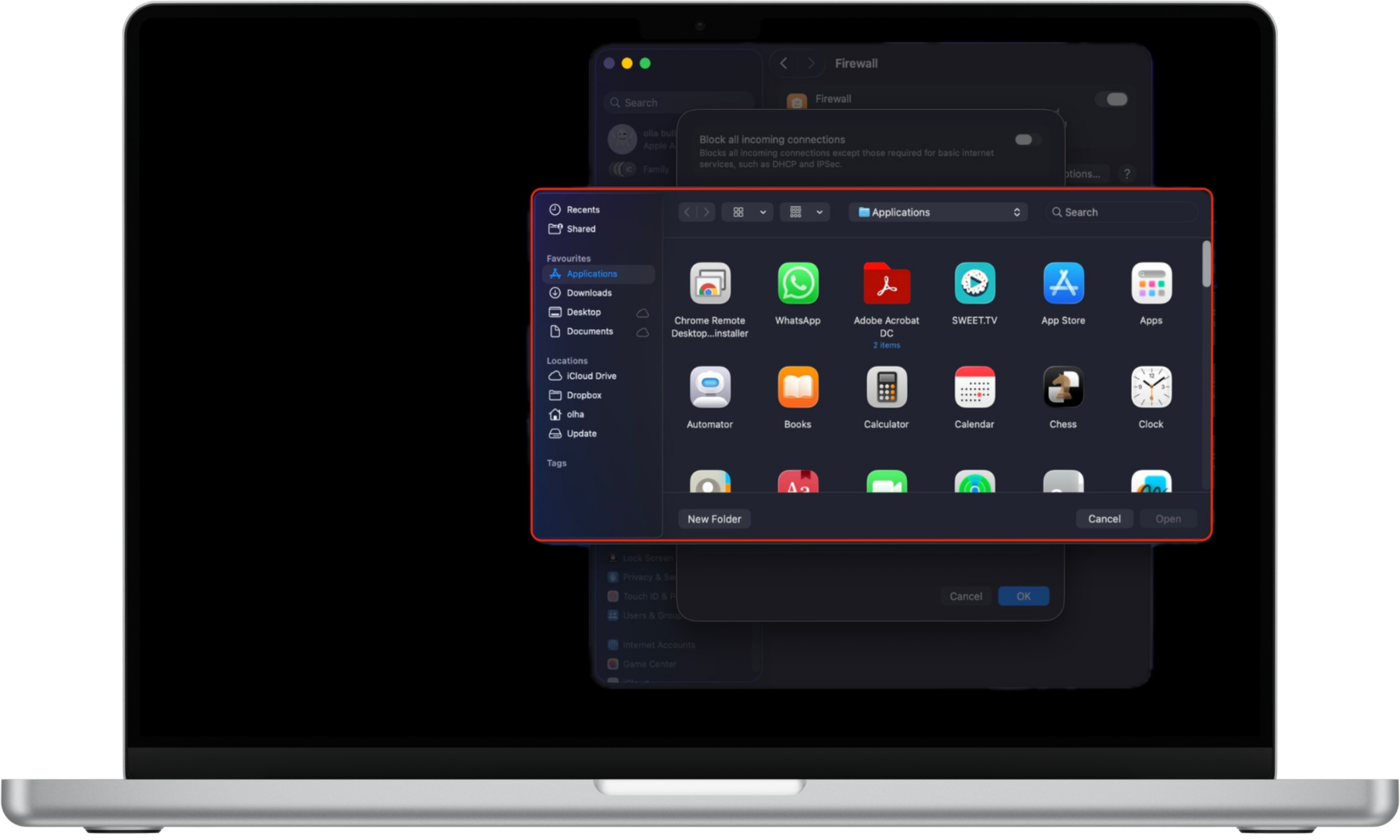
- Use the Add (+) button to allow specific apps or services.
- Choose whether each app is allowed to receive incoming connections.
Always update operating systems
Developers often release updated versions of operating systems to fix bugs and implement patches to enhance security. So rather than delaying an update, you should always install the new software as soon as it is launched by a manufacturer. This will shore up your defenses and reduce vulnerabilities surrounding a device.
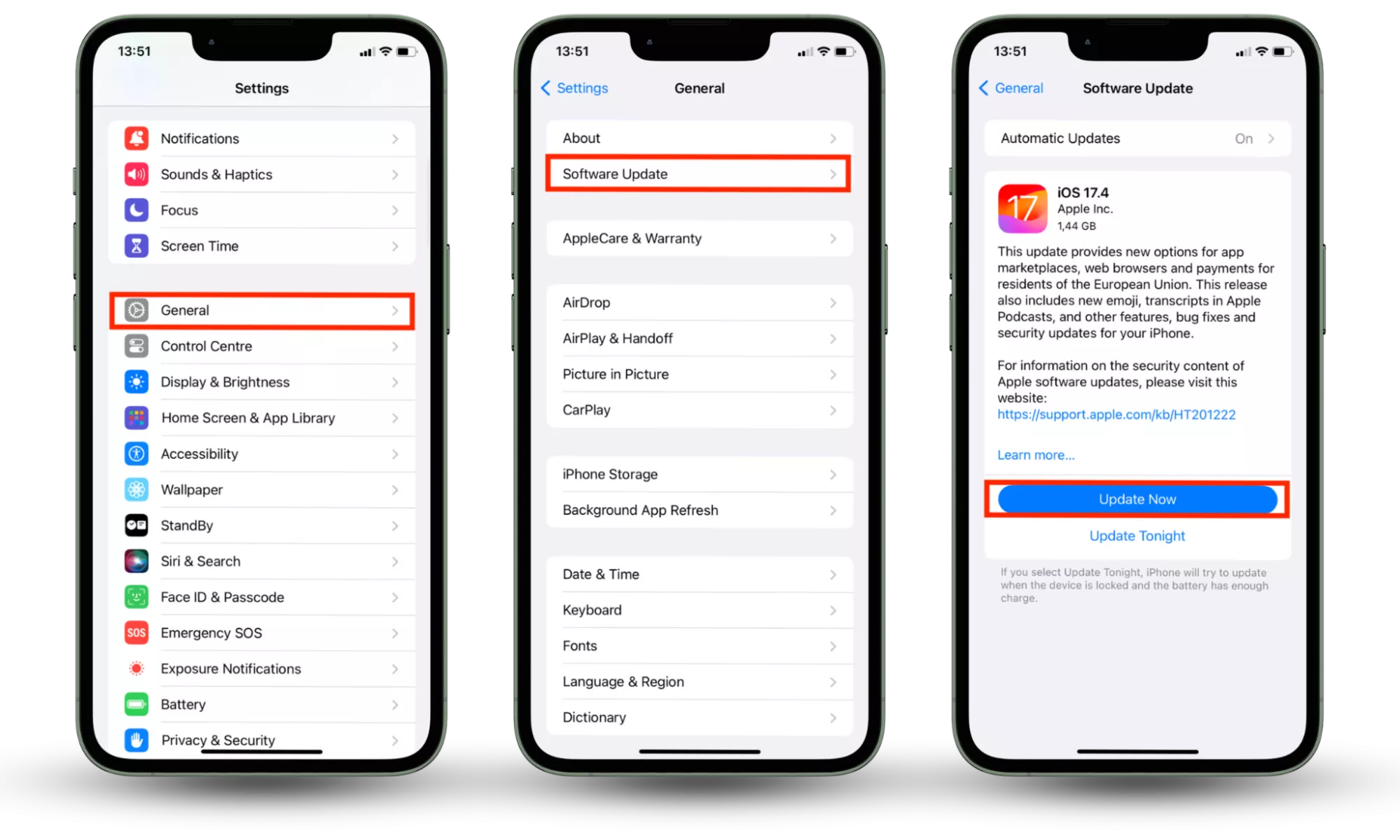
How to update the operating system on iPhone:
- Open Settings.
- Tap General.
- Select Software Update.
- If an update is available, tap Update now.
Keeping automatic updates enabled reduces the time window in which zero-day exploits can be abused before a fix is applied.
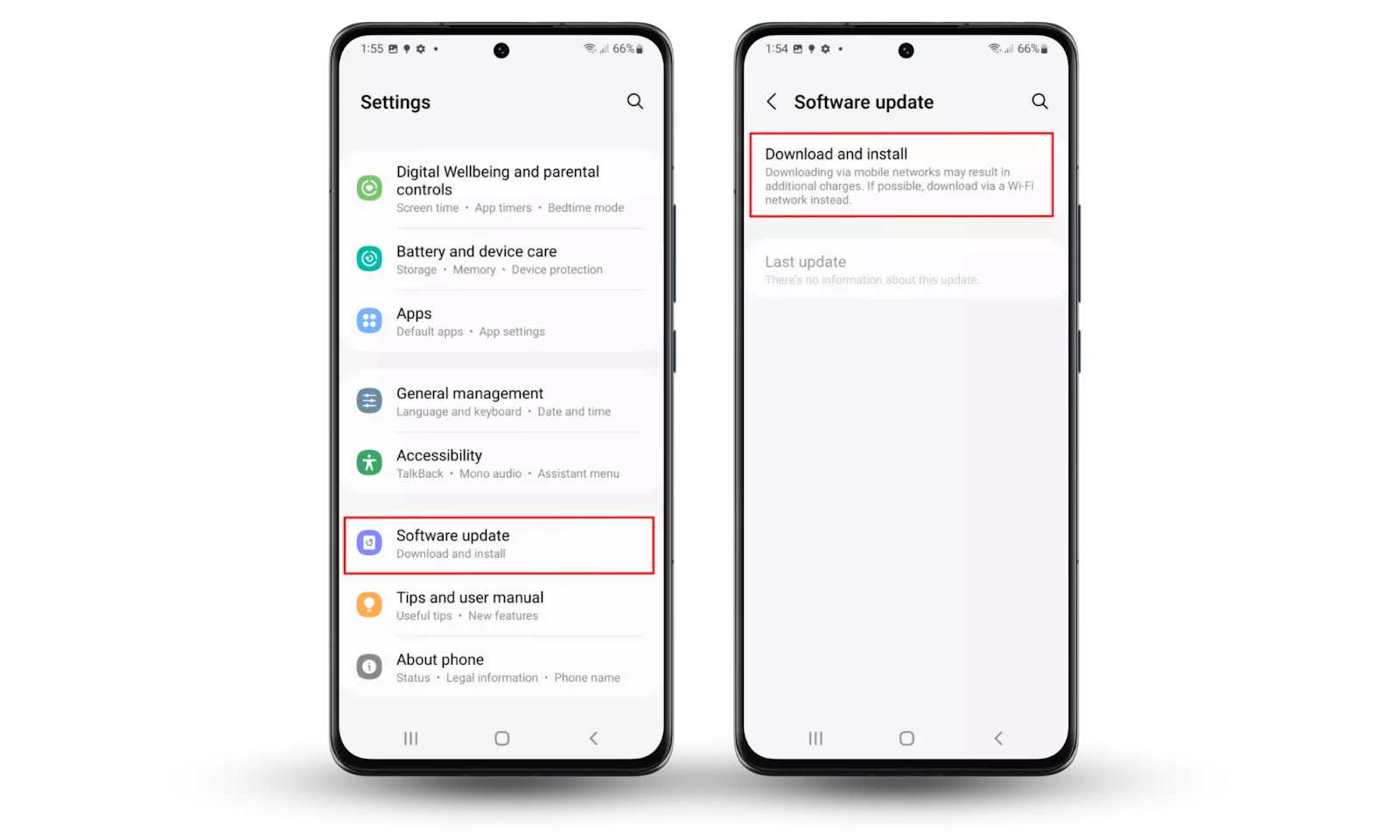
How to update the operating system on Android:
- Go to your Settings.
- Scroll down to System and tap it.
- Go to System update.
- Tap Check for update at the bottom right corner of your screen.
- If available, choose Download and Install.
Because Android updates may be released in stages, checking manually helps ensure critical fixes are not delayed.
How to update macOS:
- Click the Apple menu in the top-left corner of the screen.
- Open System Settings.
- Select General, then click Software Update.
- Install any available updates immediately.
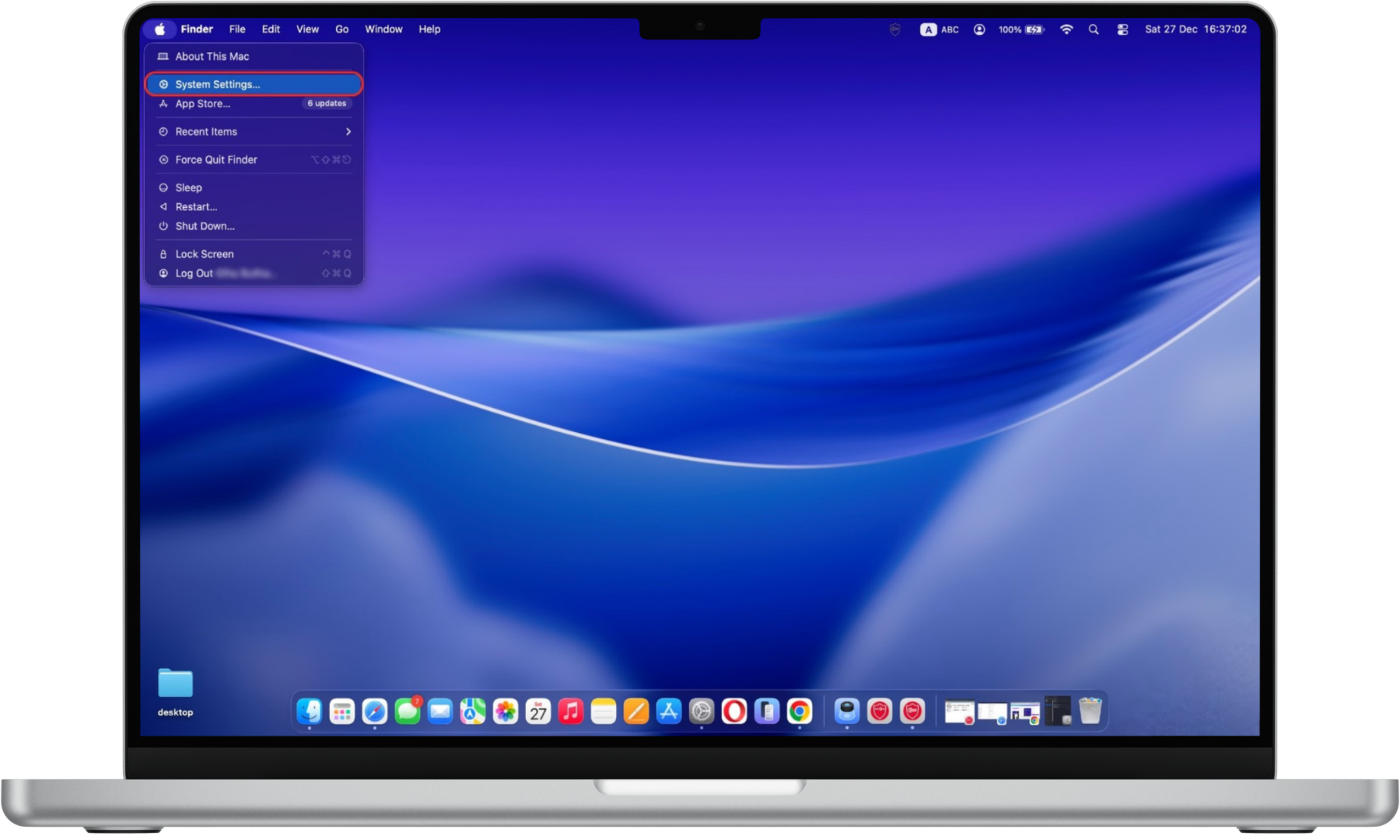
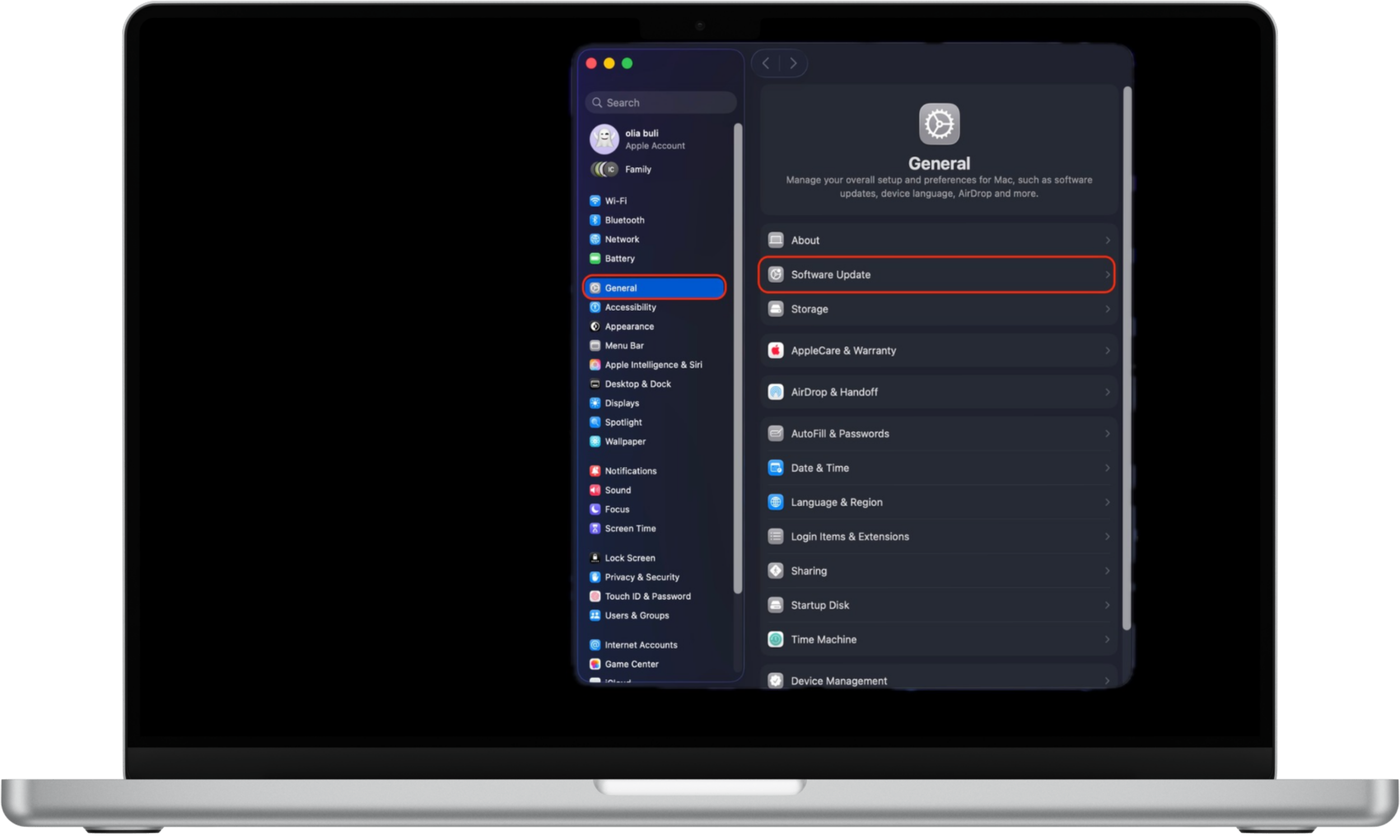
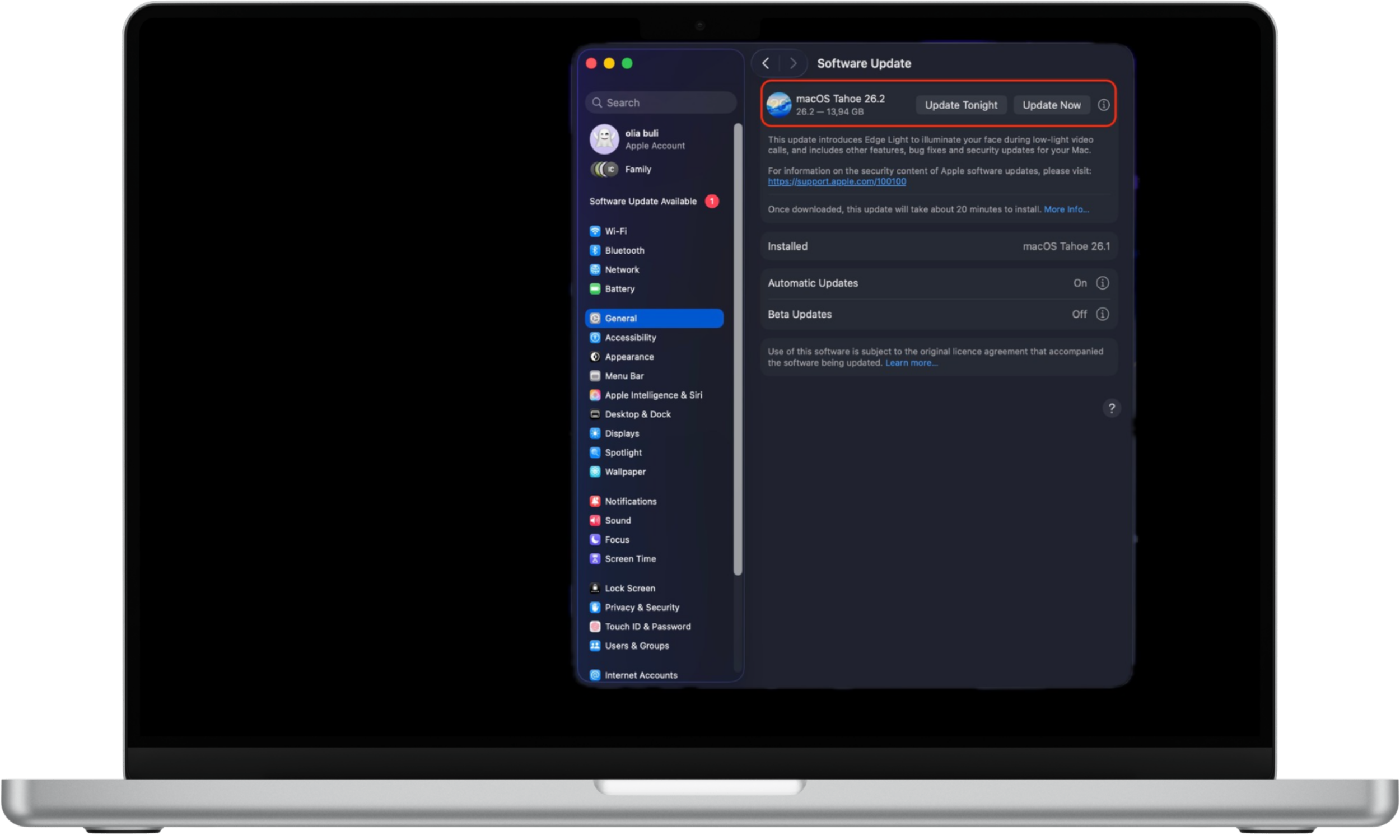
macOS security updates often address actively exploited vulnerabilities, making timely installation essential.
Limit application privileges on mobile devices
Restricting app permissions on mobile devices helps reduce the impact of zero-day exploits by limiting what compromised apps can access.
Here's how to manage app permissions on iPhone:
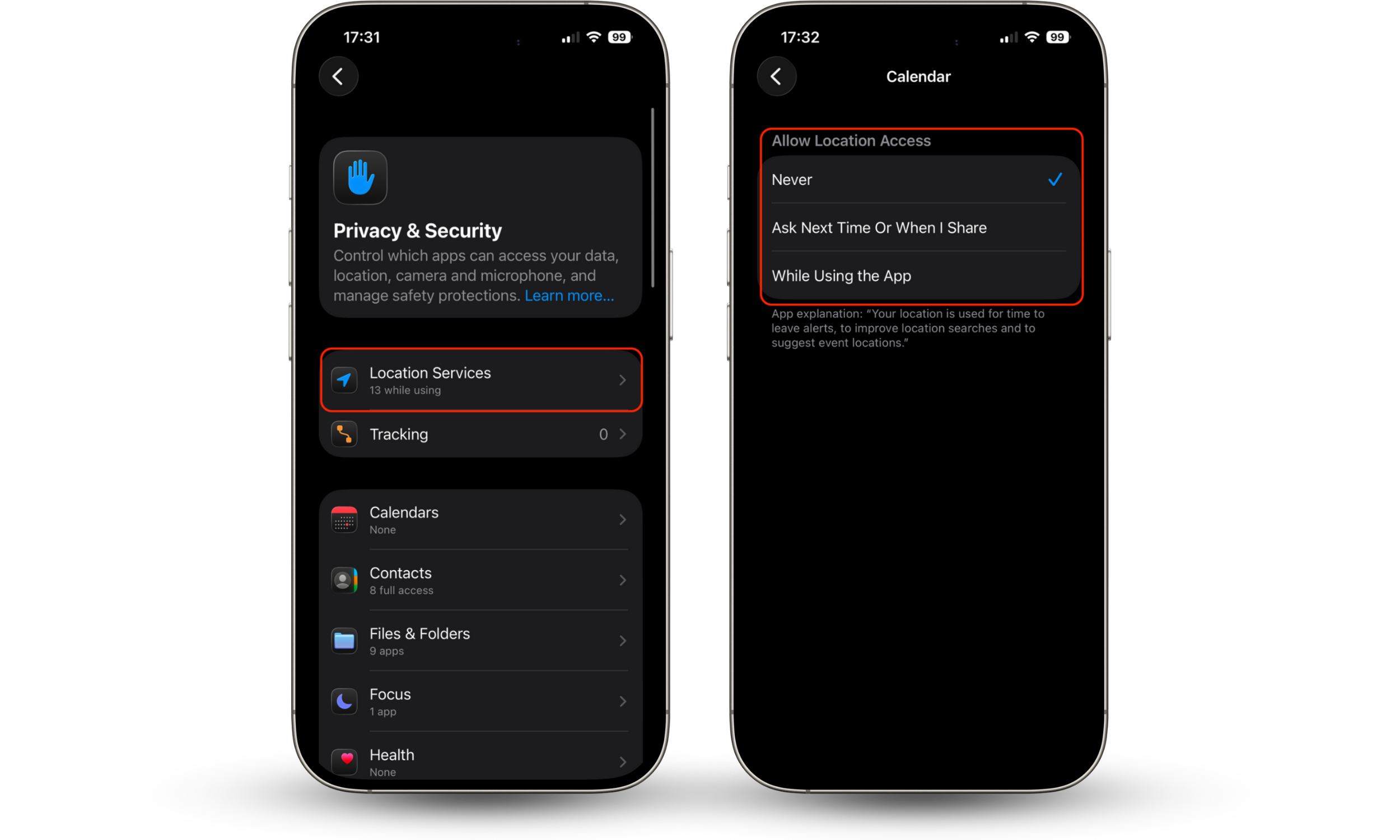
- Open Settings.
- Go to Privacy & Security.
- Select a permission category such as Camera, Microphone, Photos, or Location Services.
- Review the list of apps and disable access for those that don’t need it.
- For location access, choose “While Using the App” or “Never” instead of “Always” whenever possible.
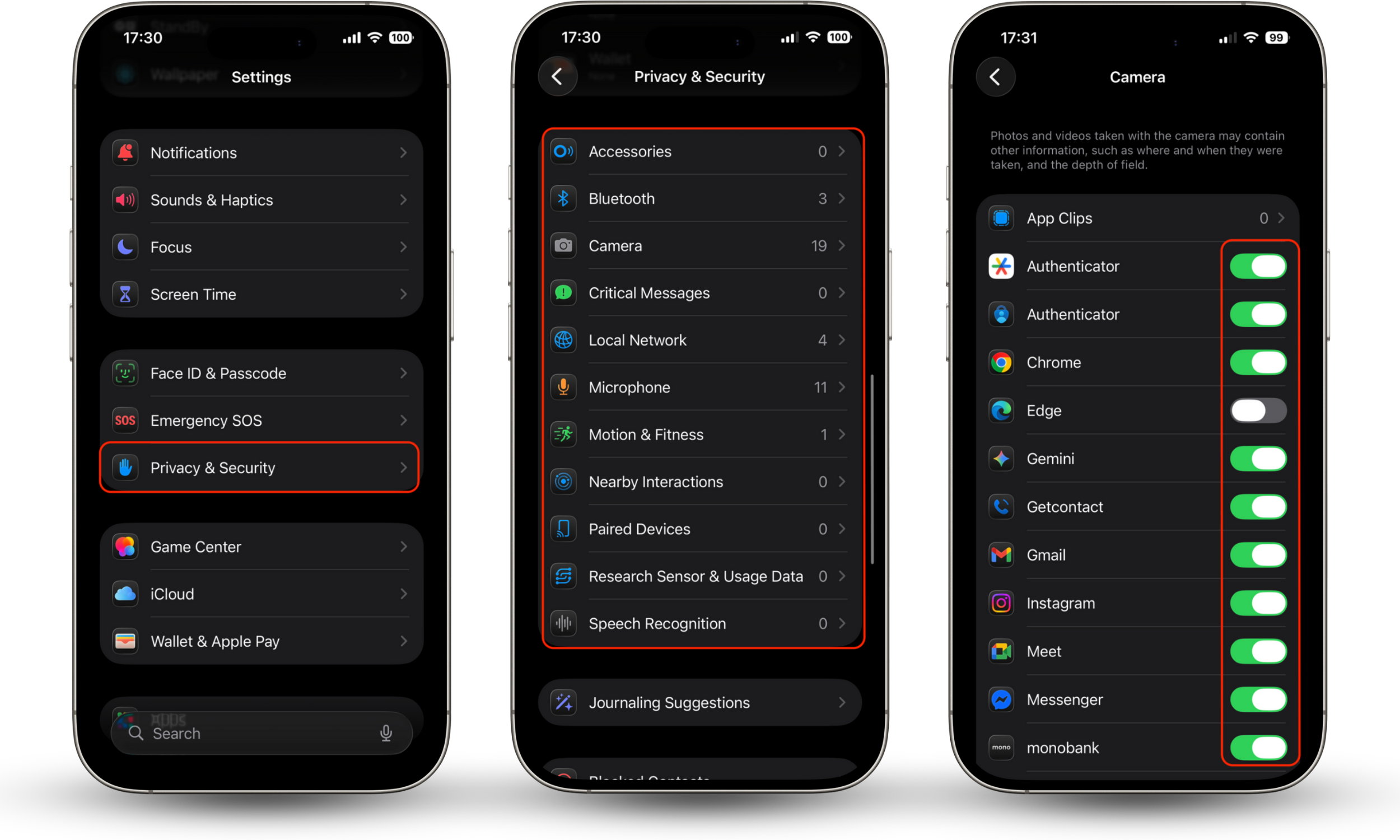
Here's how to manage app permissions on Android:
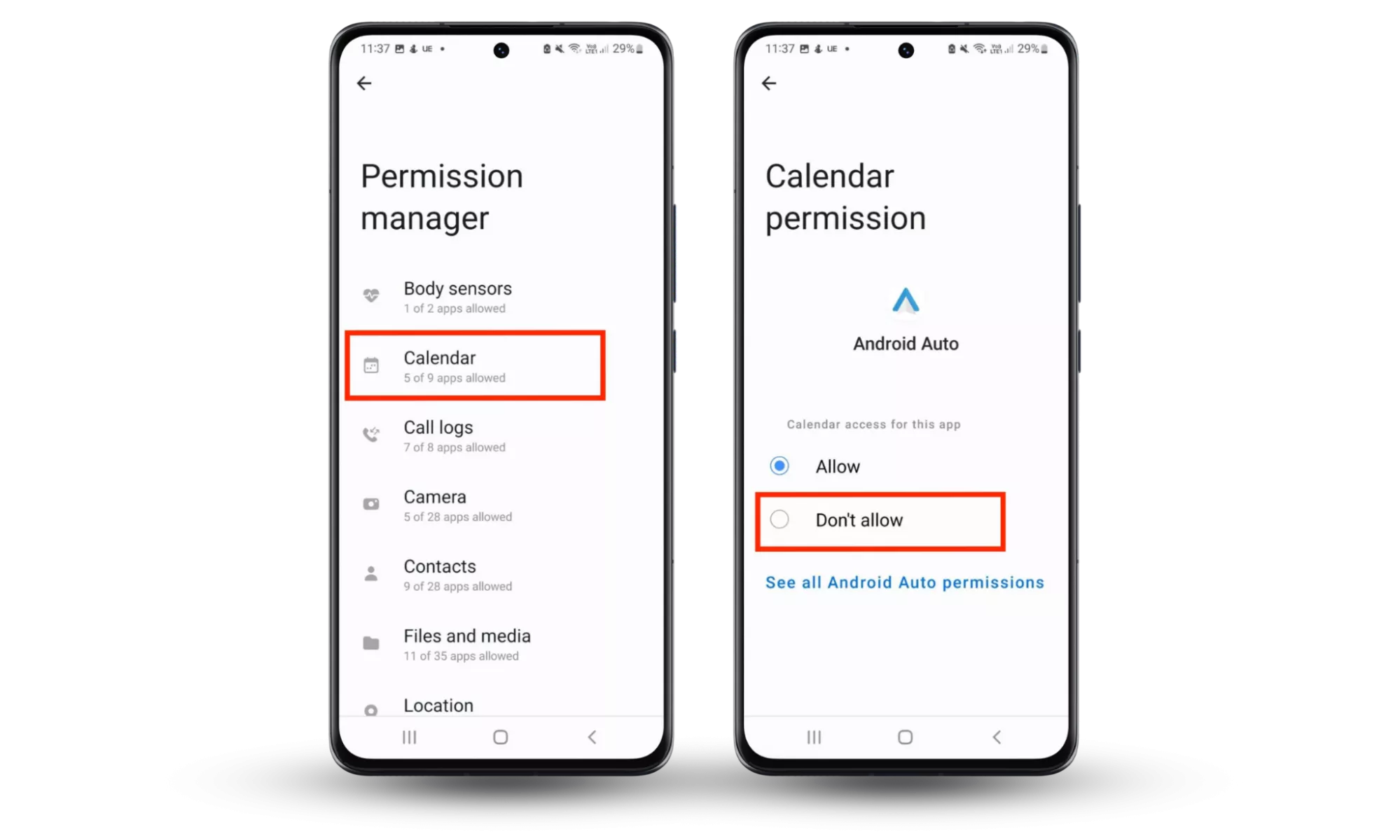
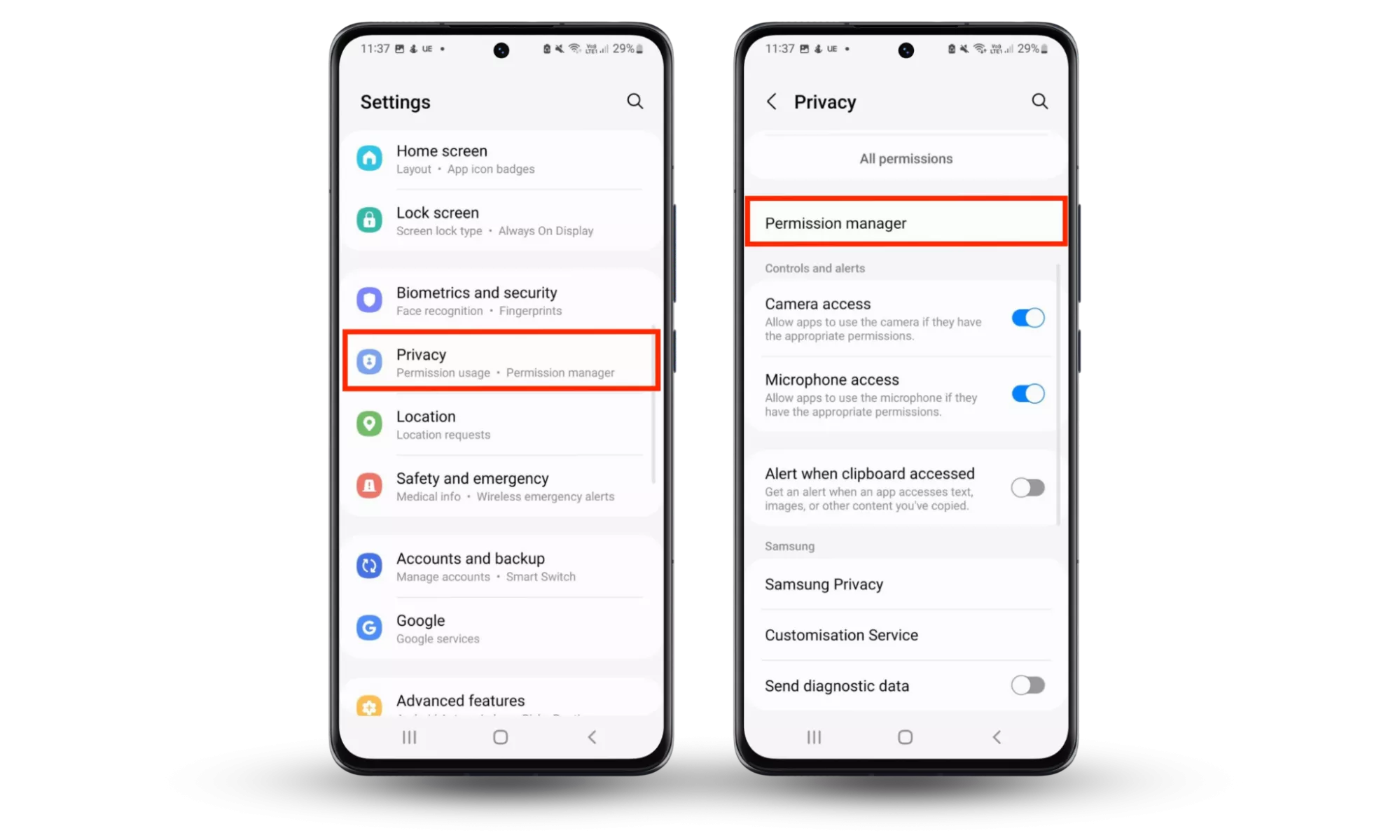
- On your Android device, open the Settings app.
- Tap Privacy, then choose Permission manager.
- Select each category (Calendar, Camera, Call Logs, etc.) and then check which apps have access to those permissions. Next, remove permissions for each app that doesn’t require them or shouldn’t have them in the first place.
Stay informed of the latest cybersecurity news
Try to stay up to date with the latest cybersecurity news and trends so you are aware of any actions you need to take. Clario’s blog is a one-stop shop for all the latest news and guides on cybersecurity issues.
Only utilise essential applications
The more applications you run, the more exposed you are to these kinds of threats. Keeping the number of trusted applications you use to a minimum will mean less vulnerabilities in your network.
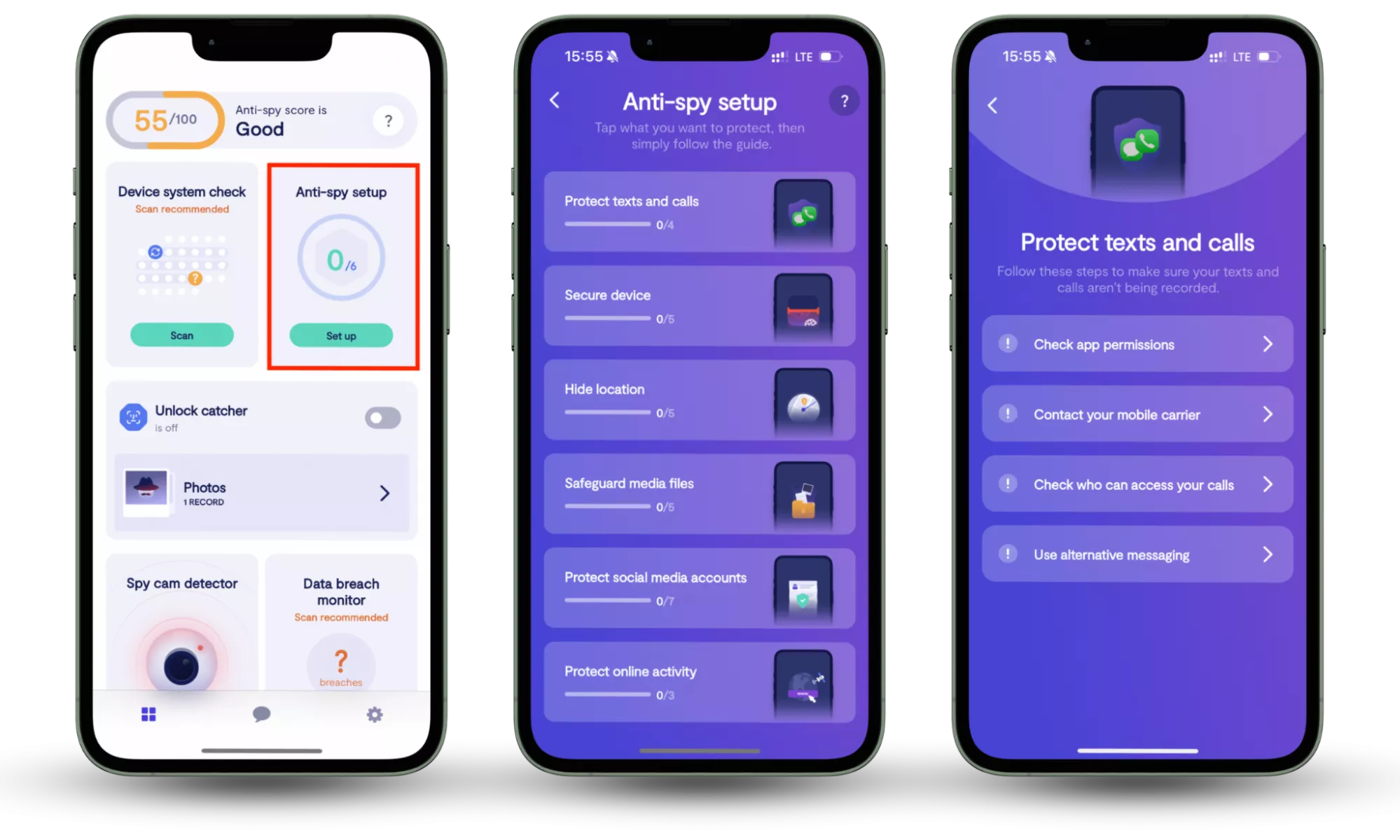
Zero-day exploits can get the best of your software's and hardware's unknown vulnerabilities, and we've just advised you on how to dodge this zero-day bullet. Now, a surefire way to safeguard yourself from known cyber threats is to use an all-in-one solution like Clario Anti Spy. By focusing on prevention rather than reaction, Clario Anti Spy helps users reduce everyday privacy risks through its Anti-spy setup feature, which guides them step by step through essential privacy settings, permission checks, and security adjustments — closing common gaps that spyware often exploits, without requiring technical expertise.
Here is how to use Clario Anti Spy’s Anti-Spy setup feature:
- Download Clario Anti Spy, create an account, and sign in.
- Under the Anti-Spy setup section, select Set up.
- Follow the step-by-step guide to secure your devices and minimize your exposure to spyware, ensuring better protection against malware and other digital threats.
Conclusion
Zero-day attacks often occur without warning which make them difficult for online users to anticipate or protect themselves against.
But by adhering to cybersecurity common sense, you should be able to limit the chances of becoming caught up in one. Stay tuned to Clario Anti Spy’s blog for all the latest news and updates on cybersecurity concerns.
Read more:


