Table of contents
- What is a data leak?
- Cyber breach notification laws
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Data Breach Prevention and Compensation Act
- Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act of 2022 (CIRCA)
- Data breach costs
- Causes of information breaches
- Insider leaks
- Payment fraud
- Loss or theft
- Unintended disclosure
- Significant data breaches
- Microsoft
- Colonial Pipeline
- Yahoo!
- SolarWinds
- Sony Pictures
- Target
- Data breach prevention
- How to recover from a data breach
What is a data leak?
A data leak, privacy breach, or information breach occurs when sensitive, private, or protected information has been obtained and leaked by hackers.
These could be individuals with malicious intent, like an organization’s previous employees, a disgruntled employee, or someone with an axe to grind. All of these individuals could potentially be a data breach risk to an organization.
Personal information that could be included in a data leak includes the following data:
- Email addresses
- Cellphone and telephone numbers
- Social security numbers
- Login information for online accounts
- Physical addresses
- Credit card information
- Medical information and history
- Personally identifiable information
- Trade secrets
- Classified documents, and more.
There are several reasons why individuals (or a group of individuals) could leak personal information from a company’s database, like the following reasons:
- To sell the information on the dark web to make some money
- To expose an organization’s security vulnerabilities.
This proves that anyone can hack into an organization’s database and leak its information — from seasoned hackers and IT professionals to teenagers who have the know-how.
That’s why it’s important that companies undertake the strictest measures to protect their databases and the personal information of individuals linked to them.
Most Famous Data Breaches
Cyber breach notification laws
The United States has cyber breach laws that mandate organizations to notify individuals of breaches of data security involving personally identifiable information.
However, the best way to stay on top of data breaches affecting you is by using data breach monitoring software.
Clario’s data breach monitor is a cybersecurity tool that helps you stay on top of data breaches involving your email in the following ways:
- It scans the dark web to look for signs that your email address has been involved in a cyber leak
- It lets you know if your email address has been involved in a data breach
- If it has, Clario guides you through the process of securing your email, so you can protect your personal information.
Data breaches can be complex. Clario makes it easier for you to manage a situation where your email has been compromised in a breach.
Follow the steps below to check if your email was involved in a data breach:
- Download Clario on your computer
- Select Data breach monitor on the home screen
- Click on the Add email option, enter your email address, and select Add email
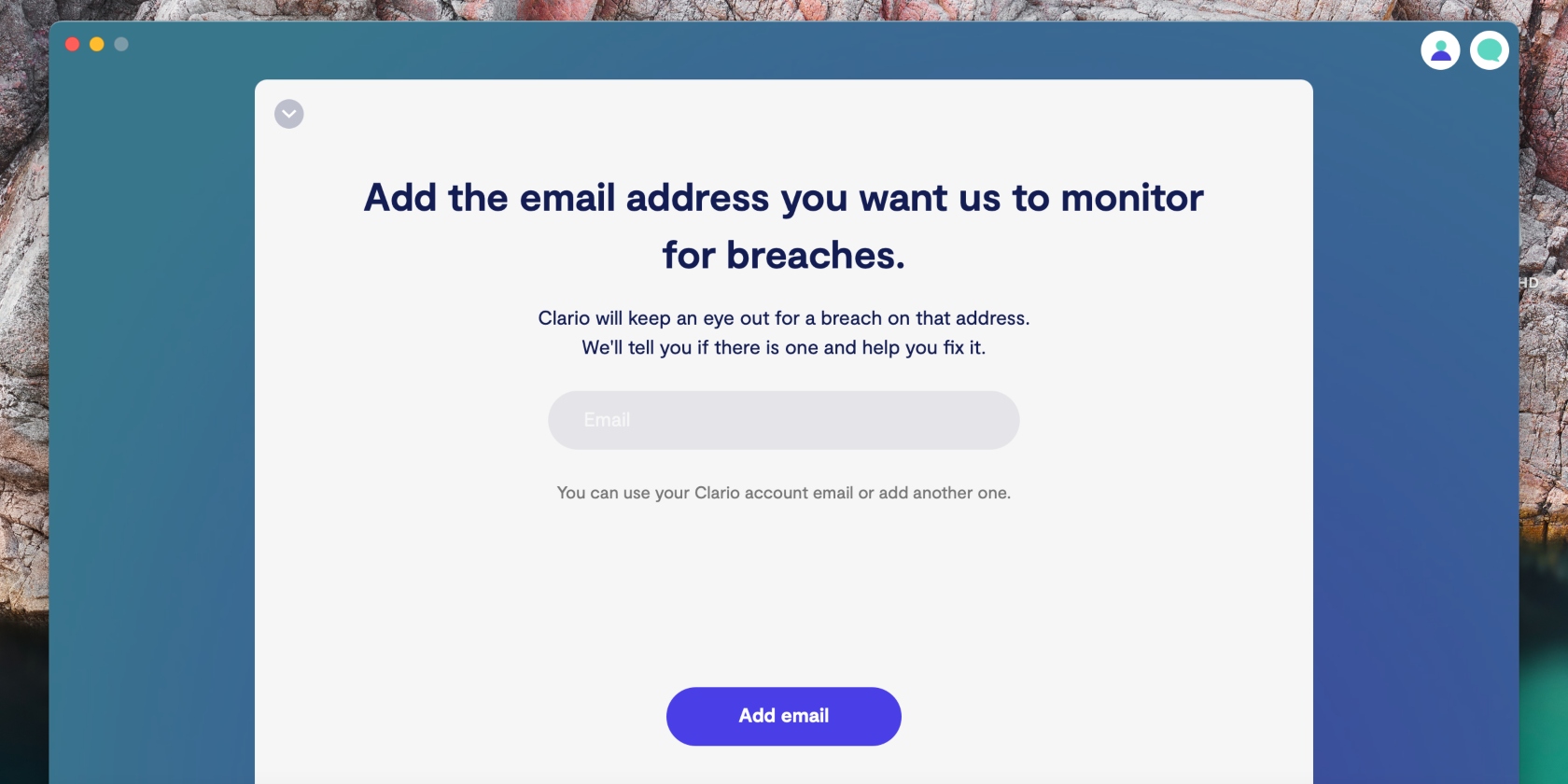
4. Clario will scan the web for data breaches containing your email. If any are found, tap Get verification code
5. Copy and paste the code from your emails to the text box and click Verify email, followed by Review a breach
6. Click on Show details to read more information about the breach and get advice
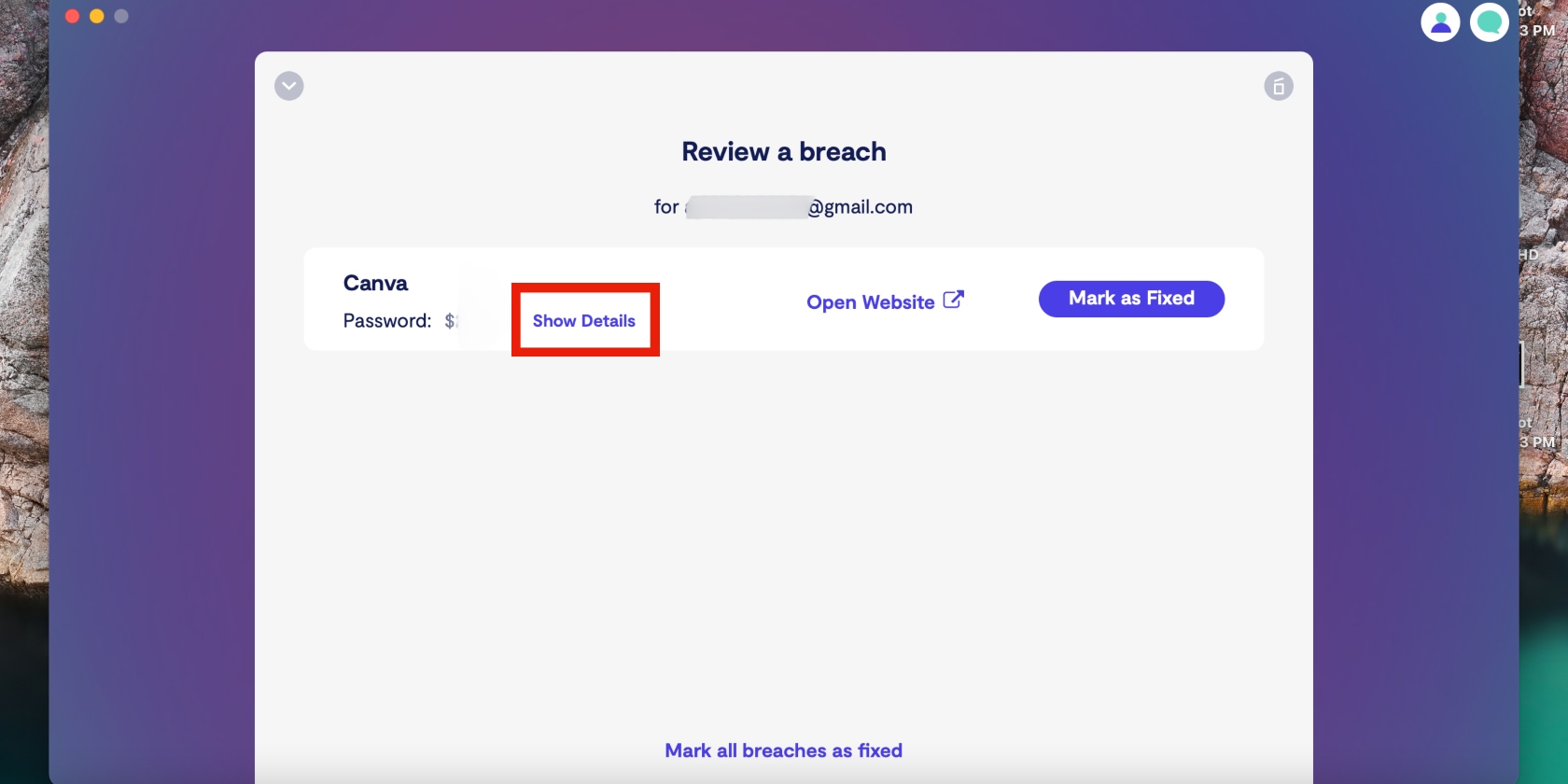
7. Now click Fix with expert to get started on fixing the breach
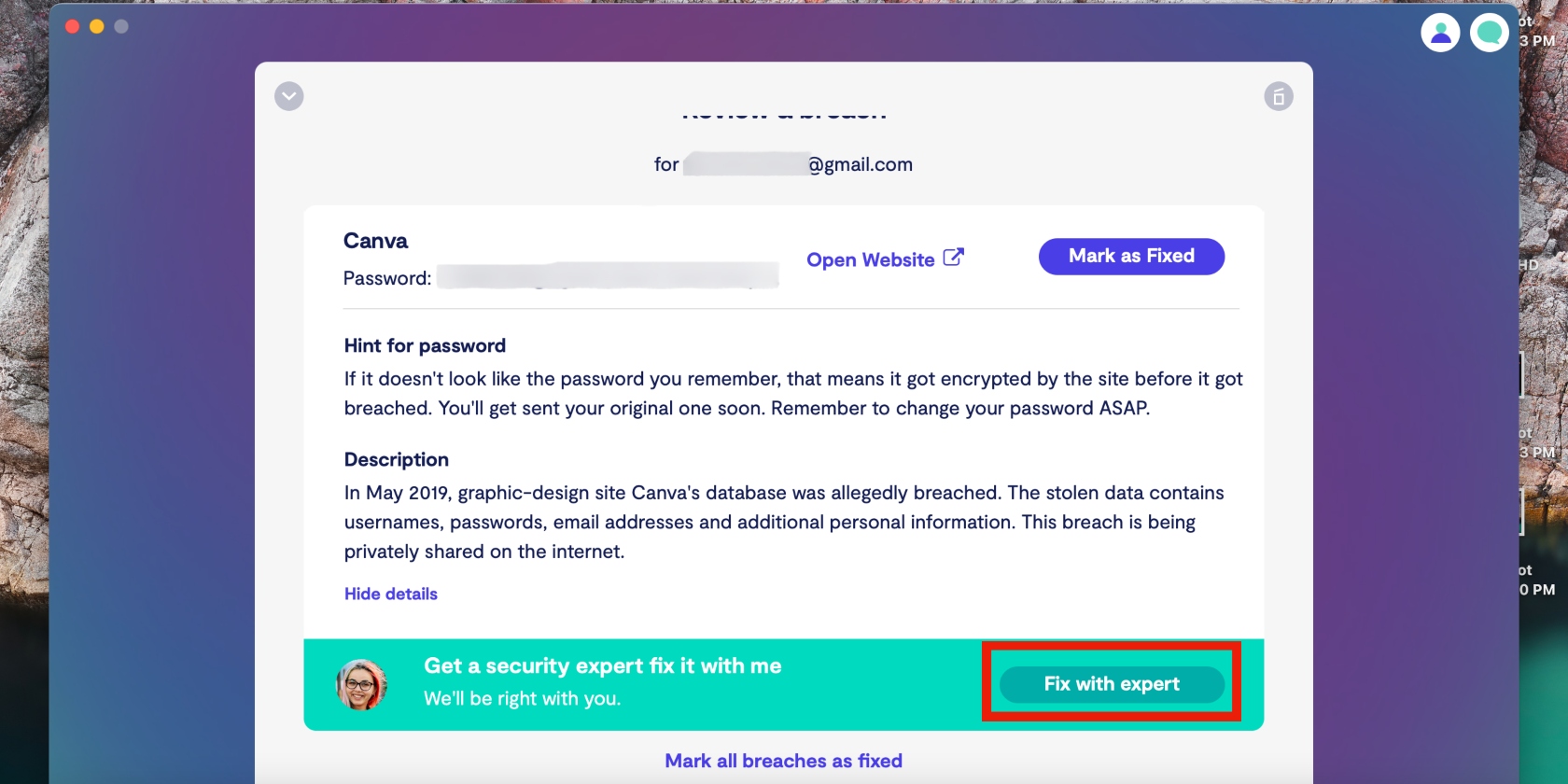
8. Repeat this process for any other breaches Clario has identified.
Once that’s done, read up on what to do after a breach. Continue to monitor your email address by keeping the data breach monitor enabled at all times.
Below are the laws that govern data leak incidents.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
Passed by the European Union (EU) in June 2018, the GDPR requires organizations to report a data leak within 72 hours. Failing which, they must provide reasons for the delay when they eventually report it.
The GDPR affects organizations located in the EU and those outside of the EU that provide goods and services or monitor the behavior of people in the EU.
Data Breach Prevention and Compensation Act
This act was passed in the US in May 2019. Through it, the Office of Cybersecurity was created at the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). The Office of Cybersecurity is responsible for the following activities at consumer reporting agencies:
- Supervising and regulating data security
- Establishing effective cybersecurity measures.
Similar to the GDPR, the Data Breach Prevention and Compensation Act requires consumer reporting agencies to:
- Notify the Office of Cybersecurity of the security measures they’ve put in place to prevent data breaches
- Notify the FTC of data breaches.
Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act of 2022 (CIRCA)
In 2022, President Joe Biden signed legislation that governs the reporting of data breaches in the US:
- The Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2022
- The Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act (CIRCIA) of 2022.
The legislations have the following requirements for organizations in certain critical infrastructure sectors (including health care, information systems, and financial services):
- Report cybersecurity incidents to the Department of Homeland security within 72 hours
- Report ransom payments made in response to ransomware attacks within 24 hours.
Data breach costs
Data breaches can be costly for both businesses and affected individuals. According to an IBM report, the cost of a data breach is:
- $4.35 million (globally) in 2022, up from $4.24m in 2021
- $4.82 million for critical infrastructure sectors — with the healthcare, finance, and pharmaceutical sectors having the highest average costs
- $9.44 million in the US alone — the highest cost of a data breach in the world
- $1.44 million in activities associated with the detection and escalation of data breaches
- $1.42 million in lost business
- $1.18 million for post-breach responses.
The financial impact of a data breach can be far-reaching for individuals whose personal information was compromised in a leak. For example, someone whose credit card information was abused or an individual whose personal information was used to scam others.
Causes of information breaches
Data breaches can come about due to several reasons or scenarios. Let’s have a look at the most common types of data breaches below.
Insider leaks
Disgruntled employees and former employees can become insider threats. They can access a company’s systems using their credentials to access and leak data for various reasons, including revenge.
Payment fraud
Payment fraud occurs when someone obtains funds or receives payments through fake or illegal transactions. Many consumers are researching ‘Is Temu safe?’ and are looking for reassurance that their payment details won't be compromised through fraudulent activity. A common example of payment fraud is a credit card breach, in which a victim’s credit card information is used for fraudulent transactions.
Loss or theft
Hardware that is left unsupervised or unsecured can be accessed or stolen, and the data it contains can be breached.
Unintended disclosure
Some data breaches are a result of human error. It’s common for individuals, employees, and IT consultants to make configuration mistakes and everyday mistakes. Unfortunately, cybercriminals are skilled enough to take advantage of them.
For example, an employee might handle sensitive data carelessly, which could result in it being exposed to cybercriminals.
Sensitive data can be accidentally stored in a location that is accessible on the internet. New IT employees or professionals could compromise an organization’s server online. Any of these scenarios could lead to a security leak.
Significant data breaches
Data breaches happen all the time, but some breaches are hard to forget due to their scale and impact. Below are examples of major data breaches that have made headlines in recent years.
Microsoft
In March 2021, Microsoft announced it had fallen victim to a cyber attack on a blog post. 60,000 business and government organizations in the US and worldwide who used Microsoft’s email servers were affected.
The hackers took advantage of a vulnerability in Microsoft’s mail and calendar server, Exchange. They subsequently exposed victims’ emails and installed malware to infiltrate businesses and governments.
Colonial Pipeline
Colonial Pipeline fell victim to a ransomware attack in May 2021 in which hackers used a leaked password to access Colonial Pipeline’s computer network. They targeted automated technologies that are used to manage oil flow — a critical part of Colonial Pipeline’s business operations.
Yahoo!
In September 2016, Yahoo! announced it had fallen victim to a major data breach in which 500 million accounts had been affected in a 2014 hack. In December, it revealed that 1 billion accounts had been compromised in a 2013 attack.
Compromised information included:
- Encrypted passwords
- Unencrypted password recovery questions
- Names
- Telephone numbers
- Birth dates.
SolarWinds
In 2020, information security company FireEye learned that SolarWinds had been involved in a cybersecurity attack. Orion, a SolarWinds IT performance monitoring system, was infected with malicious code in the attack, which compromised the systems, networks, and data of SolarWinds customers. 18,000 customers are believed to have downloaded the malicious code.
Sony Pictures
In November 2014, Sony Pictures’ network was compromised when hackers known as Guardians of Peace disabled its servers and workstations. The group stole company files, deleted original copies from Sony’s computers, and warned Sony against releasing a film that depicts North Korean leader Kim Jong Un being assassinated by Americans.
Target
In 2013, Target suffered a data breach that compromised the names and credit and debit card information of 110 million customers. Security researcher Brian Krebs was the first to report the breach. He noted that the breach affected customers who shopped at Target stores in the US between November 27, 2013 (Black Friday) and December 15, 2013.
There are too many data breaches to mention in this article. Read up on the top breaches of the 2010s.
Data breach prevention
While data leaks are difficult to manage and rectify, the good news is there are ways to prevent them:
- Educate your employees on the best practices for data safety and security
- Conduct regular assessments to check for security vulnerabilities
- Have a data backup and recovery plan
- Update your policies on allowing employees to bring their own devices to work
- Invest in good antivirus protection
- Use strong passwords and change them often
- Implement security and software updates regularly.
How to recover from a data breach
If your information has been compromised in a data breach, you can recover from it. However, time is of the essence, so the key is to act fast:
- Identify and isolate affected networks
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment to gauge the risks of a data breach
- Fix all security vulnerabilities
- Restore systems as quickly as possible
- Report breach to relevant parties
- Keep records of the incident for future reference.
Remember, the best way to stay on top of your cyber security is an early reaction. Use Clario’s Data Breach Monitor to find out if your personal data has been leaked.


