Table of contents
- What is a crypto scam?
- Types of cryptocurrency scams
- 1. Bitcoin investment schemes
- 2. Blackmail and extortion scams
- 3. Phishing scams
- 4. Investment or business opportunity scams
- 5. Giveaway scams
- 6. Pump and dump schemes
- 7. Fake cryptocurrency exchanges
- 8. Social engineering scams
- 9. New crypto-based opportunities: ICOs and NFTs
- 10. Cloud mining scams
- How to avoid cryptocurrency fraud
- 1. Check contact information
- 2. Think carefully before investing
- 3. Ignore spam messages
- 4. Protect your cryptocurrency with cold storage
- How to report crypto scams
- Conclusion
What is a crypto scam?
Crypto scam definition
A crypto scam is a fraudulent activity that tries to swindle victims out of their digital assets. For example, a scammer might use deceptive tactics, false promises, or fake information to encourage victims to invest in nonexistent cryptocurrencies or trading platforms.
Types of cryptocurrency scams
There are several types of crypto scams, ranging from phishing to complicated Ponzi schemes that trick victims into making fraudulent investments.
Here are some of the major types of online scams to look out for:
- Bitcoin investment schemes
- Blackmail and extortion scams
- Phishing scams
- Investment or business opportunity scams
- Giveaway scams
- Pump and dump schemes
- Fake cryptocurrency exchanges
- Social engineering scams
- New crypto-based opportunities: ICOs and NFTs
- Cloud mining scams
1. Bitcoin investment schemes
Bitcoin investment schemes target people who want to invest in cryptocurrencies. Typically, a scammer promises high and guaranteed returns on a one-off Bitcoin investment opportunity.
The scammer promotes the opportunity on social media, presenting themselves as an experienced crypto trader with secret insider knowledge.
When you decide to invest in the scheme, the scammer asks you to deposit your Bitcoin into their wallet. They might show you fake updates of increasing profits to encourage you to invest more money. But when you want to withdraw your funds, the scammer will deny access and ghost you.
2. Blackmail and extortion scams
Crypto blackmail scams involve scammers trying to extort your money by leveraging your personal information or sensitive data.
Usually, the scammer will gain access to your personal data through other means, like data breaches, phishing attacks, or a direct hack. Then, they’ll try to ransom the information back to you in return for your crypto assets.
The scammer might try to intimidate you into giving them money by claiming that they’re working with law enforcement or criminal organizations. However, they’ll never actually delete your personal information—they’ll just keep extorting you until you can’t pay anymore.
3. Phishing scams
In a crypto phishing scam, a fraudster tries to trick you into sharing sensitive information like login credentials, wallet addresses, private keys, and more.
Here are some of the common strategies crypto phishing scammers use:
- Impersonation. Scammers create fake websites and social media accounts that mimic well-known cryptocurrency platforms and exchanges.
- Malware and browser extensions. Scammers create fake browser extensions that steal your credentials.
- Fake emails. Scammers send hundreds of fake emails pretending to be from reputable people and companies in the crypto space. Find out how to spot a phishing email.
One of the biggest losses happened in January 2018, when hackers broke into Coincheck and stole $534 million worth of crypto. The hackers carried out this attack using phishing schemes.
Scammers often send malicious links through phishing emails, leading to fake websites resembling legitimate platforms. Even with the best prevention methods, no system is entirely foolproof.
So, what can you do? Monitor your email for potential compromises and address breaches as soon as possible.
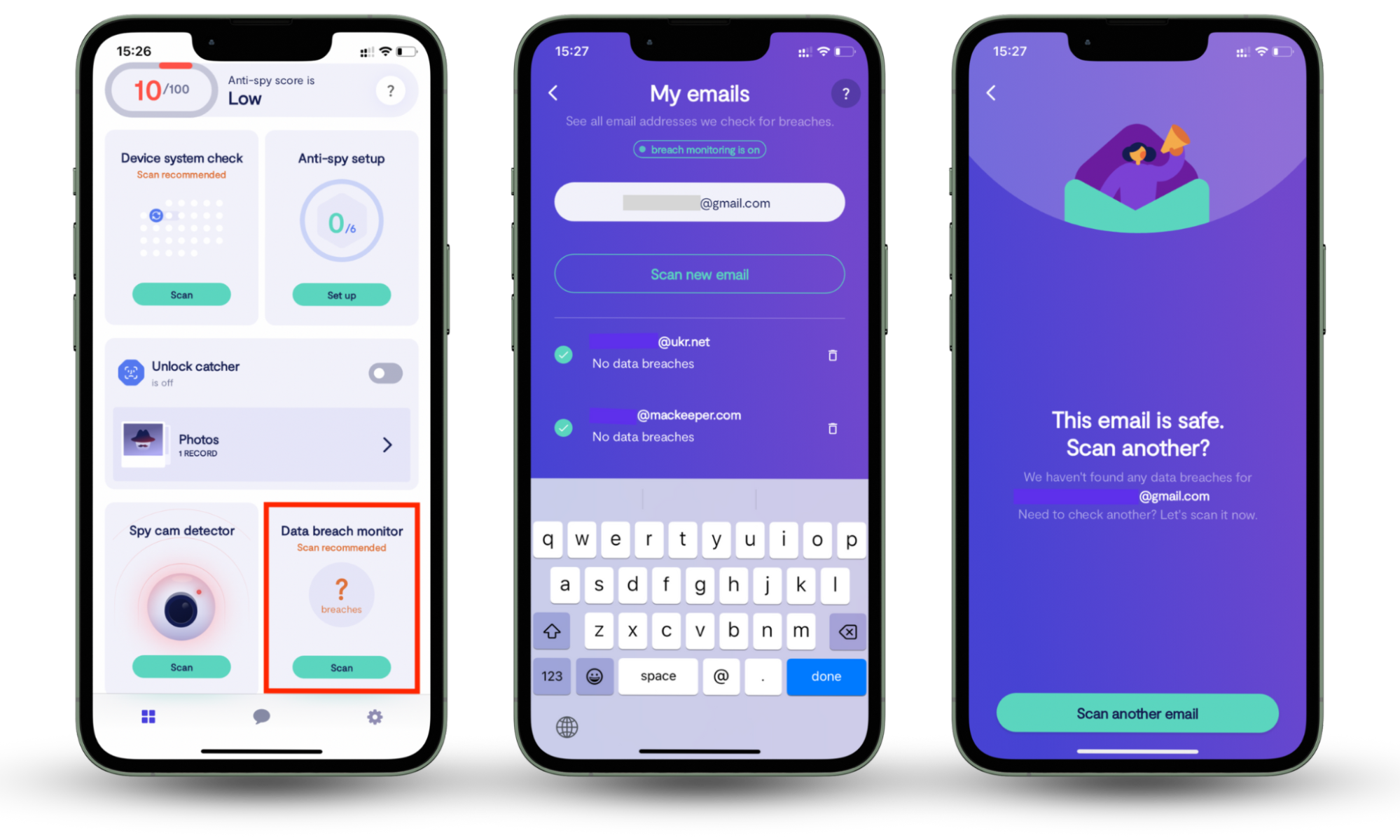
Clario Anti Spy's Data breach monitor does exactly that. It scans the email you use at checkout, identifying any breaches associated with your username or credentials. It also notifies you whenever your data has leaked online, so that you can fix the breach.
Here’s how to use Clario Anti Spy's Data breach monitor:
- Download Clario Anti Spy and set up an account.
- Go to the Data breach monitor and tap Scan.
- Enter the email you wish to check for breaches.
- Wait for results. The app will notify you whether your email is safe.
4. Investment or business opportunity scams
Business opportunity scams are fraudulent tactics targeting people looking to invest in cryptocurrency.
Scammers create an enticing offer that’s too good to turn down. For example, they might claim to have special insider information, secret trading strategies, or new technology that can generate massive profits.
They’ll create a sense of urgency and demand that you take immediate action through limited-time offers and “exclusive” opportunities. But the opportunities are all fake, and you’ll never see your money again if you invest.
5. Giveaway scams
Giveaway scams are where scammers promise crypto rewards in return for participating in a social media challenge or providing personal information.
In these scams, fraudsters will impersonate a well-known figure in the crypto industry and create fake social media profiles, websites, and email accounts.
Then, they’ll tell participants they can receive substantial amounts of cryptocurrency by following simple instructions. Often, they’ll ask for the victim to send a small amount of crypto as a verification fee or ask the victim to provide their personal keys to receive the giveaway.
However, the “reward” never appears, and you’ve given the scammer money you’ll never get back.
6. Pump and dump schemes
Pump and dump schemes are where groups of scammers artificially manipulate the price of a cryptocurrency to profit from the price increase and leave subsequent investors with a loss.
Here’s how a pump and dump scheme works:
- The scammers choose a lesser-known or unregulated cryptocurrency that can be easily manipulated.
- They buy a large amount of the coin at low prices to create a false sense of buying pressure.
- The scammers generate hype around the coin, creating inflated price predictions.
- More people invest, creating a rapid price increase (known as the “pump” phase).
- The scammers start selling off coins at inflated prices, triggering a panic sale (known as the “dump” phase). They make huge profits and leave other investors with the loss.
7. Fake cryptocurrency exchanges
Fake cryptocurrency exchanges are fraudulent platforms that deceive users and steal their funds or personal information. By mimicking legitimate exchanges, they gain credibility and attract unsuspecting victims.
Often, fake exchanges display falsified order books, charts, and trade histories, making it look like the exchange is active and trustworthy. But after you add your funds to the exchange, you discover cryptocurrency fraud.
The scam might include:
- Withdrawal limitations. Fake cryptocurrency exchanges often prevent you from withdrawing your funds or making a substantial profit.
- Misleading fees. Fake exchanges usually advertise low fees or discounts, then hit you with hidden fees or high transaction costs after you’ve invested your funds.
- Trade manipulation. Some fake exchanges manipulate trades so that you always lose out. They can do this by fake order matching and other strategies, making favorable outcomes impossible.
8. Social engineering scams
Social engineering crypto scams use physiological manipulation tactics to deceive victims. By exploiting their victim’s emotions, scammers can trick them into revealing sensitive information or transferring their funds directly into the scammer’s wallets.
Some common social engineering tactics include:
- Impersonating trusted cryptocurrency individuals, companies, and exchanges to gain the victim’s trust.
- Creating a sense of urgency or fear to manipulate people into making quick decisions.
- Posing as helpful experts and offering to guide the victim through the complex cryptocurrency landscape.
- Providing fake reviews and endorsements to make their scams look legitimate.
Social engineering scams can trick you into disclosing sensitive information, which hackers use to commit various kinds of fraud or cyberattacks. These attacks often target your social media accounts, making it essential to strengthen your security before scammers strike.
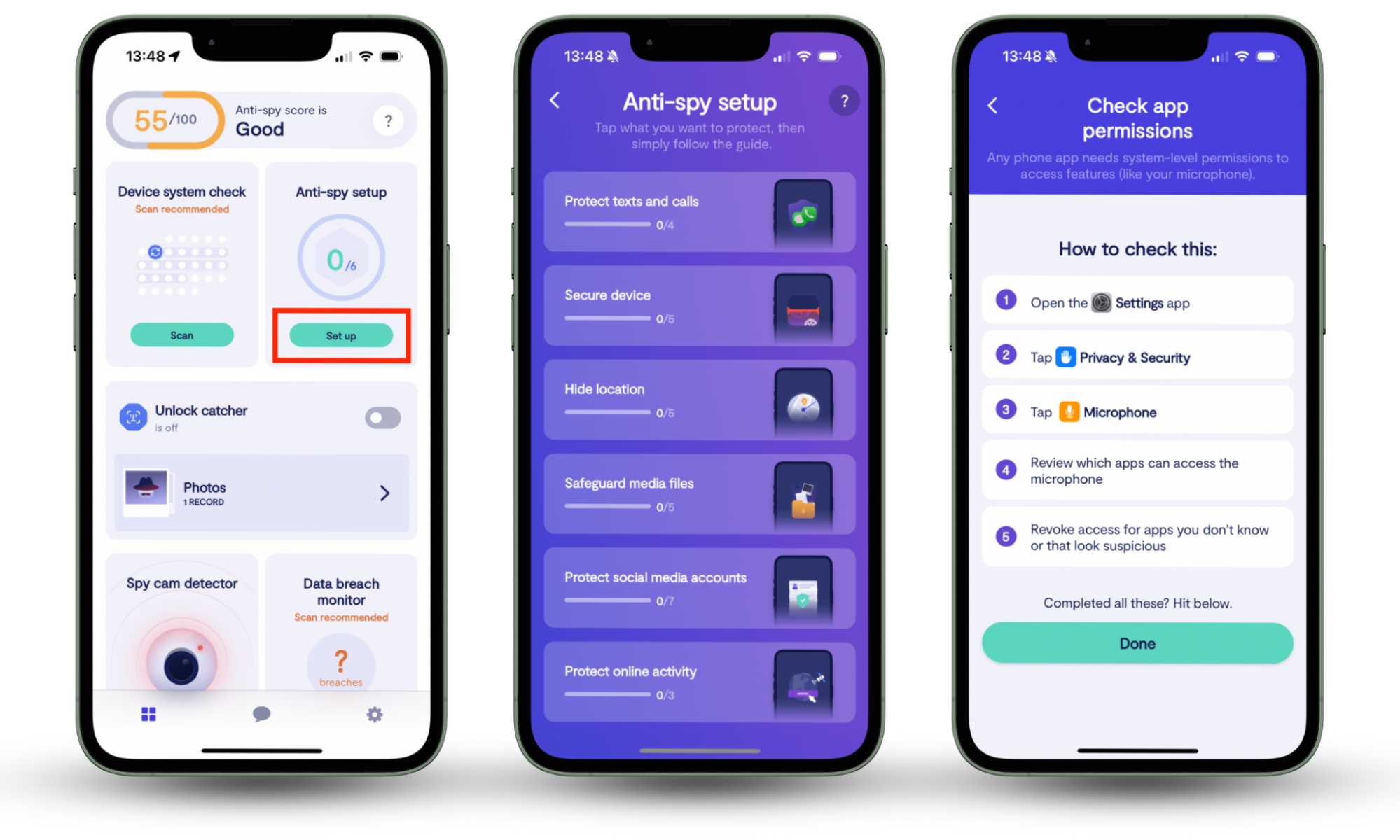
Clario’s Anti-spy setup is a straightforward, step-by-step checklist to help secure every aspect of your digital life. It will help you protect your text messages, calls, device, and social media profiles, reducing the risk of threats before they happen.
Here’s how to use Clario’s Anti-spy setup:
- Download Clario Anti Spy on your mobile and create an account.
- Go to Anti-spy setup feature and click Set up.
- Select from the menu of options what you need to protect.
9. New crypto-based opportunities: ICOs and NFTs
New crypto scams involving Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have emerged as these technologies become more popular. The most common ICO scam involves fraudsters creating fake ICO offerings.
In fake ICO offerings, scammers create a false copy of the fundraising model used by many blockchain-based projects. For example, they might create fake websites and white papers and convince investors to buy their fake tokens. But, once enough people invest, they disappear, leaving investors with worthless tokens.
When it comes to NFT scams, there are as many scams as there are with traditional cryptocurrency. Some examples include:
- Fake or counterfeit NFTs with the artwork and metadata of popular NFT collections
- Phishing scams where scammers pose as a popular NFT platform or marketplace
- “Rug pulls,” where the creator of an NFT project suddenly shuts down the project after investors have contributed funds.
10. Cloud mining scams
Cloud mining scams involve fraudulent people offering cloud mining services for specific cryptocurrencies. These services allow users to rent computing power from data centers, using it to mine cryptocurrency without needing to own the specialized equipment.
Scammers will lure investors in by making unrealistic claims about how much profits they can make. They’ll claim to have advanced equipment and show falsified proof that their customers generate huge profits.
However, there’ll often be a complete lack of transparency, and you’re expected to sit back and trust the scam operator to perform the mining and send you the profits. And, once you invest, you’ll often discover that you must pay additional fees for maintenance.
How to avoid cryptocurrency fraud
To avoid cryptocurrency fraud, you need to be proactive. Educate yourself, use reputable exchanges and platforms, and secure your wallets with strong encryption and multiple layers of protection.
Here are some other things you can do to protect yourself from crypto scams:
- Check contact information
- Think carefully before investing
- Ignore spam messages
- Protect your cryptocurrency with cold storage
1. Check contact information
Scammers often create fake websites, social media accounts, and email addresses that mimic legitimate cryptocurrency companies. Always double-check URLs, accounts, and email addresses through the company’s official channels to ensure you aren’t dealing with a scammer.
2. Think carefully before investing
To avoid scams, you need to do your research and due diligence. Before investing, conduct thorough research on the project, its team, and the potential risks and rewards. Look for credible information from reliable sources, and be skeptical. If they offer unrealistic rewards or make suspicious claims, avoid them at all costs.
3. Ignore spam messages
Scammers often use unsolicited email, social media, and text messages to promote their scams. If you receive an unexpected message from someone you don’t know, ignore it. In all likelihood, it’s a scammer who’s trying to steal your personal information. The best thing to do is to use Clario’s Anti-spy setup to protect your social media accounts, text and calls, and online activity.
4. Protect your cryptocurrency with cold storage
Cold storage securely stores your crypto and private keys offline, preventing hackers or malware from accessing it. This means you don’t need to rely on the security of exchanges or online wallets. Instead, you can use physical security methods to store your keys and personal information in secure locations.
How to report crypto scams
Reporting crypto scams can help protect other people from falling victim and initiate investigations that take down the fraudulent actors.
Here’s what to do:
- Understand what to do if you have been scammed.
- Gather as much information about the scam as possible, including transaction details, communication records, website names, and other relevant information.
- Report the scam to your local law enforcement agency. They will be able to guide you on what to do next to protect your identity and avoid falling victim again.
- Report the scam to the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) and Federal Trade Commission (FTC). This will assist in any further investigations against the scammers.
- Warn others in relevant cryptocurrency communities, forums, and social media platforms. This will help raise awareness about the scam and prevent others from falling victim.
Conclusion
The complicated world of cryptocurrency is confusing and full of risk. Understanding these risks, including the common types of scams that target crypto investors, can help you secure your funds and prevent your personal data from falling into the wrong hands.
Stay vigilant and use Clario Anti Spy. Our Data breach monitor will check and fix your personal data leaks, specifically emails. Also, try Clario Anti-spy setup to activate basic protection measures for your social media accounts, text and calls, and online activity.


