Table of contents
- The definition of cybersecurity
- Cybersecurity vs. information security
- Why cybersecurity is important
- Areas of cybersecurity
- Network security
- Disaster recovery plan
- Cloud security
- Internet of Things (IoT) security
- Application security
- The most notorious cybersecurity incidents
- Facebook cyberattack
- Twitter spear phishing attack
- Zoom credentials hack
- Marriott unauthorized data access
- The types of cyberattacks
- Social engineering
- Phishing
- Vishing
- Malicious software or malware
- Password guessing
- Denial of service (DoS)
- Man in the middle
- Advanced persistent threat (APT)
- How you can protect yourself from cybersecurity threats
- Only browsing on secured Wi-Fi networks
- Why cybersecurity matters and how to prioritize it
The definition of cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting networks, devices, and applications from damage or theft. It aims to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access to personal accounts.
Cybersecurity applies across multiple levels and affects both individuals and organizations. In practice, it focuses on:
- Protecting digital assets: Personal data, financial information, intellectual property, and business-critical systems.
- Preventing unauthorized access: Stopping hackers, malware, and automated attacks from exploiting devices and networks.
- Reducing risk and impact: Limiting financial loss, service disruption, identity theft, and reputational damage.
- Adapting to evolving threats: Addressing constantly changing attack techniques and vulnerabilities.
A successful cybersecurity tactic has several levels of protection spread across apps, networks, data, and computers that you want to keep safe. Antivirus software, malware protection, DNS filtering, and email security solutions are some of the most effective tools you can use to protect your private information online.
Sometimes, people confuse cyber- and information security, two concepts under the umbrella of data security. But here’s how they differ.
Cybersecurity vs. information security
Although the terms “cybersecurity” and “information security” are used interchangeably, they mean completely different things. Information security, also known as InfoSec, refers to the instruments and processes that protect personal data. This includes data privacy, safety, and so on.
Cybersecurity, however, is all about protecting electronic data stored on your devices from online attacks. Passwords, usernames, intellectual property, and government information systems belong under this banner.
By now, you’ve probably all grasped why practicing cybersecurity is essential. But let us give you some more information, just to be on the safe side (wink).
While the two fields overlap, they differ in scope and focus:
- Cybersecurity concentrates on protecting systems, networks, and digital assets from online threats such as hacking, malware, and unauthorized access.
- Information security focuses on safeguarding data itself, regardless of whether it is stored digitally, on paper, or shared verbally.
In simple terms, cybersecurity defends how data is accessed, while information security protects the data in any form.
Why cybersecurity is important
Identity theft, email fraud, ransomware attacks, and the sale of corporate data are just a few examples of cybercrimes. If carried out successfully, then they can have grave consequences for both ordinary internet users and corporate organizations leading to large financial losses. Only in 2020, the global cost of data breaches was nearly $3.86 million.
Note
The cost of a data breach usually includes more than just stolen money. It often accounts for business downtime, incident investigation, system recovery, legal fees, regulatory fines, and long-term reputational damage. Industry reports regularly show that breaches affecting sensitive personal data tend to be the most expensive and difficult to recover from.
Some experts predict that this figure will increase in the future, and this is exactly why we shouldn’t fool around with our approach to cybersecurity. After all, you always make sure you’ve locked the door when you leave the house and look sideways before crossing the road. Why not treat your digital life with the same level of caution?
Areas of cybersecurity
Cybersecurity cuts across all domains, from software development to data loss prevention. It can be broken down into five common areas. These areas represent different layers of risk where cyberattacks can occur. Each one focuses on securing a specific part of the digital environment, from network access and cloud infrastructure to connected devices and software applications.
Network security
It prevents, detects, and monitors for unauthorized access to computer networks (both public and private). Network security begins with authentication –– the process of verifying identities with a username and password that you usually type while logging into your email or social media account.
Insight
Authentication confirms who a user is, while authorization determines what that user is allowed to access once logged in. For example, two users may successfully sign in to the same system, but only one may have permission to view sensitive or administrative data.
Disaster recovery plan
It’s a method of recovering IT infrastructure after cybersecurity attacks and natural disasters. A disaster recovery plan ensures an organization can take back control of its business operations quickly and without suffering huge financial losses.
Note
A well-designed disaster recovery plan typically includes secure data backups, defined recovery timelines, and clear procedures for restoring critical systems. Its goal is not only to recover lost data, but also to minimize downtime and ensure essential business functions can continue after an incident.
Cloud security
When you take photos or store information online, it goes into something called the cloud—an internet server users can access remotely. The big tech companies like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon are some of the cloud providers consumers access using their applications or websites. If data in the cloud is breached, the information stored there could easily be accessed.
Cloud security covers data encryption (when data is encoded and hard to access) and threat intelligence (monitoring traffic of potential cybersecurity threats).
Note
Cloud security is based on a shared responsibility model. While cloud providers are responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, users are responsible for protecting their accounts, managing access permissions, and securing the data they upload or store in the cloud.
Internet of Things (IoT) security
You may not realise it but our information is everywhere. Our info is not just stored in our computers but also in our appliances at home. And anything with a Wi-Fi connection is vulnerable to attack from cybercriminals.
IoT security protects home appliances, wearable devices, and other things connected to the internet against cybersecurity attacks. It uses next-generation antivirus (NGAV), endpoint detection and response (EDR), and other technologies to track possible cybersecurity threats.
Insight
Poorly secured IoT devices, such as smart cameras, home routers, or wearable devices, can be taken over by attackers and used to spy on users or launch larger cyberattacks without the owner’s knowledge.
Application security
You should also be security-conscious when using apps on your phone. Though the responsibility for this falls on the shoulders of app makers, users can also protect their phone by using software that finds, fixes, and enhances app security.
As you can see, there’s more to cybersecurity than simply locking your Macbook. And now that you know the complexity of this concept, why not take a look at the magnitude of the losses breached cybersecurity may bring?
The most notorious cybersecurity incidents
No fish is too big or small for hackers. Even large corporations have suffered from cybersecurity attacks that led to data leakage and financial losses. Here are some of the biggest and most recent cybersecurity incidents:
Facebook cyberattack
Up to 533 million phone numbers and personal information of Facebook users were stolen in 2021. The leaked data impacted people from 106 countries. According to Facebook’s spokesperson, the hackers exploited a company data vulnerability dating back to 2019.
Twitter spear phishing attack
In July 2020, the Twitter accounts of Joe Biden, Kim Kardashian, Bill Gates, and other public figures fell victim to a Bitcoin scam. The hackers used spear phishing –– an attack targeted at specific people –– to make several Twitter employees reveal their credentials.
This successful attack helped scammers earn more than £80,000. The incident also raised serious questions about Twitter’s ability to protect its users and their data.
Zoom credentials hack
In April 2020, up to 500,000 passwords of Zoom users were stolen. Cybercriminals later sold this data on the dark web. This allowed prankers to crash video meetings and get email addresses and contact information from other participants.
Zoom took measures to prevent similar attacks in the future. The company strengthened its safety system and started to ask its users to create more secure account passwords.
However, creating strong passwords alone isn’t enough to protect your Zoom account and more online accounts that may contain your sensitive information from hackers. Setting up breach alerts can help you stop the domino effect caused by data leaks. Clario Anti Spy offers an excellent Data breach monitor that scans the dark web for data breaches including your email address, allowing you to take action by securing your account and updating login credentials for linked accounts to minimize the impact.
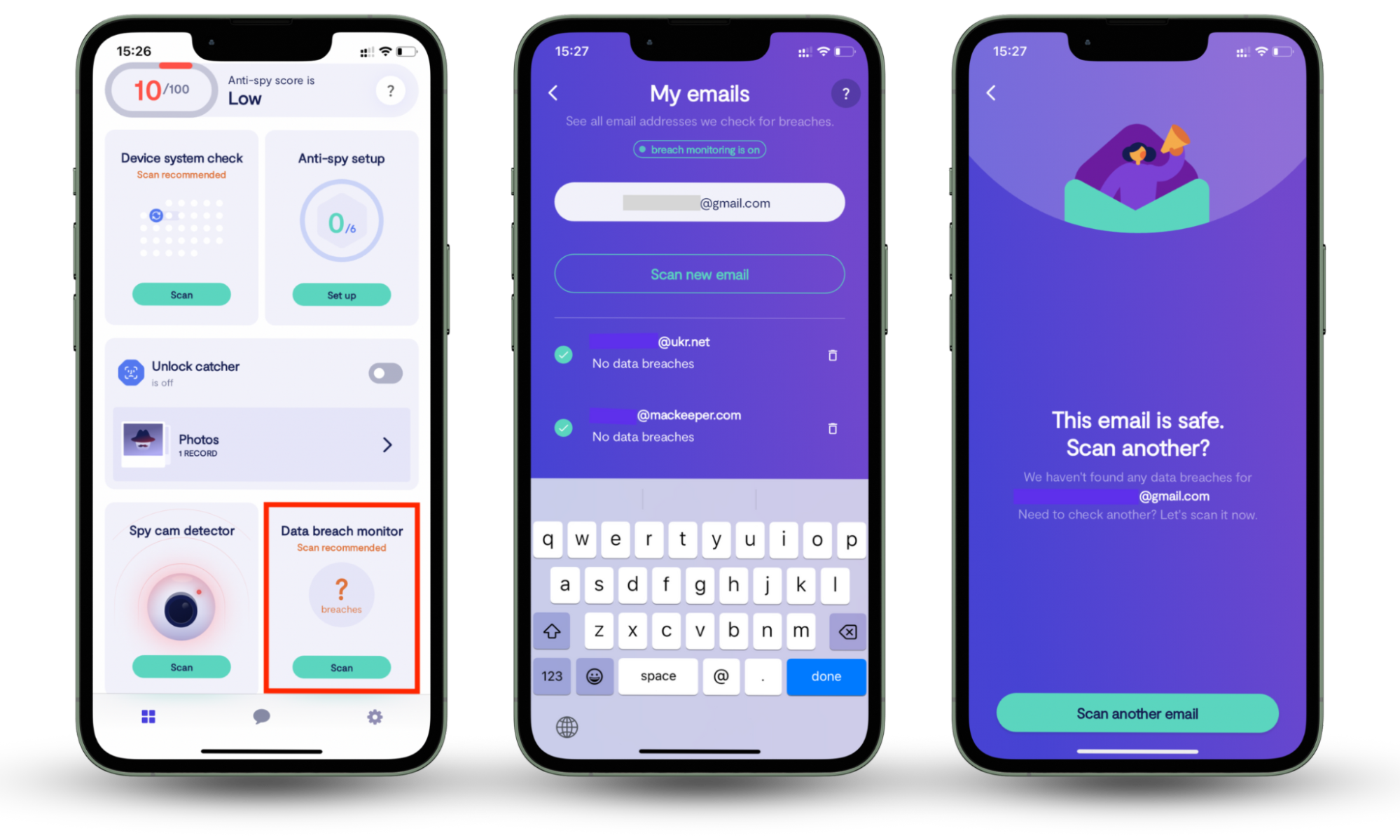
Here’s how to use Clario Anti Spy’s Data breach monitor to identify leaks involving your email address:
- Download Clario Anti Spy, get a subscription, and set up an account.
- Go to Data breach monitor and tap Scan.
- Enter the email address you want to scan, follow the on-screen prompts to start checking it, and give Clario Anti Spy a few minutes to run a scan.
- Once the scan is completed, review the report and follow Clario Anti Spy’s instructions to secure your email address if it was leaked. Alternatively, you can provide another email address you want to check by tapping Scan another email.
Marriott unauthorized data access
Up to 339 million guests were affected by a data breach that happened to Marriott in 2020. Hackers accessed the personal details of the hotel chain’s clients, including their names, phone numbers, addresses, birth dates, passport numbers, VIP status, and details of loyalty programs.
It was the second time Marriott was caught up in a data breach. The first one happened in 2018. Ouch…
Insight
Repeated data breaches at large organizations are often linked to legacy systems, complex IT environments, or slow detection of unauthorized access, which can allow attackers to remain unnoticed for extended periods of time.
Yes, cybercrime is on the rise, and it’s expected to cause $10.5 trillion financial losses by 2025. How? Because hackers are an incredibly inventive bunch.
The types of cyberattacks
These are the most common types of cybersecurity threats. Do you know all of them?
| Attack type | How it works | Common target |
| Social engineering | Manipulates people into revealing sensitive information | Individuals and employees |
| Phishing | Uses fake emails or messages to steal data | Email users and bank customers |
| Vishing | Uses phone calls to trick victims into sharing information | Individuals |
| Malware | Installs harmful software to spy on or damage systems | Personal and work devices |
| Password guessing | Attempts to access accounts using weak or reused passwords | Online accounts |
| Denial of service (DoS) | Overloads systems to make services unavailable | Websites and online services |
| Man in the middle | Intercepts communication between two parties | Public Wi-Fi users |
| Advanced persistent threat (APT) | Maintains long-term unauthorized access to steal data | Large organizations |
Social engineering
Social engineering is the act of tricking someone into divulging information using psychological tricks. Criminals usually take advantage of a victim’s natural tendencies or emotional responses.
For example, a social engineer can pretend to be a technical support person to trick a new employee into handing over their login credentials to any online accounts. They can also send emails, posing as a long-lost friend and asking for financial help from a potential victim.
Social engineering includes the following methods:
- Baiting. A hacker coaxes an employee to perform a specific task by offering an attractive reward.
- Pretexting. A cybercriminal poses as an IT support representative to request a password for supposed system maintenance.
- Tailgating. An attacker gets access to a restricted area by following an employee.
- Quid pro quo. A cybercriminal pretends to be someone else and offers money in exchange for a password.
Phishing
The most common type of social engineering is phishing. This is usually done via email with a cybercriminal posing as an insurance or banking agent. Other times, they may contact you with a bogus offer.
Be cautious of giving out your personal information to anyone. Banks and agencies will always issue official statements whenever your personal details need updating.
Vishing
Vishing, or voice phishing, is a tactic used by cybercriminals to gather confidential data about a particular individual. Cyberattacks of this type are done through phone calls. Scammers call their victims pretending to be from a bank, charity, or governmental agency. They try to coax sensitive information from their victims, including credit card data or a mother’s maiden name.
Malicious software or malware
These are any programs or files that are harmful to a computer user and include computer viruses and spyware (software that’s used to spy on a computer’s activities). If you download malware, its creators will be able to see your private information and passwords.
Password guessing
Some hackers actually apply brute force into trying to get into your account. They would guess your password using information they know about you.
So if they know your full name, your birthday, or other details, they may try to use this information as your password and see if they can gain access. This is why we don’t recommend using passwords containing information found in your ID or social media.
Expert's insight
In many cases, attackers do not manually guess passwords but rely on credential stuffing, a method that uses previously leaked username-and-password combinations from earlier data breaches to gain access to multiple accounts.
Denial of service (DoS)
This is a cybersecurity attack targeted at websites to disrupt or overwhelm the servers that run it. Since websites rely on servers and are used to a certain volume of regular traffic, they may not be able to handle the sudden flood of visits. If this happens, the website will crash and people won’t be able to access the site anymore.
DoS attackers usually target large organizations in the banking, financial, governmental, commerce, and media sectors. Their tactics include:
- SYN flood. An attacker sends a request to the server connection and continues to do so until all ports are opened.
- ICMP flood. Cybercriminals take down the computers of the targeted individuals by flooding them with echo requests.
- Buffer overflow attacks. Hackers send traffic to a network address.
Man in the middle
It’s a malicious cybersecurity tactic where an attacker secretly alters communication between two people. Hackers use it to steal confidential information such as login credentials, credit card numbers, or account details and commit identity theft or unauthorized financial transactions.
Advanced persistent threat (APT)
A prolonged and targeted cyberattack is called an advanced persistent threat or APT. Usually, these scams choose a company to infiltrate and then try to gain access to the network.
Often, they go undetected for a long period of time because they don’t necessarily change anything in the system. Instead, they monitor network activity and steal data, which they can later use to sell or blackmail the company.
We hope that you knew most of these, and not from experience. In fact, here’s a list of tips that will help you lower the chances of getting hacked.
How you can protect yourself from cybersecurity threats
After reading the cybersecurity threats mentioned above, do you think you’re at risk? The first step in protecting yourself against such attacks is to equip yourself with knowledge, then assess your risk level.
You can do this by running a network diagnostic using a security program. You can also set up a cybersecurity alert as these can be great at warning you if someone ever tries to access your valuable data.
After assessing your risk, here are some practical steps you can take to improve your personal cybersecurity.
Only browsing on secured Wi-Fi networks
Think twice before connecting to a free Wi-Fi network. There are hackers that use these networks to accesspeople’s personal details. Once you log into the “free” Wi-Fi, it’s possible that whoever owns the network can get any information you use when you’re logged in.
Scammers do this by injecting malware into the connected devices. Once a victim connects to the suspicious Wi-Fi, the hacker who set up this hotspot can then intercept data from the connected devices.
Here are some tips on how to secure yourself while using public Wi-Fi:
- Only connect to familiar networks
- Check if you use HTTPS
- Avoid using File Sharing or AirDrop
- Use a VPN for extra security
Create strong passwords for your accounts
Creating a secure password will make it harder for hackers to compromise any online accounts. If you need some guidance, here’s what you can do to create a strong password:
- Make your password long. The longer it is, the more difficult it will be for attackers to guess.
- Combine lower- and uppercase letters, symbols, and numbers. Hackers will have a hard time trying to guess a password featuring this combination.
- Use a password manager. This will help you generate a truly reliable password.
Avoiding insecure websites
There are instances when the websites you visit can compromise your security. The easiest way to know if a website is secure is to check the website URL. Does it say “https” or just “http”? The “s” at the end of the URL signifies that it’s secure.
Protecting your accounts with two-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security method requiring you to verify your identity twice when logging into your account. Once you enter your username and password in the system, you receive a verification code via text or mobile app.
The verification code changes every time you log in. This keeps your personal data safe and protects your account against unauthorized access and cybersecurity threats.
Avoiding malicious advertisements on the web
If you see an ad or pop-up that looks suspicious or illegitimate, it’s in your best interest to completely avoid them. No matter how tempting the offer, don’t fall for their tricks.
Not opening suspicious emails
Sometimes, cybercriminals will send you offers or tell you that you’ve won something but you need to send your personal details to claim the prize. Be cautious of these types of emails, especially if you don’t remember entering a contest like this in the first place.
Keeping your software updated
Often, the reason why there are software updates is because the company has enhanced its security features so that cybercriminals cannot exploit weaknesses in the system. With regular updates, you minimize your exposure to risks.
Considering a personal cybersecurity insurance
On top of all the emotional distress, identity theft victims could also be liable to financial charges. Though the basic liability of victims can simply amount to $50 for credit card usage, the damage can sometimes amount to hundreds or thousands of dollars.
One way to protect yourself financially is to take up cybersecurity insurance. This can provide reimbursement for costs associated with the theft of digital information and assets.
Some of the companies offering this type of insurance include State Farm, AIG, Chubb, and PURE. The average personal cyberinsurance endorsement covers $15,000 in combined cyberextortion and cyberattack damages for $25 per year.
CyberPolicy, Travelers, The Doctors Company, and AmTrust Financial are among the top cybersecurity companies offering this service.
Consulting with a cybersecurity expert
If you have a lot of assets online that need protecting, you may want to consider hiring a personal cybersecurity consultant. Also called information security analysts, their job is to plan and execute security measures to protect computer networks and systems.
These cybersecurity consultants have to constantly monitor for threats. More often than not, they should also be available on call. This is probably why they’re quite expensive and only large corporations and top executives can afford to hire them.
Downloading a cybersecurity app
Protecting your devices from hackers is simple with cybersecurity apps like Clario Anti Spy. Here are just some of their benefits:
- You can hide your browsing activity with Clario Anti Spy’s Virtual location tool for Android devices so that hackers find it hard to trace the websites you visit.
- Enjoy a spy-free zone and remove spy apps from your Android.
- You can get 24/7 assistance from cybersecurity experts.
- Clario Anti Spy works non-stop to ensure your personal accounts remain private.
- You can have peace of mind with Clario Anti Spy’s anti-spyware protection and data breach monitoring.
Why cybersecurity matters and how to prioritize it
It sure feels great to get to know so much about cybersecurity threats. If you combine this knowledge with installing a cybersecurity app on your devices, you’ll increase the chances of keeping your data safe. We should be free to keep pushing our digital horizons without fear of being hacked or tracked so we can live our best online lives freely. Enhance your cybersecurity measures with Clario Anti Spy’s Data breach monitor. It helps secure your email address after it was involved in a data leak, preventing further consequences like fraud and identity theft.


