Table of contents
- Digital identity definition
- Digital identity in cyberspace: how digital identities came about
- How does the digital identity verification process work?
- Digital identity for financial services
- Biometric digital identity solutions
- Digital identity use cases
- Digital identity importance in today’s world
- How to protect your digital identity
Digital identity definition
A digital identity or digital ID consists of all the elements that make up the identity of a person, device, or organization that exists online.
These elements make it possible, and sometimes easy, for other users and advertisers to identify you in the digital space. That’s why it’s closely linked to online privacy.
Think of it as your digital fingerprint, which comprises of various elements. Below are the components of a digital identity:
- Login details
- Photos uploaded online
- Date of birth
- Bank account details
- Driver’s license number
- Passport number
- Social security number
- Biometric data
Everyone has a digital identity. And no matter how careful you are, it takes one-time use of the internet to have a digital identity. This increases your risk of falling victim to fraud.
If you have accounts on online platforms or store your credit card information online, there’s no getting around it—you have to take steps to protect your digital identity.
Digital identity in cyberspace: how digital identities came about
Digital identity finds its roots in identity, which proves that someone is who they claim to be. In earlier years, the most basic forms of identity were a person’s face and name.
Identity continued to be used throughout history to identify criminals, find family members, authorize bank purchases, and much more. However, using documentation as a form of identity can be traced as far back as the 1950s and 1960s.
After William James Herschel of Europe took up a position as a magistrate in colonial India in 1958, he introduced fingerprints and handprints (instead of signatures) as forms of identification.
The system was used in the following instances and on the following documentation:
- Business deals
- Pensions
- Deeds
- Jail warrants
He found this to be a suitable solution in the fight against fraud, given India’s high rate of illiteracy.
Over the years, the fingerprint method has become digital. Overall, the world has evolved, and so has an identity, which accommodates the digital world.
Some parts of the world use digital IDs instead of physical IDs. Fingerprints are also scanned to computers to help identify people. Not to mention your computer’s unique IP address, which belongs to only that device.
Given that the internet is evolving at such a fast pace, who knows how many more digital identifiers will come up in the future?
How does the digital identity verification process work?
Identity verification is about verifying that a person is who they say they are. Digital verification works similarly.
It involves comparing the information presented by an individual about who they are against existing information. Below are examples of instances when you’d need to verify your digital identity:
- Logging in to your banking app
- Unlocking your smartphone
- Unlocking your car (some cars can be unlocked with the owner’s thumbprint)
- Signing in to your email account
- Signing in to your social media accounts
- Entering your place of work
- Recovering a forgotten password for an online account
- Using your credit card to make online purchases
- Entering your gym facility
- Getting booked in after an arrest
The information you provide is compared against existing data. This can be a database of some sort or any official data available, depending on where you’re verifying your digital identity (like in the examples listed above).
For example, you can only successfully unlock your iPhone with your thumbprint if you’ve previously set it up before in the setup process. That’s because your iPhone already has a record of it.
Other examples of databases include criminal databases used by police to help capture criminals or link related cases.
Workplaces have databases of employees who are authorized to enter the building. Likewise, gyms have databases of members who can enter and use the facilities.
Below are some common examples of a digital identity verification process:
- ID document verification
Checks that the information provided by an individual (like an ID document or passport) matches with government databases
- Biometric verification
Scans one’s fingerprint or face to compare against that of the person who initially signed up using that data
- One-time passcode (OTP) verification
Sends a single-use numeric code to a person’s registered mobile number or email address
- Two-factor authentication (2FA)
Requires confirmation of identity in two layers before signing in to a platform: a password and via another digital platform, like a Gmail account
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Requires the user to confirm their identity using two or more verification factors when attempting to log in to a platform
- Selfie video detection
Typically involves requiring users to turn their head in different directions as per the on-screen prompts
- Liveness detection
Uses algorithms to determine whether a user has provided a fake or genuine picture of themself. Some dating sites use this technique to prevent catfishing
- Knowledge-based authentication (KBA)
Asks the user security questions about the account holder to verify their identity
- Trusted identity network
Compares the user’s data against existing data with other providers to determine their true identity
- Database verification methods
Leverages data from available online databases to verify someone’s identity. These include social media networks
A digital identity verification process is an essential step in confirming one’s digital identity. It also helps prevent fraud from bad actors using fake identities and bots.
Digital identity for financial services
Financial crimes affect financial institutions (FIs) around the world. Feature Space’s fraud and financial crimes report puts everything into perspective. The key findings below are for the US in the 2021-2022 period:
- FIs lost $102m in scams
- 6/10 FIs saw an increase in their fraud rate
- Fraud rates and losses were up for most payment types in 2021
- 43% of FIs saw a rise in their false positive rate
- 62% of FIs reported a year-on-year increase in fraud volumes
- Most FIs experienced a rise in financial attacks, with smaller FIs getting targeted the most
- Average fraud losses amount to 1.29 bps per transaction for FIs
- Authorized fraud scams are on the rise
It’s clear that financial crimes are on the rise. Digital identity verification is important in the fight against these crimes in the financial services industry.
This can be achieved through a reliable digital identity management solution to protect people’s data no matter what.
Biometric digital identity solutions
Biometric digital identity solutions include the use of software and other technology to verify people’s identities using the following measures:
- Face recognition
One of the popular biometric digital identity solutions, face recognition technology scans a user’s face to determine if it’s the right person using a device or logging on to a platform. They’re faster, cheaper, and convenient.
- Voice recognition
This is a contactless method of verifying a person’s identity. It makes use of unique biological characteristics in one’s voice to authenticate their identity.
- Fingerprint scanning
Fingerprint scans are a widely used form of biometric digital identities. That’s because fingerprints are unique, and scanning them takes a minimal amount of time.
Digital identity use cases
Industries that commonly use digital identity solutions include:
Retail/eCommerce
- Fast checkout
- Verification of customers’ age for the purchase of restricted items
- Fast and remote authentication of those working in gig economies
- Increased conversion rates
- Know Your Customer (KYC) compliance purposes
Financial services
- Transaction monitoring
- Credit risk assessment
- Saving on transaction costs
Compliance with the following regulations:
- Anti-money laundering
- Know Your Customer (KYC)
- Customer Identification Program (CIP)
- Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC)
Security
- Background checks
Healthcare
- Faster onboarding of patients
- Protection of patient information
- Confirmation of patient identity
Telecommunications
- Fraud prevention
- Provision of seamless customer experiences
Government services
- Real-time identity authentication
- Quicker access to services (signing in online to use services instead of commuting to physical branches)
- Management of asylum applications
Travel and tourism
- ID document verification
- Biometric verification
Education
- Serve and manage students internationally
- Better management of coursework and programs
- Verification of students for online tests and exams
Smartphones and devices
- Touch and Face ID prevent unauthorized access
Digital identity solutions help organizations across various industries to develop products and applications for verification purposes.
They enable organizations to extend their digital presence and automate their business processes.
Finally, biometric digital identity solutions help organizations protect their users’ data from bad actors.
Digital identity importance in today’s world
The internet is a goldmine for hackers and bad actors who are well-versed in digital identity-related scams.
They know how vulnerable people can be in the digital world, mostly due to their lack of knowledge and ignorance. But hackers aren’t the only culprits—internet service providers (ISPs) are also known to sell private browsing logs to advertisers.
The implications can be dire. That’s why it’s important to inform yourself about digital identities and do what’s needed to protect yourself.
How to protect your digital identity
There’s no getting around it—digital identities are real, and are not going anywhere. Instead of figuring out how not to have a digital identity, focus on protecting it.
Be proactive by taking the steps necessary to prevent bad actors from exploiting your digital identity. Follow the guide below:
1. Use a VPN religiously
If you care about protecting your digital identity, this is a non-negotiable. But the key is using a safe VPN. Clario’s VPN is a safe, secure, and reliable tool that allows you to browse the web anonymously, thereby protecting your data.
It achieves this by throwing hackers off your trail by connecting you to a different server and hiding your IP address. You can use Clario on Android, iOS, and macOS devices.
You can get Clario up and running within minutes by following these simple steps:
- Download Clario on your device and create an account
- Tap Browsing, then toggle Browsing protection on
- Tap Allow on the pop-up window
- Clario will choose a location that has the fastest server, but you can change it by tapping the country and choosing from the list
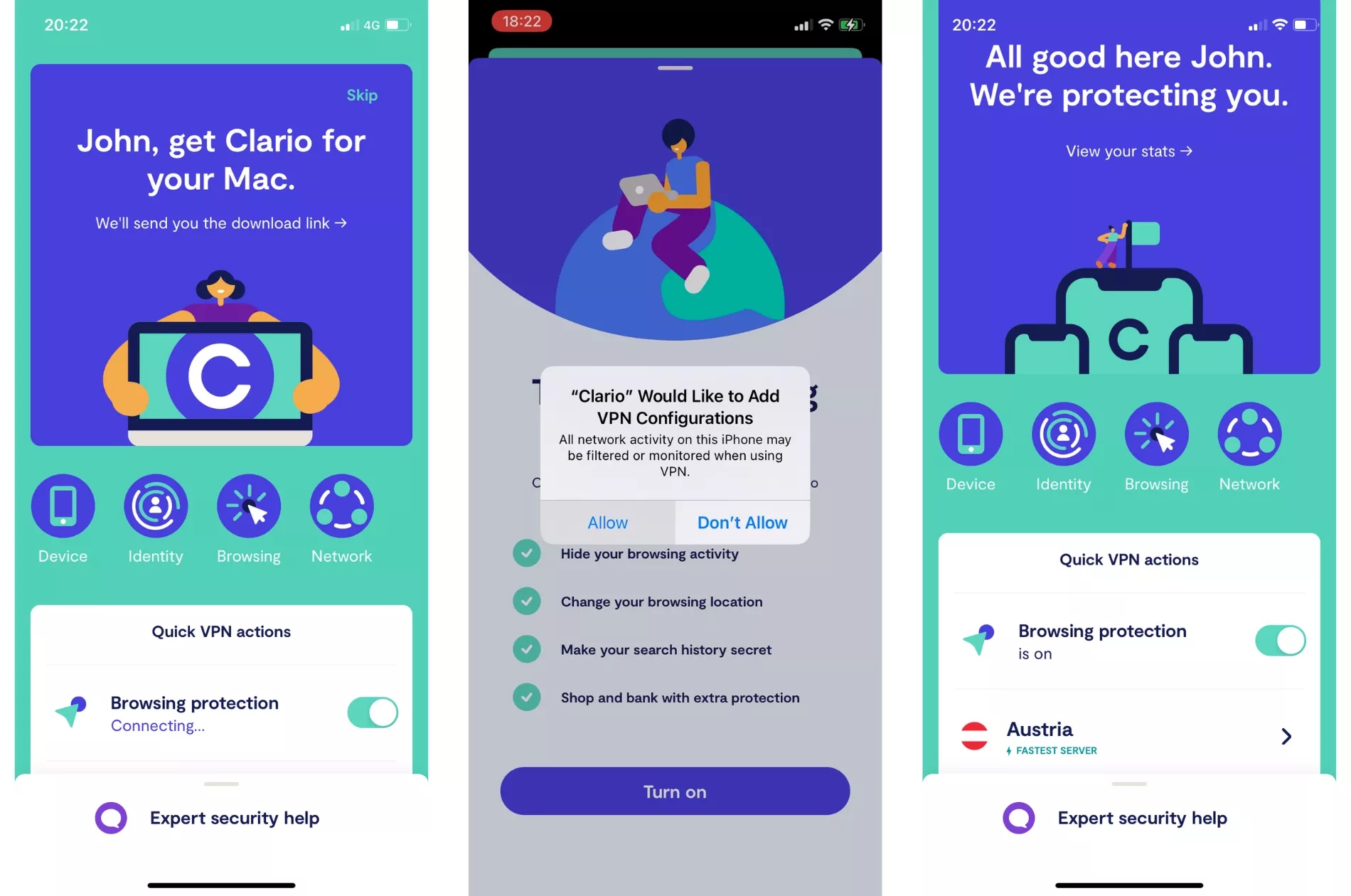
Using a secure VPN like Clario’s is also a good way to protect your digital privacy.
2. Protect your passwords
Find a reliable password manager that allows you to manage passwords across multiple devices. Never share your passwords with anyone
3. Use a private browser
As an additional step, try to avoid using the internet as we know it. Instead, use Google Chrome’s Incognito Window, or better yet, a private browser that shields you from trackers. DuckDuckGo is one such browser, but there are others you can try.


