Table of contents
- What is a QR code, and how does it work?
- What makes QR codes great?
- The direction of scanning doesn’t matter
- 2D arrangement of data
- QR codes do not live-track you
- Resistant to data loss
- QR codes collect valuable first-party data
- Security risks of scanning QR codes
- Malware attacks
- Phishing attacks
- Financial fraud
- Your location might be compromised
- Clickjacking using QR codes
- Third parties could get your personal information
- Tips for using QR codes safely
- Avoid scanning random QR codes
- Avoid making payments through a site navigated to from a QR code
- Check the code for suspicious elements
- Verify the URL
- Install an antivirus for additional security
- Avoid using third-party applications to scan the QR code
- Enable two-factor authentication on your accounts
- Turn off the live location
- Keep your devices updated
- QR code security best practices for businesses
- Custom brand your QR code
- SSL-certify your webpage
- Invest in a compliant QR code generator
- Choose protection with a QR password
- Partner with a certified QR code solution provider
- Use an SSO-enabled QR code generator
- Are QR codes safe?
What is a QR code, and how does it work?
QR code definition
QR code is a square graphic of tiny black dots on a white background that stores data in a vertical and horizontal format. It is scannable by a smartphone camera or a QR code scanning app.
Initially, QR code was used for tracking and inventory in the manufacturing industry. But the QR code technology has come a long way since 1994 when Denso Wave, a Toyota subsidiary, created it to address the shortcomings of barcode scanners.
QR code, which stands for “quick response” code, is a commonly used technology today — for restaurant menus, business cards, ads, brochures, and even signing into apps like WhatsApp. Businesses and professionals use QR codes because of their simplicity and functionality. After a few seconds of scanning, users can access a web page or a document, making it a valuable tool for marketing and sharing information at a budget-friendly cost. We can see how valuable the QR code technology is when restaurants, hotels, and other businesses started using QR codes to serve their clients contactless during the 2020 pandemic.
What makes QR codes great?
Before we discuss how safe QR codes are for businesses and individuals, let’s talk about the benefits of QR codes that made them so popular among businesses.
- The direction of scanning doesn’t matter
- 2D arrangement of data
- QR codes do not live-track you
- Resistant to data loss
- QR codes collect valuable first-party data
The direction of scanning doesn’t matter
QR codes have three large squares on the bottom left, upper left, and upper right corners known as “modules.” They are detection tools called “finder patterns.” QR codes also have an alignment pattern, a small square at the bottom right corner that makes QR codes readable from any angle, skewed and otherwise.
The finder and alignment patterns allow QR code scanning devices to detect and read QR codes from any angle the user scans without worrying about data loss or scanning speed.
2D arrangement of data
Unlike barcodes which store digital information strictly in vertical format, QR codes store data in two dimension format, horizontally and vertically. Hence, QR codes can save significantly more content than barcodes.
Nota bene: You can tell barcodes and QR codes apart by their designs, while QR codes have a square matrix design, barcodes have a rectangular shape with parallel lines. Additionally, barcodes have a typical storage capacity of 100 bytes, while QR codes can store up to three kilobytes of data, about 3,000 bytes.
QR codes do not live-track you
While QR codes collect timestamps, number of scans, location of scans, and operating systems of the scanning devices, it doesn’t track the user. QR codes collect this information to share with the QR code creator to monitor the performance of the QR code. But people scanning QR codes don’t need to worry about QR codes live-tracking them or accessing their personally identifiable information (PII).
Resistant to data loss
QR codes have an L-shaped line between the three finder pattern squares that helps the QR code scanning device identify each square on a QR code. The L-shaped line is called a timing pattern, and it ensures that a QR code is recoverable and readable even when up to 30% of the code is damaged, missing, or unclear. As a result, the risk of experiencing data loss on QR codes is low compared to barcodes.
QR codes collect valuable first-party data
Since QR codes collect timestamps, number of scans, location of scans, and operating systems of the scanning devices, you can use them to collect valuable first-party data. You can encode a questionnaire, survey, or any user interaction content on a QR code and share the QR code with your target audience. You will receive insights showing the difference between the number of scans and the number of successful user interactions. With that, you can conclude that users who successfully complete the user interaction content are high-intent potential leads.
Security risks of scanning QR codes
Let’s look at some of the ways cybercriminals are using QR codes to commit all kinds of cybercrimes that are posing major risks to businesses and their customers.
- Malware attacks
- Phishing attacks
- Financial fraud
- Your location might be compromised
- Clickjacking using QR codes
- Third parties could get your personal information
Malware attacks
Malicious QR codes became so threatening in the cybersecurity industry that the FBI released a statement warning about cybercriminals using QR codes to steal from people. Cybercriminals are putting fake QR codes with files containing malware, ransomware, and viruses in public places, and even pasting them on top of authentic QR codes.
Nota bene
Scanning a malicious QR code can download dangerous malware into your device to hack into your personal data, such as banking credentials.
Phishing attacks
Cybercriminals have had almost three decades since 1994 to discover clever ways to use QR codes for phishing attacks. QR code phishing attacks, also known as “QRishing,” disguise clone URLs of legitimate websites, which are then used to trick unsuspecting people to enter their login credentials. Like other phishing attacks, “QRishing” cybercriminals collect login credentials and use them later to access their victims’ accounts on trusted websites.
Financial fraud
QR code as a payment method has become a common practice in the last few years. So it’s no surprise that cybercriminals are disguising QR codes as a payment method for genuine transactions from a legitimate company. But instead of paying to the trusted company account or the correct amount for the product/service, the QR code will redirect to a different account.
Your location might be compromised
Remember we mentioned that one of the features of QR codes is collecting timestamps and location of scans and other scanning data? Dangerous criminals who deal in location-based crimes, such as kidnapping, stalking, and human trafficking, can use QR codes to determine the approximate location of their targets. You might think you’re scanning a Google Maps QR code, but it’s a fake QR code created by a criminal entity to determine your location.
Clickjacking using QR codes
Clickjacking is a cyberattack which is a type of user interface (UI) redressing that makes victims click, engage with, and agree to a hidden call to action (CTA). Upon scanning QR codes used for clickjacking, it will go to a legitimate-looking website and ask users to click a few buttons or links — for example, “book a free massage session.” However, in reality, the “book a free massage session” button has been cleverly placed on top of a hidden button with a malicious CTA such as “confirm payment transfer.” So, if a user who is already logged into their banking site clicks “book a free massage session,” the “confirm payment transfer” button will take effect in the background.
Third parties could get your personal information
Cybercriminals can use malicious QR codes to hack into their victim’s personal information and take over control of the scanning device. QR codes cybercriminals can force your device to carry out an action, such as sending a text or placing a phone call, and even connecting to an unsecured Wi-Fi.
Because hackers can use malicious QR codes to take control of your phone, they can force it to download third-party apps that can make your phone vulnerable to data breaches.
Tips for using QR codes safely
Despite the security risks of scanning QR codes, the good news is that you can scan QR codes safely without compromising your privacy and security, and we will discuss how below.
- Avoid scanning random QR codes
- Avoid making payments through a site navigated to from a QR code
- Check the code for suspicious elements
- Verify the URL
- Install an antivirus for additional security
- Avoid using third-party applications to scan the QR code
- Enable two-factor authentication on your accounts
- Turn off the live location
- Keep your devices updated
Avoid scanning random QR codes
The first step to protecting yourself against cyberattacks is to practice secure browsing with all your internet activity, including your interaction with QR codes. Avoid scanning random QR codes in public places and online. Remember, cybercriminals tend to disguise malicious QR codes as legitimate ones.
Don’t be moved by the fear of missing out (FOMO) when there’s a trending QR code that you will neglect your safety concerns about the internet.
Avoid making payments through a site navigated to from a QR code
QR code as a payment method is cute and futuristic, but don’t let that fool you into using it to make payments and risk exposing your financial data to unknown entities. No matter how seemingly trusting they are, remember that a legitimate company will have other reliable payment methods that won’t expose your credit card details. Besides, you can manually type the URL of the company on your browser by yourself to pay instead of paying off a QR code link.
Check the code for suspicious elements
When you are in a mandatory QR code situation or curious to see what happens when you scan a QR code, check if the QR code is valid before scanning. Sometimes, it’s almost as if cybercriminals leave suspicious clues you can identify to differentiate malicious QR codes from real ones. So, check the frame texts, logo, colors, and other design elements of the QR code and compare them with the brand the QR code is supposed to represent. You can conclude that any QR code design that doesn’t match the brand design of the company it is supposedly representing is a malicious QR code and avoid scanning it.
Verify the URL
The good thing about scanning QR codes with smartphones is that they show pop-ups of the URLs on the QR codes for you to decide whether or not to click and visit the URLs. It’s an opportunity to scrutinize the URLs to spot any security discrepancies, such as a missing SSL certificate which is supposed to give the URL the “s” in the (https://). Don’t be quick to tap the URL when it pops up after scanning a QR code without verifying.
Install an antivirus for additional security
As long as you browse and do stuff on the internet, you can’t completely escape cyberattacks. However, you can mitigate whatever threats you run into from scanning QR codes by installing a reliable antivirus on your devices.
Instead of wondering whether PDFs can have viruses after unknowingly scanning a QR code with a PDF carrying malware or ransomware, you can rely on your antivirus to give you additional protection.
If you're worried about accidentally scanning a malicious QR code, Clario Anti Spy can help. Its Device system check quickly identifies security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious apps, while the Anti-spy setup walks you through the steps to stay safe online.
Here's how to protect your phone with Clario Anti Spy:
- Download Clario Anti Spy and subscribe to create an account.
- Tap Scan under Device system check.
- Follow the onscreen instructions to address any security threats.
- Tap Set up under Anti-spy setup.
- Work through the steps to enhance your phone's privacy and security.

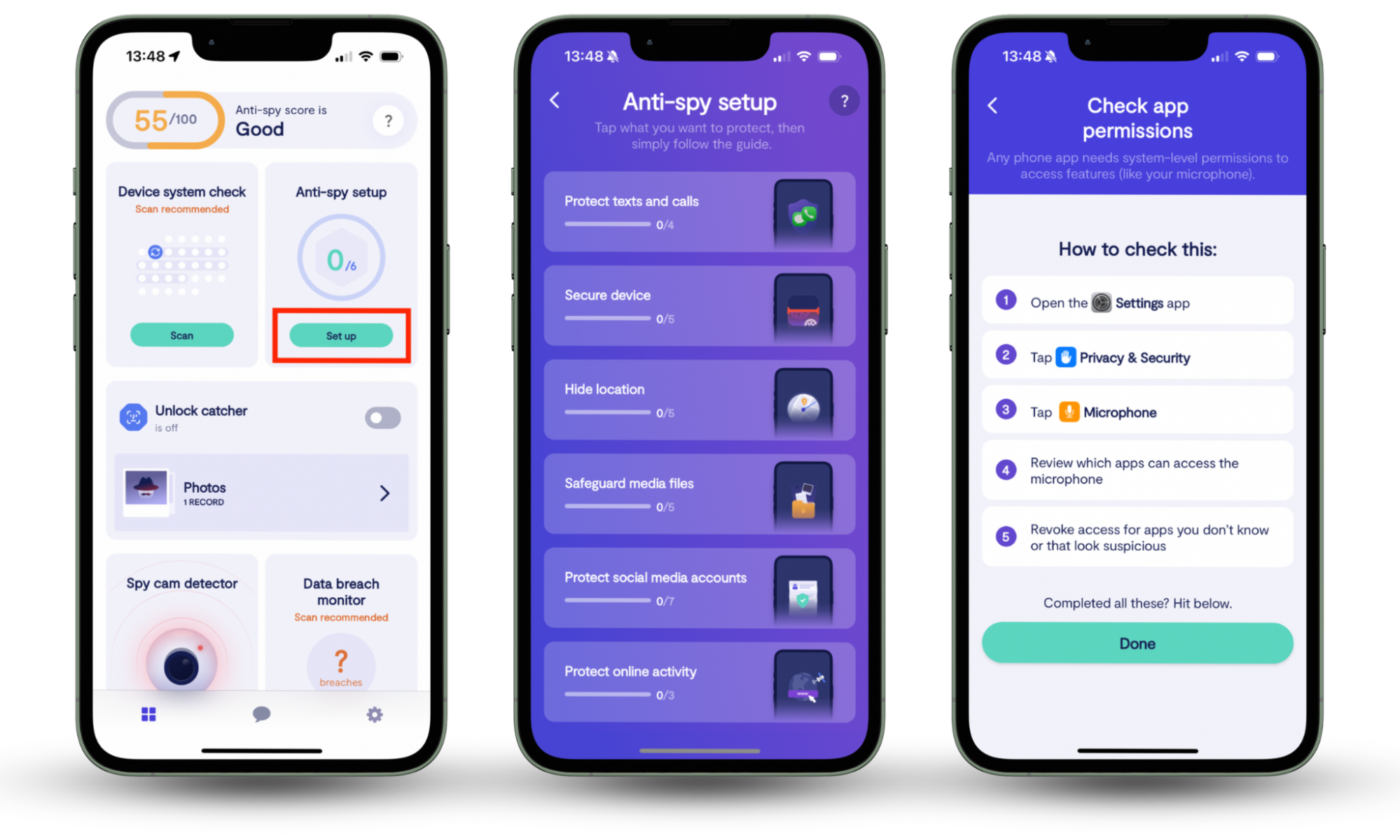
Clario Anti Spy also includes a spyware scanner for Android. If you think you may have scanned a malicious QR code, run a scan to check for harmful or invasive apps. To do that, tap Scan under Spyware scan.
Avoid using third-party applications to scan the QR code
The cybercrime industry is large and connected, so it’s no surprise that some third-party QR code scanner apps can expose your phone to cyberattacks. Since it’s common practice to give installed apps settings permissions, malicious third-party scanner apps can access some privacy settings and turn them off when scanning QR codes.
Instead of installing a third-party scanner app, use your in-built phone camera to scan QR codes.
Enable two-factor authentication on your accounts
If all else fails, two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security measure you can trust to remain effective when cybercriminals have your login credentials. Cybercriminals know that many people use the same password across different platforms. Once they have your login credentials, they will try to access your account on different platforms. Hence, you should enable 2FA across all platforms to protect against unauthorized login before you get a chance to change your password across.
Turn off the live location
Safe QR codes collect scanning data, including the location of scans. Cybercriminals can also use QR codes to collect similar location-based data. Such location-based information getting into the hands of people with malicious intent is a risk you can’t afford to take.
Ensure to practice QR code privacy by turning off live location settings to limit apps from accessing your exact location.
Keep your devices updated
While you can’t always be sure that a QR code is safe to scan, you can protect your device against cybersecurity threats by keeping it updated. Device manufacturers tend to release updates with security patches that can protect your device against scams, so don’t hesitate to update your device.
QR code security best practices for businesses
While individuals are responsible for their online security, it is your duty as a business to ensure that your customers enjoy safe QR code interactions with your brand.
- Custom brand your QR code
- SSL-certify your webpage
- Invest in a compliant QR code generator
- Choose protection with a QR password
- Partner with a certified QR code solution provider
- Use an SSO-enabled QR code generator
Custom brand your QR code
As a brand, design your QR codes with your existing brand design elements — colors, font, logo, etc., so that your customers can easily identify them. Doing this will help your customers avoid suspicious QR codes claiming to represent your brand.
You should also consider security-conscious customers that will not engage QR codes that don’t look professional and legitimate.
SSL-certify your webpage
Many internet users in today’s world only visit websites with SSL certificates, and they can confirm by checking URLs for “https://.” It stands for hypertext transfer protocol secure. So, if the URLs on your QR codes don’t have SSL certificates and encryption, some of your target audience will conclude that your QR codes are a potential cybersecurity threat.
Whether you’re partnering with other brands or using a free QR code generator, avoid using URLs with only “http://.”
Invest in a compliant QR code generator
As a brand, invest in a QR code generator that complies with data privacy laws and regulatory bodies, such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Free QR code generators are great, but a premium QR code generator with enterprise-level security and privacy protection can secure your customer data against unauthorized third parties. Ensure to confirm that your QR code generator also offers data encryption.
Choose protection with a QR password
When sharing your QR code data with employees and other trusted entities, limit access by enabling password protection. Doing this will ensure that other employees and outsiders without permission-level access to the QR code data can’t access delicate customer PII.
Partner with a certified QR code solution provider
Your QR code generator should also have SOC-2 Type-1 and SOC-2 Type-2 certification, which is created by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants. The SOC 2 certification is an assessment that checks the security level of data management in companies. Ensure to mention to customers that your QR code solution provider is SOC-2 certified.
Use an SSO-enabled QR code generator
Another way to protect your customers from cyberattacks when scanning your QR codes is by making your QR codes support single sign-on (SSO) login. SSO allows users to access multiple connected platforms without entering their username and password multiple times — Google platforms, YouTube, Gmail, Chrome, etc. are good examples.
An SSO-enabled QR code generator will eliminate the need for your customers to reenter their login credentials after scanning your QR codes, thereby reducing the risk of untrusted entities stealing their login credentials.
Are QR codes safe?
Yes, QR codes are safe as long as you follow the online safety rules mentioned above. QR code technology is a valuable tool for businesses and individuals, but as with all popular technologies, cybercriminals use QR codes to exploit unsuspecting people. Until there’s a definite way to stop the cybercrime industry, individuals and businesses must take necessary precautions to protect themselves and their customers against threat actors in the QR code industry. Clario Anti Spy can also help you keep your phone secure by ensuring your system software is up to date, and your privacy settings are properly configured.


