Table of contents
- What is browser fingerprinting?
- What is the difference between browser fingerprinting and tracking cookies?
- Is browser fingerprinting legal?
- How does browser fingerprinting work?
- What are the different browser fingerprinting techniques?
- How to do a browser fingerprinting test
- How to prevent browser fingerprinting
- Protect your data with Clario
What is browser fingerprinting?
Browser fingerprinting, also known as digital fingerprinting or online fingerprinting, is an online tracking technique companies use to gather more information about individual users. Essentially, each unique internet user has an online fingerprint based on a data set that companies can use to identify them. A company can compile individual data points that act as a unique ID or fingerprint.
Even when you use multiple browsers or incognito mode, online fingerprinting techniques can track users with up to 99% accuracy.
Some of the data that make up your device or digital fingerprint include:
- IP address
- Installed fonts
- Installed hardware
- Screen resolution
- Browser extensions
- Browser privacy settings
- Keyboard layout
- Operating system
- Language settings
- Timezone
- User-agent string
- Cookie settings
- And many more
You may be concerned about your safety with all this data collected about you. Indeed, digital fingerprinting poses a risk of violating one's privacy. While this data-gathering technique does not expose your identity, the personal information collected across platforms and devices can be used to identify an individual. For instance, if a website has a weak security infrastructure, hackers can access your data and use it for fraudulent purposes.
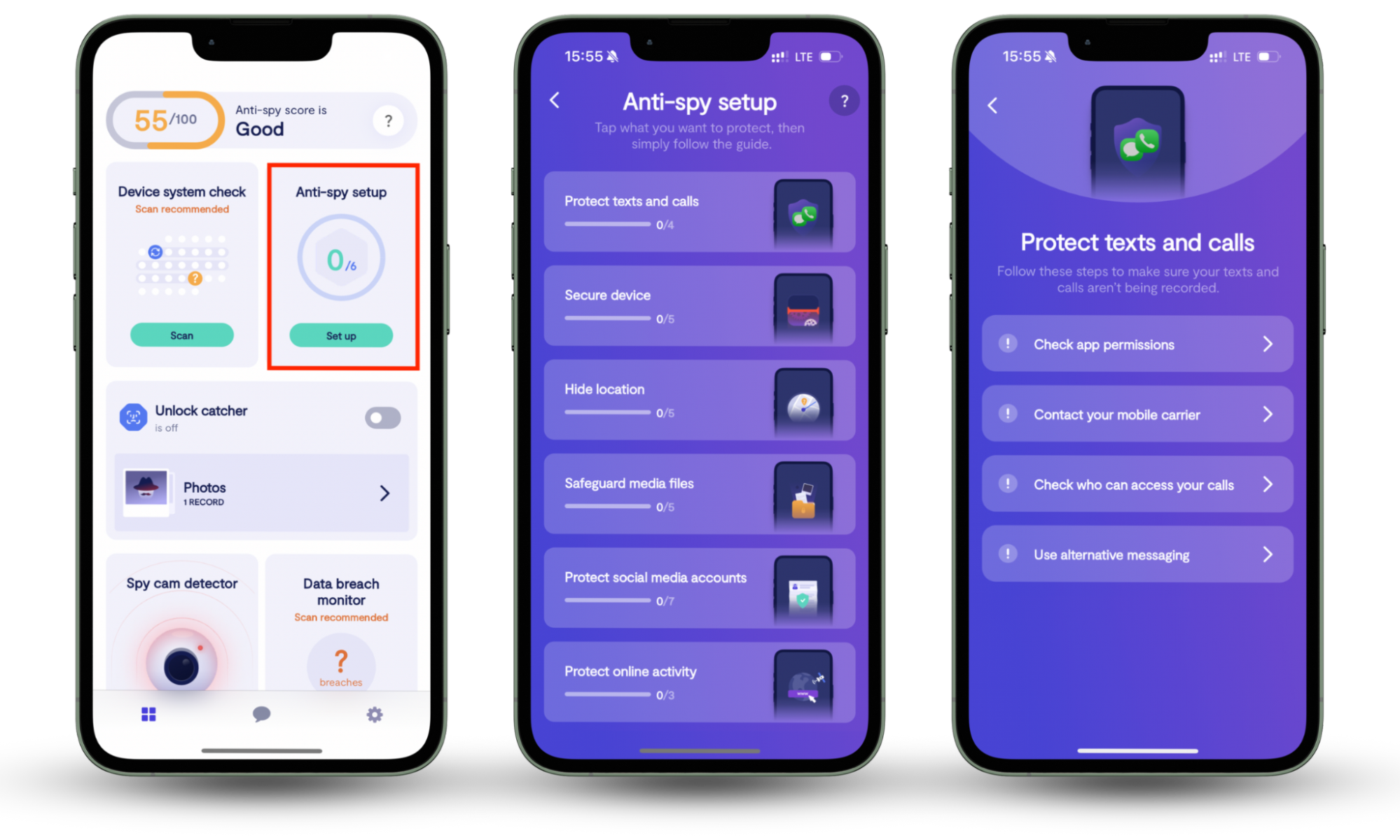
Companies also collect data about your online activities, device types, current life circumstances, etc. That is why we created Clario Anti Spy—to help users ensure their personal information remains intact. Our Anti-spy setup feature is designed to secure your device, keep your online activity safe from prying eyes, hide your location, and much more.
Here's how to start using Clario’s Anti-spy setup:
- Download Clario Anti Spy on your mobile device.
- Create an account.
- Go to the Anti-spy setup feature and click Set up.
- Choose what you want to protect.
What is the difference between browser fingerprinting and tracking cookies?
You may be more familiar with cookies that track your history as you browse the internet. Digital fingerprinting is a little different.
Cookies are much more regulated, particularly in the European Union, and require permission from users to start tracking them.
You've likely seen a cookie pop-up notification on a website that asks you to allow cookie tracking on your device. Unfortunately, browser fingerprinting doesn’t give you the same courtesy because it isn’t regulated and doesn’t require your permission.
Digital fingerprinting generally takes place silently, and you’ll likely never be aware that it’s taking place.
And unlike tracking cookies, which you can delete, you cannot delete your browser fingerprint. This unique fingerprint is an observation of a compilation of the data we mentioned above (IP address, hardware, OS, etc.). Therefore, companies that use browser fingerprinting can identify individuals based on their unique combination of this data.
This doesn’t mean they know exactly who you are–they can’t see your name, address, and private information through this process–but it does allow them to apply a unique identifier to you so they can personalize advertisements to your interests.
Is browser fingerprinting legal?
Browser fingerprinting is legal. This is because it only gathers information that is considered public; therefore, it isn’t breaking any privacy laws.
Even the GDPR and CCPA, which impose strict restrictions on cookie tracking and online data privacy, don’t have any current restrictions against digital fingerprinting.
How does browser fingerprinting work?
Whenever you visit a website, it collects unique user data, even if you haven’t opted into its cookie tracking. It can collect public data like your IP address, device type, operating system, and more. It generally does this through the use of web scripts.
Browser fingerprinting works by compiling this data and helping websites to identify unique users so companies can advertise to them across the various platforms they use (Facebook, YouTube, TikTok, other websites, etc.).
What are the different browser fingerprinting techniques?
Companies may use several different techniques of digital fingerprinting. These include:
Canvas fingerprinting
Canvas fingerprinting is one of the most commonly used fingerprinting methods. It uses the canvas element of HTML5 to make your browser draw an image or add some text invisibly in the background of any given site. Then, based on the drawing or text your browser provides, the website fingerprinting can gather data on things like your font, drivers, graphics card, OS, browser, and more.
WebGL or rendering fingerprinting
Similar to canvasing, these two fingerprinting methods force your browser to render images off-screen. Then, they will use that image to identify information about your device’s graphics card and hardware.
Device fingerprinting
Device fingerprinting is a technique that allows a website to identify all of the media devices on your computer, like your audio and video card. This can even include the specific type of headphones that you have connected to your device.
Audio fingerprinting
Instead of forcing your device to draw an image, this technique observes how your computer or device plays sound. It will use the soundwaves from your device to identify information about your drivers, audio hardware, and software.
Cross-browser fingerprinting
The other techniques we’ve mentioned often use this technique as well. It is the fingerprinting method that allows companies to track your data across multiple browsers. So even if you jump from Chrome to Firefox, they can still identify your unique attributes based on the information they already have.
How to do a browser fingerprinting test
There are tons of resources out there that can show you the exact information that companies can access from browser fingerprinting.
Here are a couple of resources you can visit to do a browser fingerprinting test for free:
To test your browser fingerprinting data, click one of the links above and follow the prompts.
We’ll use AmIUnique as an example.
- First, go to their website: amiunique.org.
2. Then, click View my browser fingerprint.
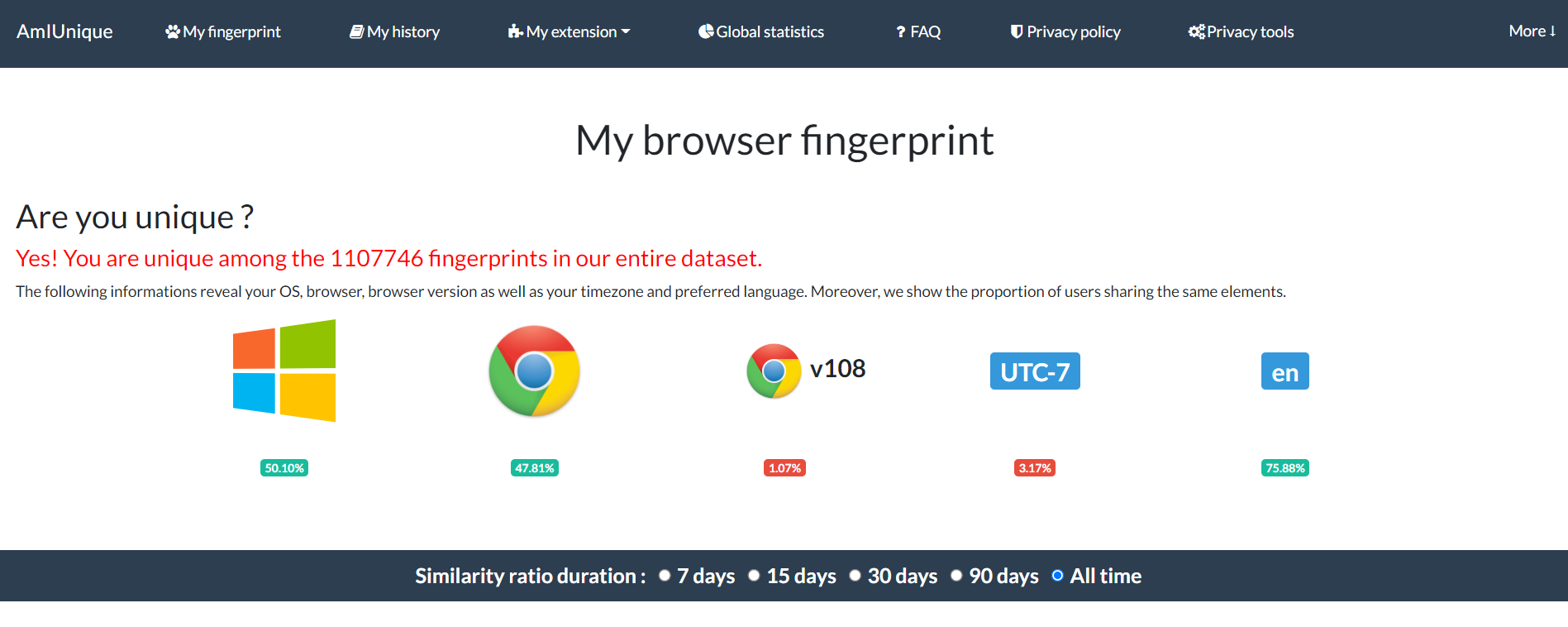
3. The website will tell you if your data gives you a unique ID and how many fingerprints are in their dataset.
4. Scroll down that page to see your unique identifiers.
How to prevent browser fingerprinting
Basic data privacy tactics–like blocking cookies, going incognito, and even using a VPN–won’t prevent browser fingerprinting. So you’ll need to find other ways to keep your data secure.
You can use a couple of techniques to help: generalization and randomization.
- Generalization helps manipulate browser API results to allow you to blend in with the internet crowd. It basically makes your attributes too generic to be identifiable.
- Randomization changes your attributes regularly so that your data points are always different, making it difficult to identify you.
Several services provide antitracking features to enable generalization and randomization as you browse the web. Here are some of the best ones:
- Browser extensions (e.g., Privacy Badger, uBlock Origin).
- Privacy-focused browsers (e.g., Brave, Tor Browser).
- VPN services with anti-tracking features (e.g., NordVPN, ExpressVPN).
- Search engines with privacy emphasis (e.g., DuckDuckGo, Startpage).
- Operating systems with privacy features (e.g., Tails, Qubes OS).
Protect your data with Clario
Browser fingerprinting can be useful for delivering tailored user experiences. However, it comes at a cost—your privacy. Every step or action you take online is being monitored. And while with cookies you have the option to decline, you cannot turn off browser fingerprinting.
But you can take measures to protect your data. Clario’s Anti-spy setup feature was created exactly for that. It can help you secure your device and protect your online activity for a more private browsing experience.


