Table of contents
- What are Wi-Fi security protocols?
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy): Definition & Meaning
- WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access): Definition & Meaning
- WPA2: Definition & Meaning
- Differences between WPA & WPA2
- WEP vs. WPA vs. WPA2
- WEP: Advantages and Disadvantages
- WPA: Advantages and Disadvantages
- WPA2: Advantages and Disadvantages
- What about WPA3?
- Wi-Fi encryption tools
- How to identify your Wi-Fi security type
- Check your Wi-Fi security type on macOS
- Check your Wi-Fi security type on Windows
- Check your Wi-Fi security type on Android
- Check your Wi-Fi security type on iOS
- Which Wi-Fi security type suits me the best?
What are Wi-Fi security protocols?
Wireless network protocols were initially created to achieve and maintain protection on home Wi-Fi networks. During the course of the past four decades, Wi-Fi security protocols have gone through a number of significant upgrades to boost their security (we’ll dive more deeply into their evolution below).
From the inception of Wi-Fi security protocols to today, people across the world make use of the following four wireless security protocols on both private and public Wi-Fi networks:
- Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
- Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
- Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2)
- Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3)
While each of these wireless security protocols’ core mechanisms is unique from one another, they ultimately serve the same purpose: offering security to wireless networks.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy): Definition & Meaning
WEP is the original Wi-Fi security standard established by the Wi-Fi Alliance in 1999. It set out with the mission of providing a comparable level of security when using a wireless connection to that of a wired connection.
At its core, WEP encrypts traffic using a 64- or 128-bit key. This means that all traffic, regardless of the device it comes from, is encrypted using a single key. This is where the WEP security protocol’s vulnerabilities take shape, as the key that encrypts traffic can be reused. Reusing keys is a major cryptographic weakness in any security system, leaving networks susceptible to attack.
Although certain older systems continue to use WEP after its official retirement in 2004, it isn’t a security standard for today’s cybersecurity landscape. Thus, any systems still using WEP should upgrade their Wi-Fi security protocol to a newer and more capable standard.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access): Definition & Meaning
Making its debut in 2003, WPA is the Wi-Fi security protocol that was created largely as a response to the most significant weaknesses undercovered in the WEP protocol over time.
Whereas WEP was created before attack methods targeting routers were fully understood, WPA made significant progress in mitigating these exploits. This was aided by the fact that WPA requires users to password-protect their network, and on top of that, its encryption capabilities are much improved from those of WEP.
At the center of WPA’s encryption is the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), a component that enables the dynamic generation of keys per packet with the use of the RC4 cipher.
While undoubtedly an improvement from the encryption abilities of WEP, the fact that TKIP was designed to be implemented onto WEP systems via firmware updates means that it remains vulnerable to certain attacks, namely those originating in the same network as well as pre-shared key attacks.
But no matter how secure your Wi-Fi is, your privacy is still at risk if you haven't tightened the settings on your mobile devices. That's where Clario Anti Spy comes in. This anti-spyware solution offers an Anti-spy setup that guides you through the basics of protecting your iPhone or Android from spyware.
Here's how to run an Anti-spy setup with Clario Anti Spy:
- Download Clario Anti Spy and subscribe to create an account.
- Tap the Set up button under the Anti-spy setup section.
- Work through each category to enhance your phone's privacy and security.
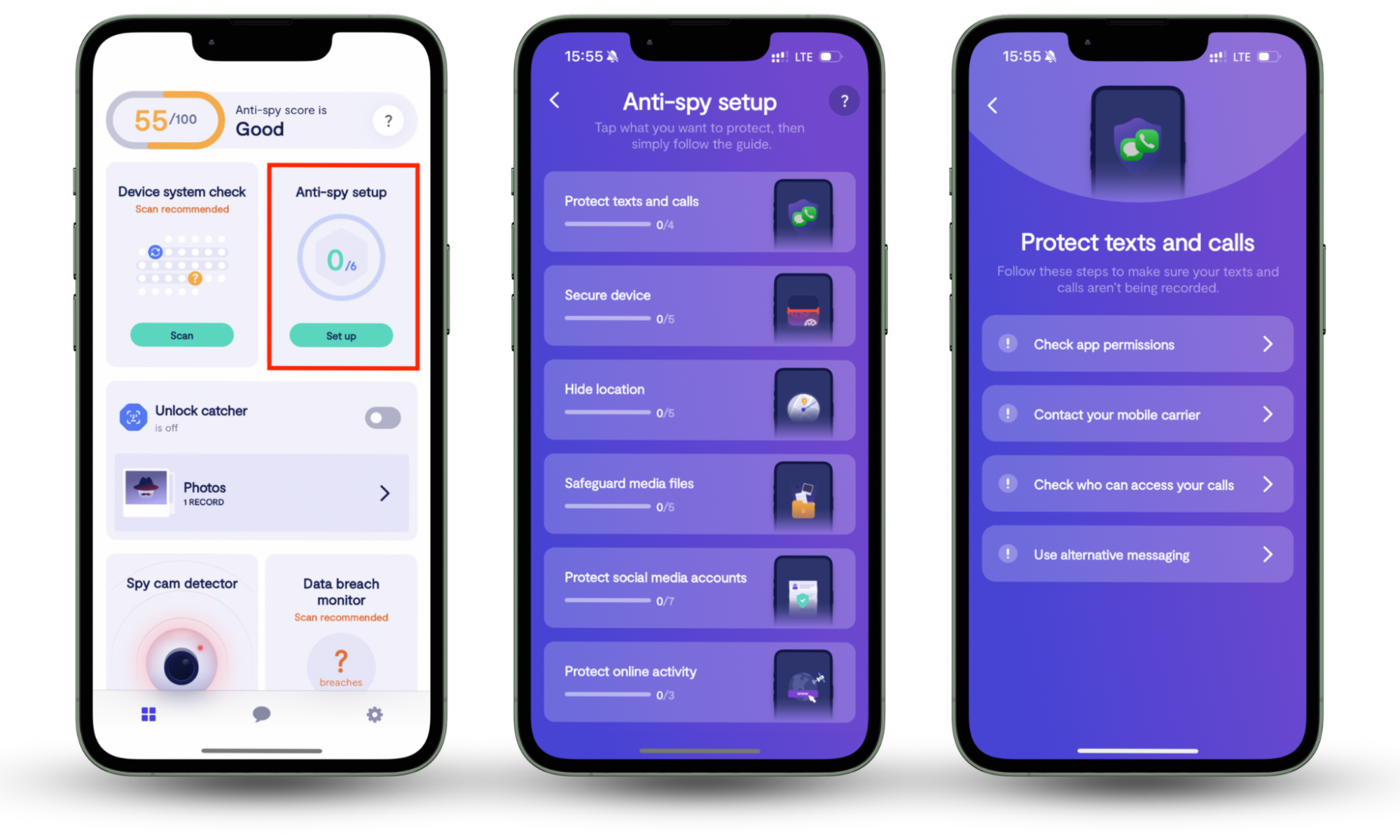
In addition to that, Clario Anti Spy warns you about jailbreaks and rooting attempts, alerts you to data breaches, and even records unauthorized attempts to unlock your phone. On Android, it also includes a spyware scanner and a location-hiding feature to maintain anonymity, even without a VPN.
WPA2: Definition & Meaning
WPA2 was created just one year after its predecessor, first being released in 2004. Encryption is at the center of the WPA2 protocol. To bolster the protocol’s encryption, the TKIP system was phased out. In its place, the Advanced Encryption System (AES) security protocol was introduced. AES provides a high level of security to both home and enterprise users.
Unlike the former WPA protocol’s TKIP system, WPA2’s AES is compatible solely with hardware that has implemented the AES standard, which results in a higher standard of security.
Differences between WPA & WPA2
As both WPA and WPA2 security protocols are still widely used, there’s a good chance that your Wi-Fi router has both options available. When you enable your router’s Wi-Fi encryption, the most trustworthy choice is to go with WPA2.
In simple terms, WPA2 is the new and improved version of WPA. As we’ve outlined above, WPA’s encryption relies on the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), while WPA2 makes use of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for added security.
As both WPA and WPA2 security protocols are still widely used, there’s a good chance that your Wi-Fi router has both options available. When you enable your router’s Wi-Fi encryption, the most trustworthy choice is to go with WPA2.
WEP vs. WPA vs. WPA2
Let’s break down the good, the bad, and the ugly of WEP, WPA, and WPA2.
WEP: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Works with devices that are too old to support newer security protocols | Contains many exploitable security vulnerabilities |
| Relies on 64-bit and 128-bit keys for encryption | |
| Difficult to configure |
WPA: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Supports older software | Doesn’t offer solutions for enterprises |
| Requires shorter passwords | Provides inferior security to WPA2 |
| Provides superior security to WEP |
WPA2: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Offers solutions for enterprises | Requires a high level of processing power, which can result in decreased network performance |
| Addresses many of WPA’s security flaws | |
| Most secure option available due to its use of AES |
What about WPA3?
WPA3 is the newest iteration of the Wi-Fi security protocol and was introduced in 2018. With its robust encryption and heightened security, WPA3 security offers solutions for both personal and enterprise networks, including password protection and added protection against brute force attacks — all within a user-friendly experience.
Through its use of the Perfect Forward Secrecy encryption type, WPA3 can protect your data even in the case that your password becomes compromised. Due to the fact that WPA3 is still being implemented, compatible and WPA3-certified hardware isn’t available to most people just yet.
Wi-Fi encryption tools
Wi-Fi security protocols have become standard to protect Wi-Fi networks. However, using Wi-Fi security protocols isn’t everything that you can do to stay safe while using Wi-Fi.
There are numerous ways to secure your home Wi-Fi network from hackers. A VPN is one of the best Wi-Fi encryption tools to protect your data. Importantly, a VPN encrypts your outgoing web traffic and safeguards your personal data from being stolen or maliciously used by cybercriminals.
How to identify your Wi-Fi security type
Depending on the device you have, there are various ways to find out which type of Wi-Fi security protocol you’re using.
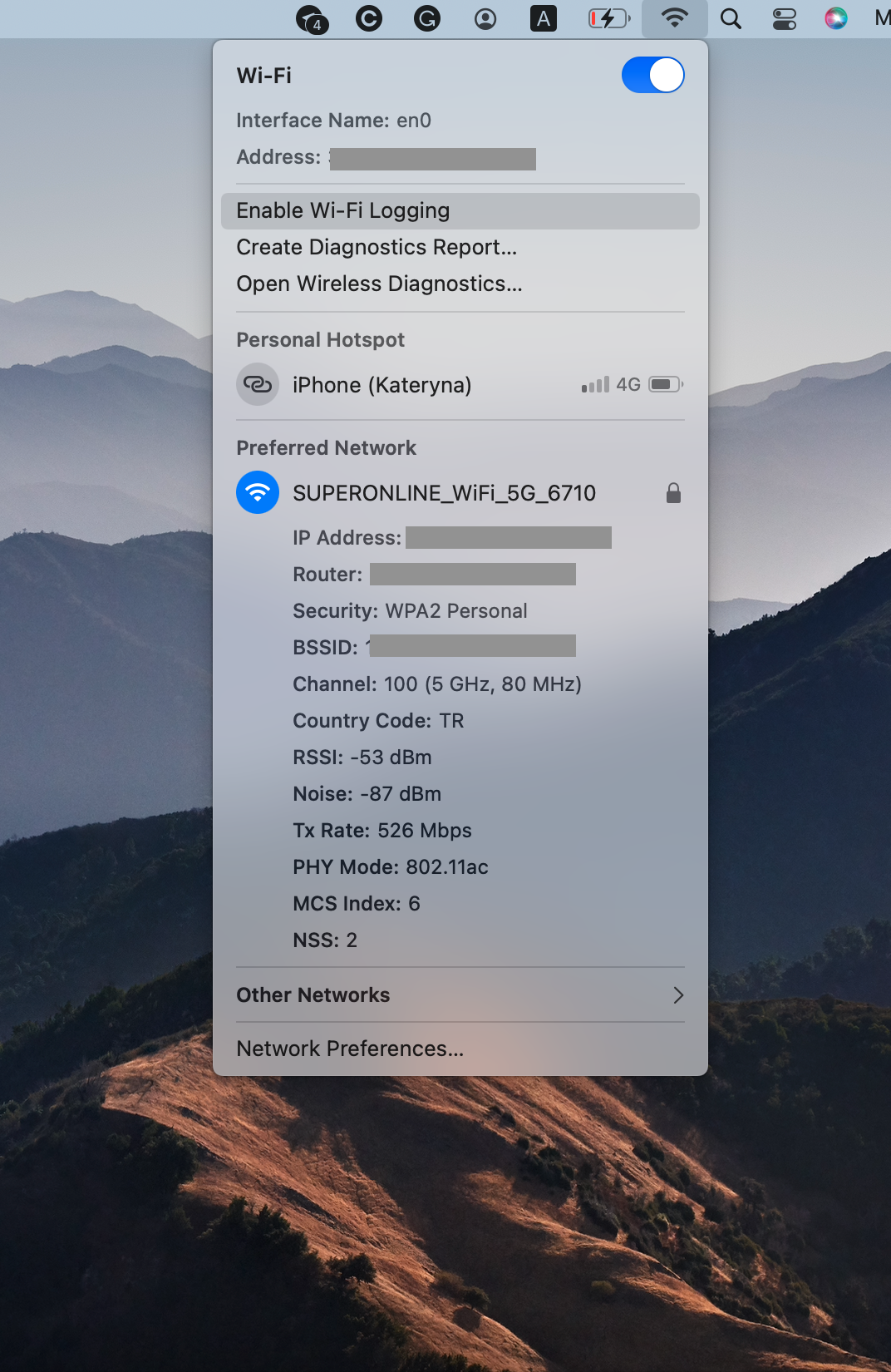
Check your Wi-Fi security type on macOS
Checking the Wi-Fi security type on macOS is straightforward. Simply press and hold the Option key and select the Wi-Fi icon in the toolbar or Control Center. This will display the details of the network that you’re currently using, including its security type.
Check your Wi-Fi security type on Windows
On Windows 10 and 11, you can use the following steps to determine your Wi-Fi security type:
- Locate and select the Wi-Fi Connection icon in the taskbar
- Under your current Wi-Fi connection, select Properties
- Within Properties, locate the Wi-Fi details
- Look for Security Type, which displays your Wi-Fi security type

Security type ‘Open’ means it is not protected, and anyone can access it without a password within the network range.
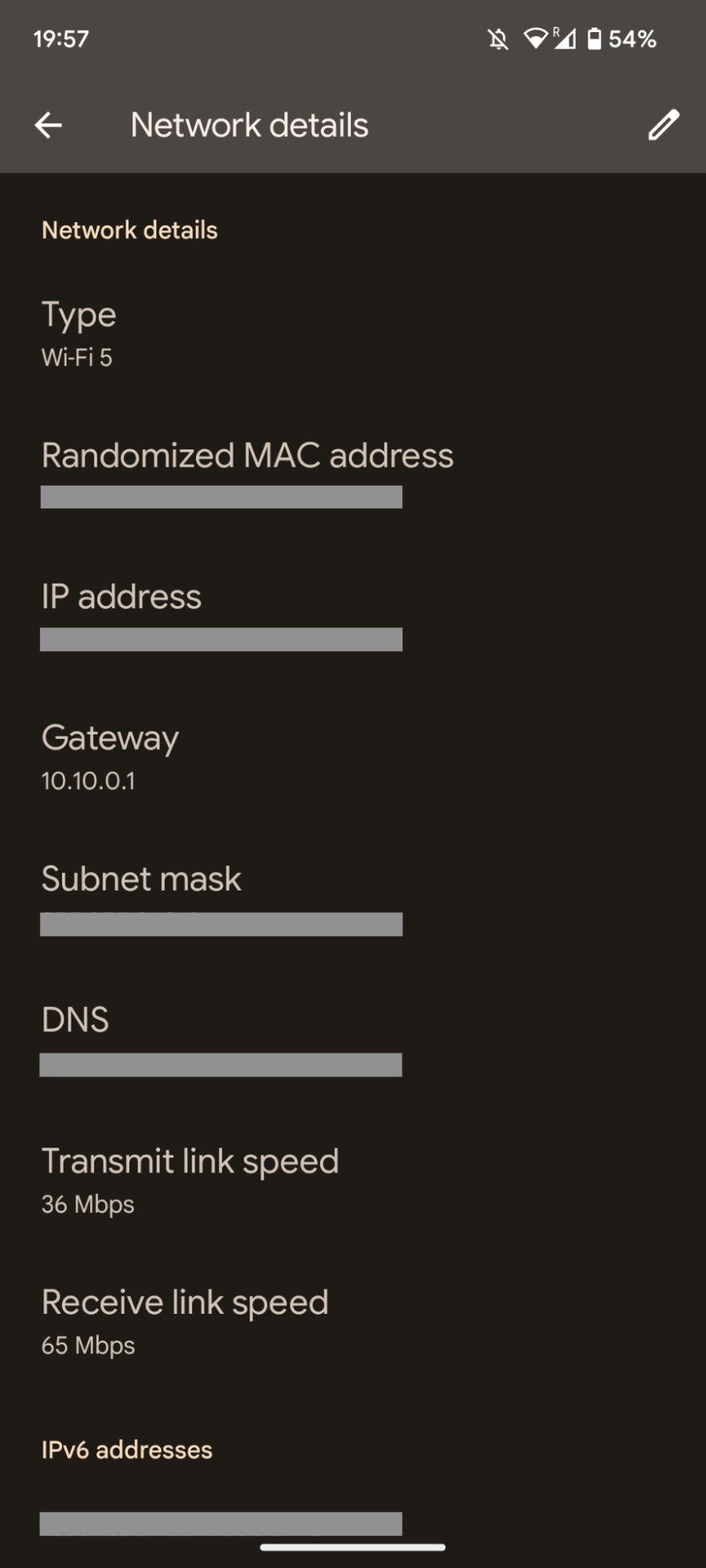
Check your Wi-Fi security type on Android
To check your Wi-Fi security type on an Android device:
- Navigate to Settings
- Open the Wi-Fi category
- Select the Wi-Fi network that you're connected to
- In the network details, your Wi-Fi security type will be specified
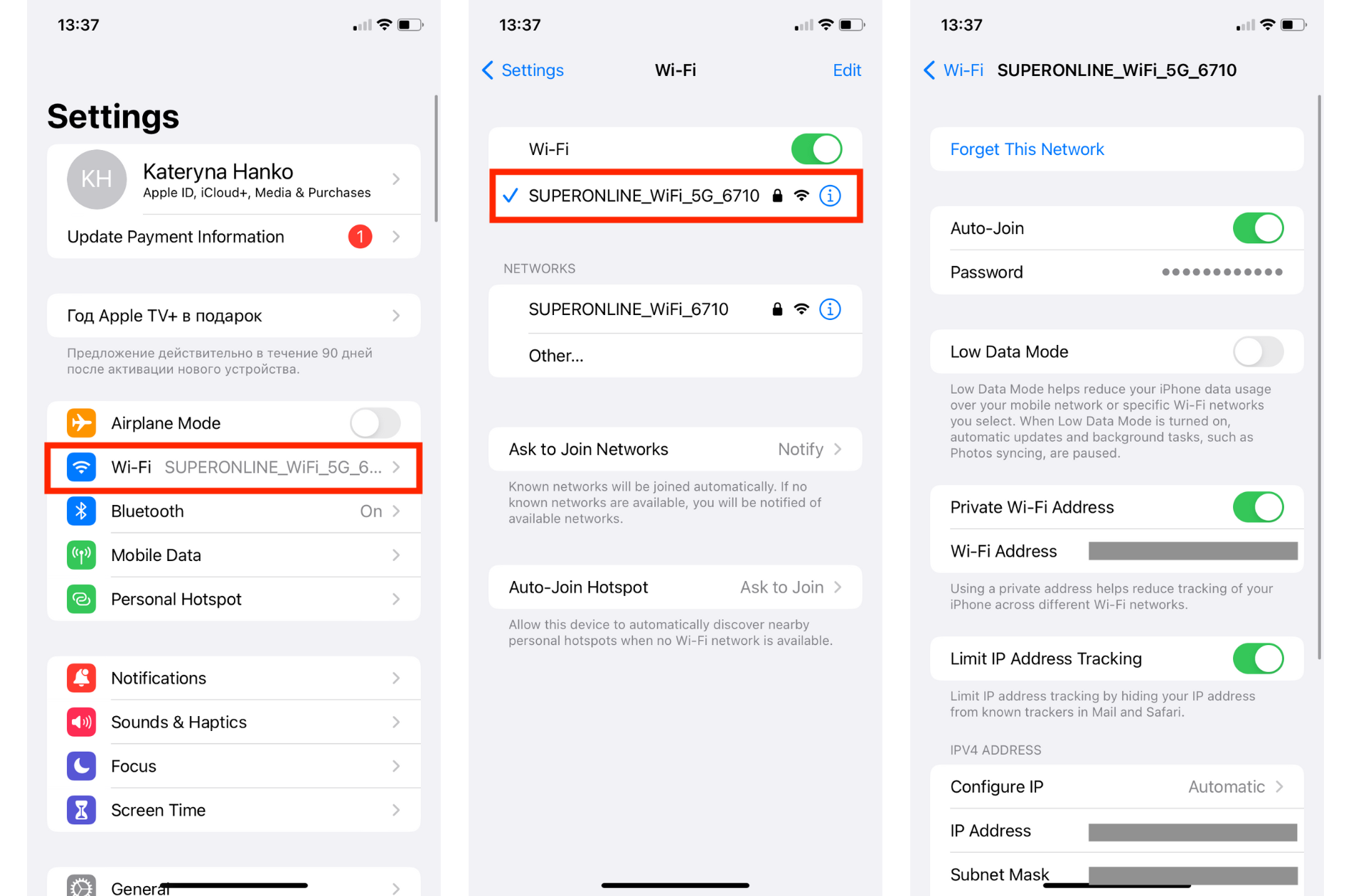
Check your Wi-Fi security type on iOS
Unlike other operating systems, there's no way to determine your Wi-Fi security type directly on an iOS device. With this being the case, it’s best to use a computer or log into your router to analyze your network’s security settings.
However, viewing security options enabled on your Wi-Fi network is possible using an iOS device. To do so:
- Select the Wi-Fi from the Settings app
- Select the Wi-Fi network that you’re currently using
- Its security settings will be displayed at the top of your device’s screen
Which Wi-Fi security type suits me the best?
We’ve already told you the pros and cons of each Wi-Fi security type out there. As WPA2 is the most up-to-date security protocol widely used, it remains the most reliable standard for protecting your Wi-Fi network.
Whichever Wi-Fi security protocol you choose to use, your browsing experience can be boosted with the help of a VPN.
VPNs are a crucial security tool in your arsenal, as they make it possible to encrypt your data, conceal your IP address, and keep it simple to stay safe while using Wi-Fi networks. Without a VPN, you’re not anonymous, and your data is unsecured, meaning that it can be intercepted by hackers or even your own internet service provider (ISP).
For better results, use your VPN alongside Clario Anti Spy. This anti-spyware utility can quickly help you patch out security vulnerabilities on your mobile devices and warn you about data breaches. You can also use Android to hide your location.


