Table of contents
- What is a data backup?
- Why is data backup important?
- Backup methods
- What files should you back up?
- Data backup options
- 1. Backup software
- 2. Cloud backup services
- 3. Hardware appliances
- 4. Redundancy
- 5. External hard drive
- 6. Removable media
- The 3-2-1 backup strategy
- 1. Backup regularly
- 2. Choose more storage space
- 3. Make physical copies
- How to recover files on your computer
- Conclusion
What is a data backup?
Data backup definition
Data backup saves copies of the data stored on your devices, like your cell phone, tablet, or computer, in another location (a hard drive, iCloud, etc.) for safekeeping.
This ensures that you can restore the original data should anything happen. For example, if your data gets lost or deleted by mistake.
Data protection definition
What is data protection? Data protection refers to methods of protecting your data from online threats by implementing various cybersecurity measures, including data backups.
Why is data backup important?
People back up their data to have a reliable archive of their sensitive information and can retrieve it when needed. Natural disasters, device failure, human error, corrupted files, viruses, and malware are common occurrences. When these scenarios play out, your backups become critical to data recovery. Without them, it could damaged beyond repair or lost forever. In some cases, you can end up losing money or reputation.
Did you know?
According to a 2023 Verizon Breach Incident Report, 82% of breaches are caused by cyber attacks involving human error.
Examples of human error-empowered attacks include:
- Mistakes
- Misuse
- Spear phishing attacks
- Social engineering attacks.
This highlights the importance of saving your data in secure archives.
There is a misconception that only businesses need to back up their data, but this couldn’t be further from the truth. Individuals and families should also back up their files and data in case of loss.
So, what can you back up as an individual or a family?
- Important family documents
- Family photos
- Memories from family vacations, holidays, birthday celebrations, and important milestones
- Personal files that contain sensitive information, like documents and banking information, etc.
Rule of thumb
If it is important, back the file up.
Backup methods
There are various types of backups you can implement:
- Full backups to back up all your data
- Incremental backups for files that have changed since the last full backup
- Differential backups for files that have changed since the last backup, regardless of whether it was a full backup
The backup you choose depends on several factors, like the size of your backups and how often you want to back up your data.
Here’s what each backup type does:
- Full backups. This comprehensive backup method archives all the files on your device. As such, this process takes a little longer, sometimes hours, depending on the amount of data. It’s advisable to do a full backup when backing up your data for the first time.
- Differential backups. A differential backup archives files you've either made changes to or added since the last time you performed a full backup. For this reason, the process doesn’t take as long as a full backup.
- Incremental backups. Similar to a differential backup, incremental backups only back up data you’ve changed or files you’ve added since the last time you archived your data. But unlike differential backups, incremental backups archive files regardless of the type of backup you last implemented. Incremental backups are done more frequently and may need to be implemented by backup software.
What files should you back up?
The type of files you should back up depends on the capacity with which you’re archiving them. Individuals should back up files containing sensitive information, like banking information, intimate media, work-related documents, etc. Businesses should back up files containing information like employee records, customer records, and financial records.
Data backup options
Below are backup methods you can use:
- Backup software installed on your system
- Cloud backup services store data on remote servers
- Backing up data to a device connected to your network
- Creating copies of your data, also known as redundancy
- Backing up to an external hard drive
- Backing up to removable media
The method you choose depends on the scope of your backups.
1. Backup software
No matter what you’re backing up, you must use backup software as one of your methods. The benefit of using this technology to archive your data is that it streamlines the process. Hardware can get lost or damaged. The software lets you quickly retrieve your files, even when your hardware fails.
You don’t have to spend a ton on backup software; there are affordable options on the market, but it all depends on your requirements. The price of each one correlates with the features it offers, so you may find more advanced backup software to be on the pricey side. Do your research to find software that works for you.
Below are a few features you should look for when choosing backup software:
- Automation. The tool you choose should allow you to schedule regular backups so you’re not under pressure to remember to archive your data manually. Convenience is the name of the game.
- Incremental and differential backups. Try to use software that only backs up what is needed, saving time and space. You don’t have to implement a full backup every time.
- Encryption. You should think of encryption every time you think of data. Ensure the software you choose offers encryption to keep your data secure.
- Compression. To save on space, go with software that offers compression options. Otherwise, you may need to update your storage, which can be costly.
- Multiple backup destinations. This is known as redundancy and includes backing up your data to multiple locations. It strengthens the security of your backups in case one or more of the locations are compromised.
2. Cloud backup services
Cloud backup is a convenient method of archiving your data because it allows you to access it from anywhere, provided you have an internet connection.
- Benefit: it typically offers redundancy, automated backups, and encryption, making it secure.
- Downside: high risk of data breaches. While it’s mainly secure, hackers can easily access it using phishing attacks, social engineering, or simply brute force your password. Cloud backup services can also be costly when backing up large amounts of data.
Cloud backups make your files easy to access and increase your exposure. Hackers often break into online accounts through phishing, weak passwords, or leaks on the dark web.
This risk is often overlooked because people assume their cloud login is secure enough. In reality, many breaches happen without users realizing their email or password was exposed months earlier.
That’s why you need to go beyond simply storing files in the cloud. You also need to monitor whether your accounts have been breached.
Here’s how to use Clario Anti Spy’s Data breach monitor:
- Download Clario Anti Spy and create an account.
- Go to the dashboard, and tap on Data breach monitor.
- Enter the email address linked to your cloud storage or accounts.
- Review the list of breaches tied to that email.
- Follow the recommended actions to secure each account.
- Add more emails to keep your entire digital footprint protected.

3. Hardware appliances
Another convenient measure is storing your data on hardware appliances like backup tapes. It means you know exactly where your data is stored and can access it easily. Hardware appliances are also easy to install and use.
The drawback of using them for storage is that they can be damaged, lost, or stolen. Unless you use them as a secondary backup solution, you run the risk of losing your data forever.
4. Redundancy
This involves storing your data in multiple locations as a security measure. Should your local backup be compromised, you have the peace of mind of knowing that your data is safely stored in multiple areas. Redundancy minimizes the risk of losing your data due to unforeseen circumstances like loss, damage, and human error.
The level of redundancy you choose depends on the importance of your files and the level of security needed. For example, personal photos and videos require limited, if any, redundancy. However, you should store files containing your financial information or information relating to your will and life policies in multiple secure locations.
5. External hard drive
External hard drives are separate devices connected to your computer to back up your data, like a USB disk. They come in different sizes and offer a range of storage options. The more storage you want, the more you can expect to pay. Some hard drives are small and compact, while others are bulky and more conspicuous, making them difficult to carry around.
6. Removable media
Removable media refers to small devices used to transfer files from one device to another. A USB flash drive is an example of removable media, but it also includes old-school devices like DVDs and CDs. They’re compatible with computers and laptops.
Unlike other storage devices, removable media is compact, offering minimal storage capacity and limited features. Their physical size also makes them susceptible to loss and theft.
The 3-2-1 backup strategy
The 3-2-1 backup strategy involves making three copies of your data using two storage methods and keeping one of your copies off-site for safety purposes. This method ensures that your files are secure and easily accessible, reducing the risk of losing them.
Below are the best practices for backing up your files.
1. Backup regularly
Your data is most vulnerable in between backups. That’s why it’s vital to back it up as often as possible. Keep this in mind when choosing backup methods or software. You want to pick solutions that will require limited intervention on your part; automate the process to back up regularly.
2. Choose more storage space
Ensure you’ve backed up to a location with ample space to back up your files, depending on the size and frequency of your backups. You need more space if you:
- Change your files frequently
- Add more files to your backup.
When in doubt, choose more storage, as it’s better to have more than you need than less and have to upgrade.
3. Make physical copies
While storing your files virtually is great, you must supplement your backups with physical copies. These can come in handy when your online storage is compromised.
Below are the types of documents you can make physical copies of for safekeeping:
- Bank statements
- Financial documents
- Wills.
Keep these somewhere safe, like in a personal safe or with your lawyer.
Backing up regularly and making physical copies protects you from accidents, but there’s another threat: device vulnerabilities. If your phone or computer is tampered with, your backups can be copied or stolen before you even realize it.
Outdated settings, risky permissions, or hidden apps can quietly weaken your device’s defenses. In those cases, a well-planned backup strategy will not matter; your data will already be exposed.
To reduce these risks, check your device for weaknesses and lock down any gaps before storing sensitive backups.
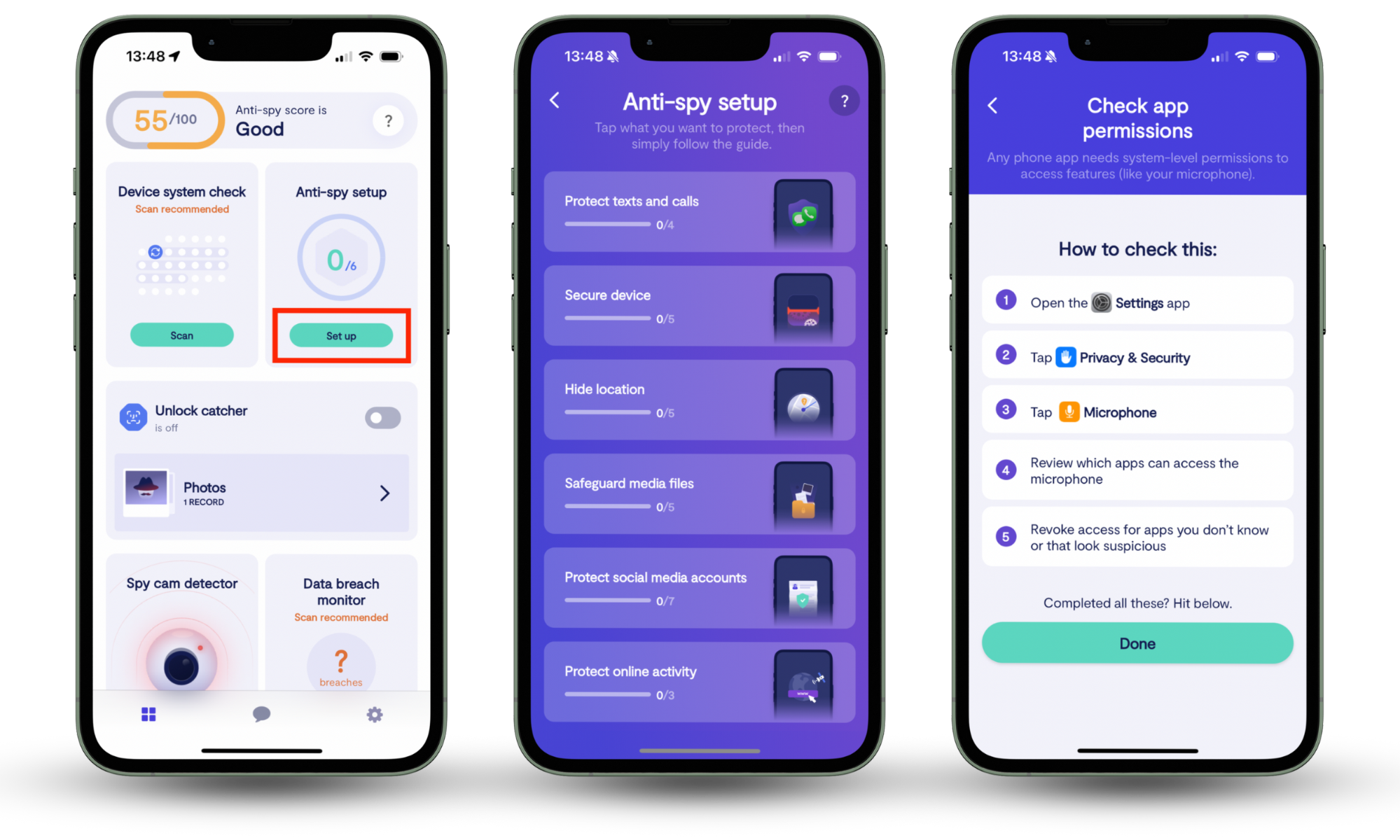
Follow these steps to use Clario’s Anti spy setup:
- Download Clario Anti Spy and create an account.
- Select Anti spy setup on the dashboard.
- Follow the checklist to review risky settings and suspicious permissions.
- Apply the recommended fixes to harden your device.
- Repeat the process regularly to keep your backup storage safe from hidden threats.
How to recover files on your computer
Follow the detailed steps below to recover deleted items on your computer.
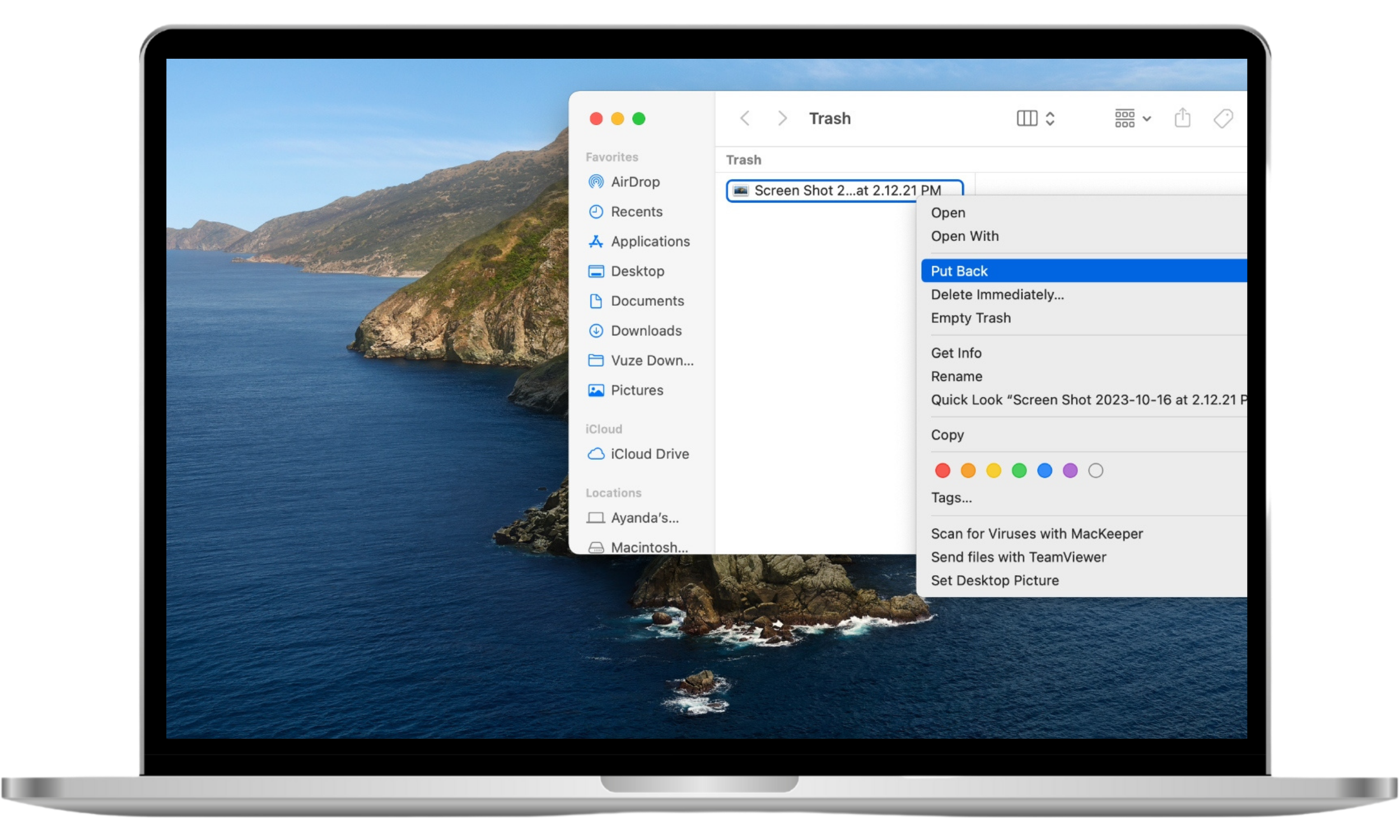
To recover files on a Mac:
- Click on the Trash icon in the Dock (it’s in the bottom-right corner of the screen)
- Right-click on the item you want to recover and select Put Back.

To recover files from a backup (external storage) on a Windows device:
- Type Control Panel in the search bar and select it from the results
- Click Backup and restore (on Windows 7)
- Connect the external storage device that you saved your files in
- Now, choose another backup to restore your files from, select the device location, and follow the prompts to recover the items.
To recover files from OneDrive:
- Create a similar file using the same file type and file name
- Click Properties > Previous Versions and pick the file version you want to restore.
No matter how carefully you handle your data, there’s always a risk of losing it due to human error or a malicious attack. For instance, people who spy on you can access your data and put it on the dark web. Anyone can do this, including:
- Professional hackers
- Bad actors
- People who know how to compromise computers.
Fortunately, there are ways to reduce these risks. Clario Anti Spy is a mobile security and anti-spy app that helps you protect your personal information and keep prying eyes away. It lowers the chances of threats with simple, effective tools that anyone can use, even without technical knowledge.
Here’s how Clario Anti Spy protects you from data thieves:
- Hidden app scan scans your phone for spyware or stalkerware apps and highlights suspicious permissions that may expose your data. This gives you control over who can access your personal information and how it’s used—a clear example of data privacy vs. data protection.
- Data breach monitor alerts you if your email or accounts appear in a data leak, so you can act quickly before attackers exploit your information. If you’re asking yourself what a data leak is, it’s a breach that exposes the sensitive information of individuals and businesses.
- Anti-spy setup runs a guided checklist that reviews your device settings and app permissions, then points out what needs fixing, so spies can’t take advantage of weak spots.
- Device system check reviews your phone’s system for jailbreaks or other serious security issues and confirms that your software is updated with the latest protections.
- Unlock catcher discreetly uses your front camera to snap a photo of anyone who unlocks your phone, and saves it with the exact time in your Clario Anti Spy report.
- Spy cam detector lists every device on your Wi-Fi network so you can quickly spot suspicious ones, including hidden cameras.
- Virtual location masks your real GPS coordinates and lets you set a different spot on the map so trackers can’t see where you actually are.
- Anti-theft alarm triggers a loud alert when someone tampers with your phone so you can catch the person right away.
- 24/7 expert help gives you instant access to security professionals who can solve anti-spy issues anytime.
Conclusion
If you’ve ever wondered whether you need to copy your data, the answer is yes. Your data holds the keys to troves of personal information that should be guarded at all costs. Therefore, you must have data backup and recovery plans and systems in place.
As the adage goes, preparation is key. Implementing data backup strategies ensures you don’t lose data when the unthinkable happens. Use this article as a guide to back up your data securely. For extra security, use Clario Anti Spy to prevent spies from accessing and compromising your data.


