Table of contents
- What is rooting?
- 8 disadvantages of rooting Android
- 1. Update problems
- 2. Loss of warranty
- 3. Reduced performance
- 4. Impairment of device security
- 5. Potential privacy issues
- 6. Unavailable services
- 7. Data loss
- 8. Bricking risk
- Conclusion
What is rooting?
Rooting is the process of gaining administrator-level access (called “root access”) to your Android device’s operating system. It lets you modify system files, install unauthorized apps, remove pre-installed software, and customize your device beyond manufacturer limits.
But why is rooting Android bad? The problem is, rooting can introduce a range of serious problems that can open you up to malware and hackers.
It’s similar to jailbreaking on iOS devices but only possible with Android’s system architecture.
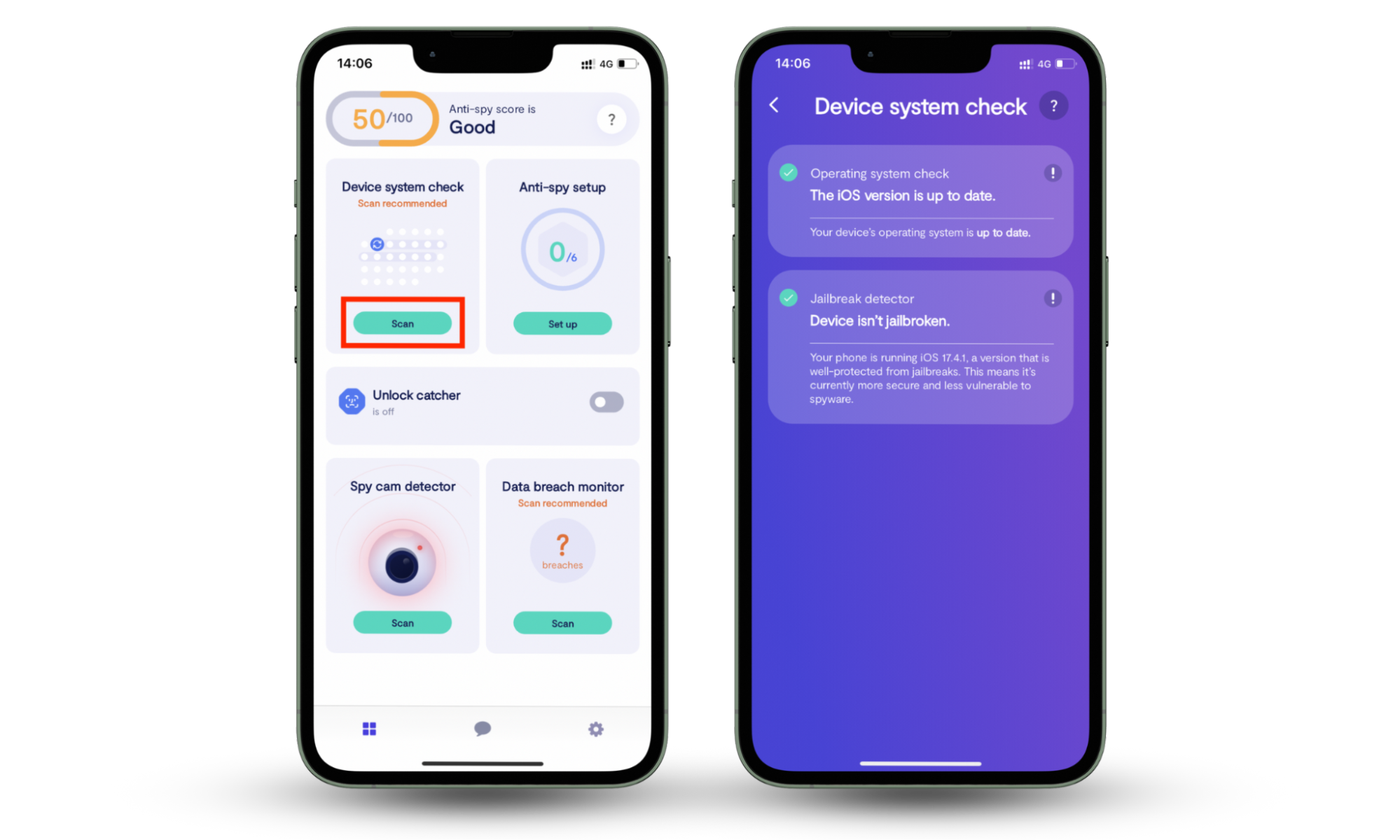
If you’re concerned that someone else has rooted your phone, Clario Anti Spy can help. With Clario Anti Spy’s Device system check, you can scan for vulnerabilities like rooting (or jailbreaking on your iPhone).
Here’s how to use Clario Anti Spy’s Device system check:
- Launch Clario Anti Spy and make an account.
- Locate Device system check, then press Scan.
- Wait for Clario Anti Spy to check your device. If it says your device is secure, you’re in the clear.
8 disadvantages of rooting Android
Rooting your Android phone comes with serious downsides that might not be worth the customization perks. You remove your phone’s protective barriers, making your phone vulnerable to security threats and potentially exposing your personal information.
Rooting can “brick” their device (making it unusable), make you lose warranty coverage, and cause frustrating performance issues. System updates often fail on rooted phones, and malicious apps can gain dangerous levels of access to your data.
Before rooting, ask yourself if the following cons of rooting your Android are worth the benefits of customization. If, after reading the disadvantages of rooting Android, you decide to go ahead—make sure you know how to secure Android devices.
1. Update problems
When you root your phone, it’ll sometimes fail to install system updates properly. Android designs its updates for unmodified phones, so your rooted device no longer matches what the update expects to find.
Because of this, you’ll experience failed updates, crashes after updating, or updates that remove your root access entirely—forcing you to start over after each update.
2. Loss of warranty
Most manufacturers won’t honor your warranty if you root your phone. When you send in your device for repair, the technicians can test if you’ve tampered with the system—even if you try to fix it by “unrooting” it first. This means you could end up paying full price for repairs that warranty should cover.
3. Reduced performance
While rooting promises to make your Android perform better, it can do the opposite over time. Rooted devices can have faster battery drain, overheating issues, and random crashes.
Custom modifications that originally sped things up often caused problems with system processes. These incompatibilities lead to sluggish performance and frustrating glitches.
Keep your eye out for Android phone hacked signs—these are very similar to the side effects you’ll get from rooting.
4. Impairment of device security
Rooting breaks down Android’s built-in security mechanisms that restrict your app’s permissions. It’s like taking away the walls of your house—suddenly, everything has access to everything else. This makes it easier for malicious apps to steal your passwords, banking information, and personal data.
5. Potential privacy issues
On a rooted phone, apps with root permission can silently access your private information without your knowledge. This includes passwords, messages, photos, and browsing history.
Even worse, tracking software (like stalkerware for Android) can hide more effectively on rooted devices, potentially recording your screen, logging your keystrokes, or monitoring your calls without triggering security warnings.
Learn how to find hidden spy apps on Android to protect yourself from this risk—especially if you decide to go ahead with rooting.
6. Unavailable services
Many important apps don’t work on rooted phones. Banking apps, payment services like Google Pay, and streaming platforms like Netflix often block rooted devices. They detect your phone’s compromised security and automatically prevent the apps from working.
7. Data loss
Rooting increases the chance of you losing photos, contacts, and messages. When root processes go wrong, they damage the phone’s file system. This can make it impossible to recover data. And, root-enabled apps can delete or corrupt important system files, potentially wiping out your data without warning.
8. Bricking risk
Bricking means turning your phone into an expensive paperweight. During the rooting process, you modify critical system components that control how your phone starts up.
If something goes wrong (power loss, incorrect file changes, incompatible software), your phone might become completely unresponsive. It’ll be unable to turn on or connect to a computer for recovery, and you might lose everything.
Conclusion
Rooting your Android might seem tempting, but the risks usually outweigh the benefits. When you root your phone, you break down important security features that keep your personal information safe. This can lead to crashes, failed updates, and apps that suddenly stop working.
Want to check if your phone has been rooted without your knowledge? Use Clario Anti Spy's Device system check to scan for security problems and protect your personal information.


