Table of contents
- How does Google collect information
- What does Google know about you
- What is Google profiling
- How does Google profile you
- What does Google do with your data
- Google and the NSA
- How to stop Google from spying on you
- Android
- iOS
- Windows and macOS
- Final words
How does Google collect information
Google uses various methods across its several platforms to collect information about you. Mostly, they collect the information you provide when using their services (Google Maps, Chrome, Google Cloud, Gmail, etc). Also, Google actively tracks your online activity and device information.
Here are ways Google collects your information:
- User input: When you sign up for a Google account or provide any information for your profiles
- Searches: When you use Google’s search engine
- Location services: When you use services like Google Maps
- Browsing activity: When you use Google Chrome
- Device information: When you use any Google service on a smartphone or other device
- App usage data: When you use Google’s mobile apps
- Voice and audio data: When you use voice-activated services like Google Assistant
Though it may sound sinister, Google purports that all data collection is used to improve their products and provide you with better-personalized ads based on your activities and interests.
Still, this excessive data collection has always been a hot topic among users concerned about data privacy. Following a 2020 case accusing Google of misleading consumers about how much data it collects, privacy scrutiny has intensified. If you are uncomfortable with this amount of your data being gathered and want to safeguard your privacy, then Clario Anti Spy may be just what you need.
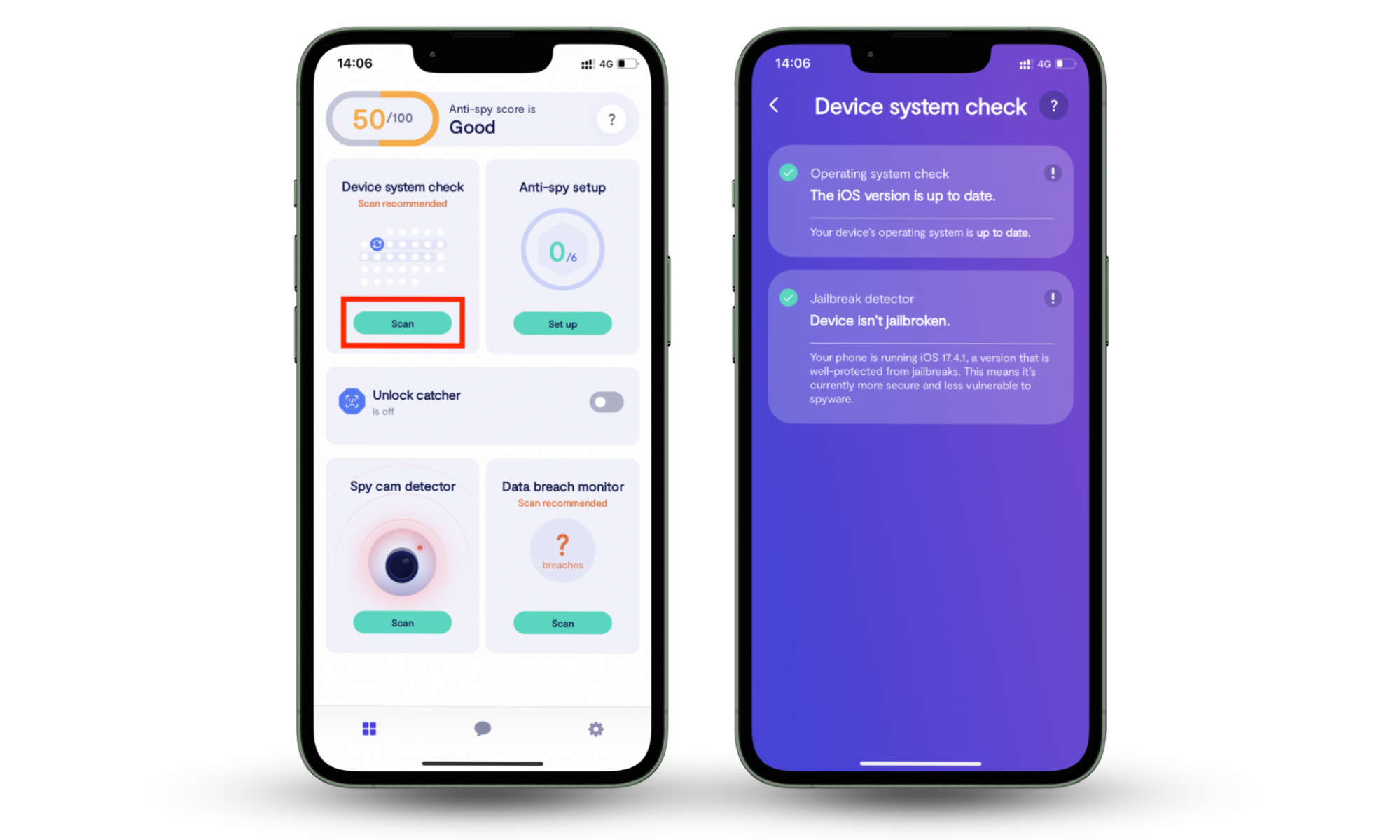
Clario Anti Spy is a simple yet powerful mobile app that stands guard for the safety of iPhone and Android users. With the Device system check feature, iPhone users can check if their device’s OS is up to date. But more importantly, it scans the device for signs of jailbreak, which is the biggest safety threat for iPhone users so far. This is because only a jailbroken iPhone can easily be hacked and monitored.
Here’s how to start using Clario Anti Spy’s Device system check:
- Download Clario Anti Spy on your iPhone.
- Create an account by filling in basic info (email, name, etc.).
- Under the Device system check feature, tap Scan.
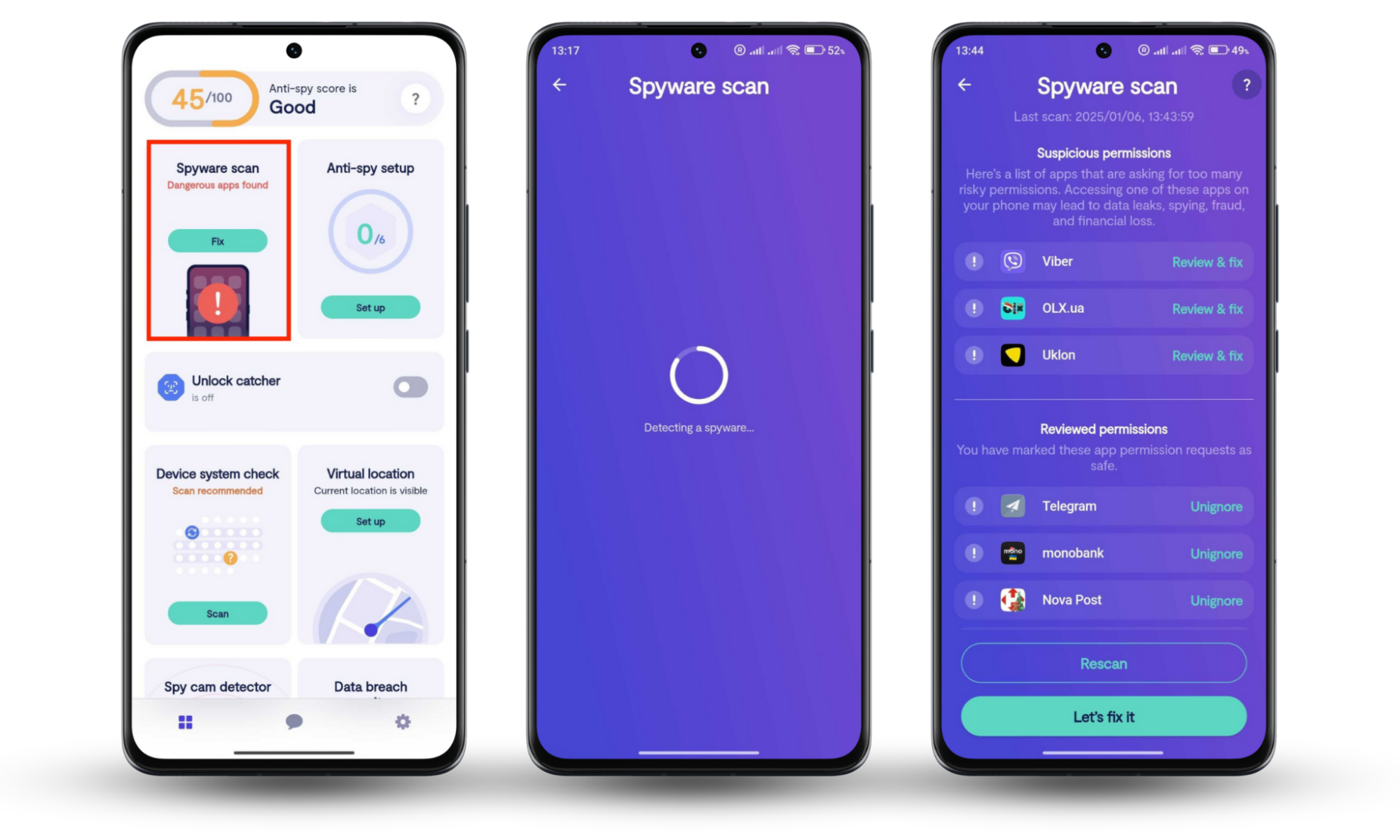
Spyware Scan feature checks Android devices for hidden spyware, unauthorized parental control apps, or suspicious app permissions.
Here’s how to start using Clario Anti Spy’s Spyware scan:
- Download Clario Anti Spy on your Android.
- Create an account by filling in basic info (email, name, etc.).
- Under the Spyware scan feature, tap Fix.
What does Google know about you
Considering the information contained within Google’s services, Google can potentially collect a wide variety of data on you. This can include personal information about who you are and where you live, as well as information about your web habits and devices.
Here’s what Google knows about you:
- Search data: Information about your Google searches, including terms, the times/date of the searches, and what results you click.
- Location data: Information about your device's location, including GPS data, Wi-Fi access points, and nearby cell tower locations.
- Device information: Information about your devices, including model number, operating system, and other device identifiers.
- Usage data: Information about how you react to Google’s services, including app usage, websites you visit, videos you watch, and everything on your Google Drive and Google Calendar. It’s also unsafe to use Google sign-in for other accounts.
- Personal information: Information you provide when you create a Google account (name, address, and phone number).
- Cookies and similar technologies: Information about your online activity, including browsing history, preferences, and what ads you click on.
- Voice and audio information: Voice and audio recordings may be stored to improve voice-activated services, like Google Assistant.
Yes, Google is collecting a lot of data—but actual hackers can be worse. Some hackers can see through your phone camera. In case you ever feel targeted, it’s crucial that you learn how to stop someone from spying on your phone. Your data is very valuable, so protect it at all costs.
What is Google profiling
Google profiling is the process by which Google creates a detailed profile based on your online activities and interactions with Google’s services. Profiling involves collecting and analyzing user data to understand preferences, behaviors, and interests. Google uses profiles to improve user experience and deliver personalized services and ads.
How does Google profile you
Google profiles you by collecting your personal data in various ways, including search results, IP address tracking, cookies, and ad tracking. We reveal so much of ourselves through our web activity. Based on this data, Google can render a fairly accurate user profile.
Here’s how Google profiles you:
- Search results: Like it or not, Google tracks you through your search results. But Google is not interested in your individual browsing history—rather, Google tracks your results gradually to create a user profile.
- IP address tracking: Your IP address identifies and locates your devices on a network—it also reveals the physical location of a device. Google can use IP tracking to determine your geolocation. They also use your IP address for analytics and personalized ad delivery.
- Cookies: Cookies are bits of data stored on your device after you visit a website. They are primarily used to improve user experience when you revisit a site. But they also contain user information, which Google tracks long-term for profiling user behavior.
- Ad tracking: Google keeps track of all your ad interactions as part of its profiling campaign. Understanding what you like (or dislike) helps them create a richer profile about your interests to serve you more relevant ads.
Though these are the essential elements of Google profiling, the tech giant can incorporate other ways to create a more vivid profile of its users, including social media integration and cross-device tracking.
What does Google do with your data
Google uses your data for various purposes—but mainly to improve its services, enhance user experience, and personalize the ads you receive. Here are some of the ways Google uses your data:
- Improving services: Google uses your data to analyze and improve its own suite of services. This includes improving its algorithm, optimizing the user interface, and just refining the overall user experience.
- Personalizing: Google uses your data to provide a more personal experience. This means adjusting your search results and offering products and services based on your user profile.
- Ad targeting: Google uses data like your search history and previous ad interactions to serve ads targeted to your interests. Advertisers generally pay more for these types of ads because they are more likely to convert sales.
- Google Analytics: Website owners and businesses use Google Analytics to get important data on how users interact with their websites. This anonymized data helps them improve their sites, services, and products.
- Other Google services: Many Google services require your data to function properly. For instance, location-based services can only serve you with your actual location. Your data may also be used to enhance security and lockout possible intruders.
Google and the NSA
Google’s privacy policies claim they only use your data to serve you better—but that’s not entirely true. In 2013, former NSA contractor-turned-whistleblower, Edward Snowden, exposed a mass data collection program that monitors private citizens—and Google is involved.
Through the PRISM program, the NSA collects digital communication from at least nine major companies, like Microsoft, Facebook, Apple, and, you guessed it, Google. They randomly bulk-collect and claim it’s for national security reasons.
It should be noted that Google has denied giving the NSA direct access to its servers and claims to only provide data in response to legal requests. But it’s no secret that the government spies on us and their surveillance programs are shrouded in mystery. So it’s important to listen to Google’s word with a healthy dose of skepticism.
How to stop Google from spying on you
While it’s not possible to completely stop Google from monitoring you, it’s possible to minimize the damage. Adjusting your Google account settings, managing location services, and opting out of personalized ads are some ways to limit the private data you freely give to Google.
Here are some ways to stop Google from spying on your various devices:
Android
Here are ways to reduce Google data collection on Android:
- Review and adjust Google settings:
- Tap Settings > Select Google.
- Tap your Google account and review your settings.
- Manage location services:
- Tap Settings > Location.
- Adjust location services for Google or consider only enabling it when needed.
- Opt out of personalized ads:
- Open the Google Settings app > Select Ads.
- Tap Opt out of Ads personalization.
How secure is your email account?
Learn how to secure your Gmail account on mobile to avoid data leaks.
iOS
Below are ways to reduce Google data collection on iOS.
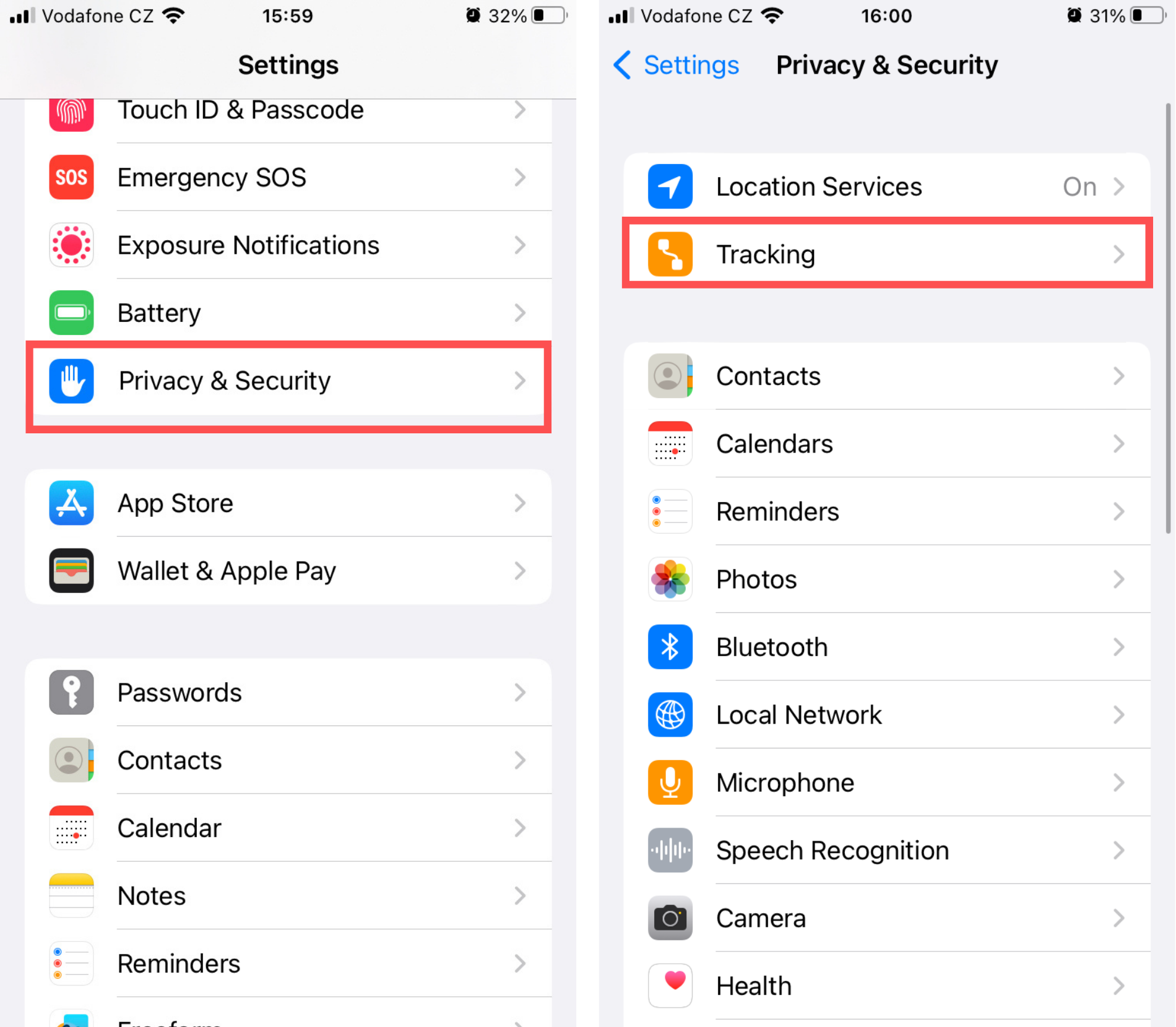
Adjust Google tracking permissions
- Tap Settings > Privacy & Security > Tracking.
- Adjust Google’s tracking permission according to your preferences.
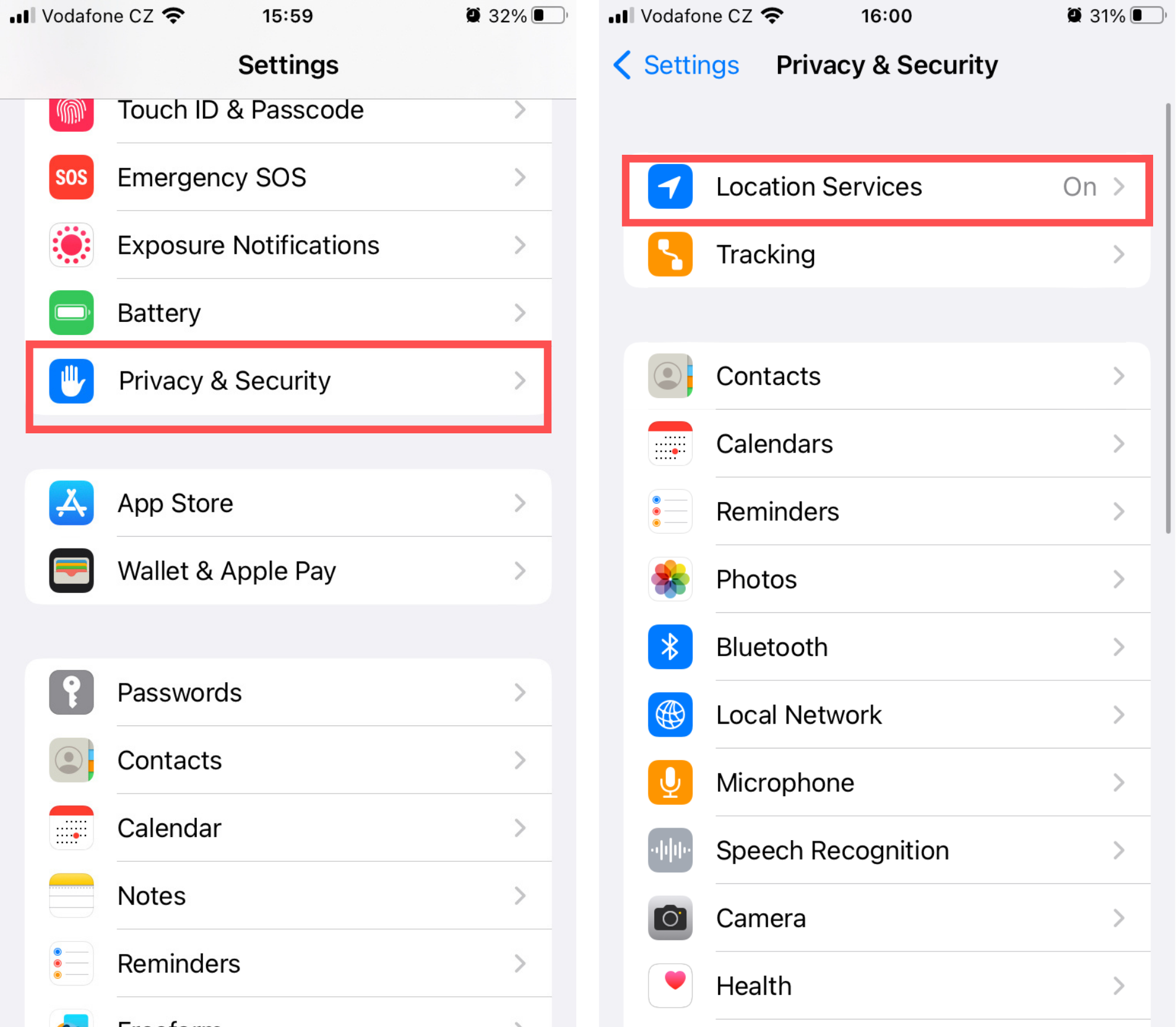
Manage location services
- Tap Settings > Privacy & Security > Location Services.
- Review the location services permission for Google’s apps.
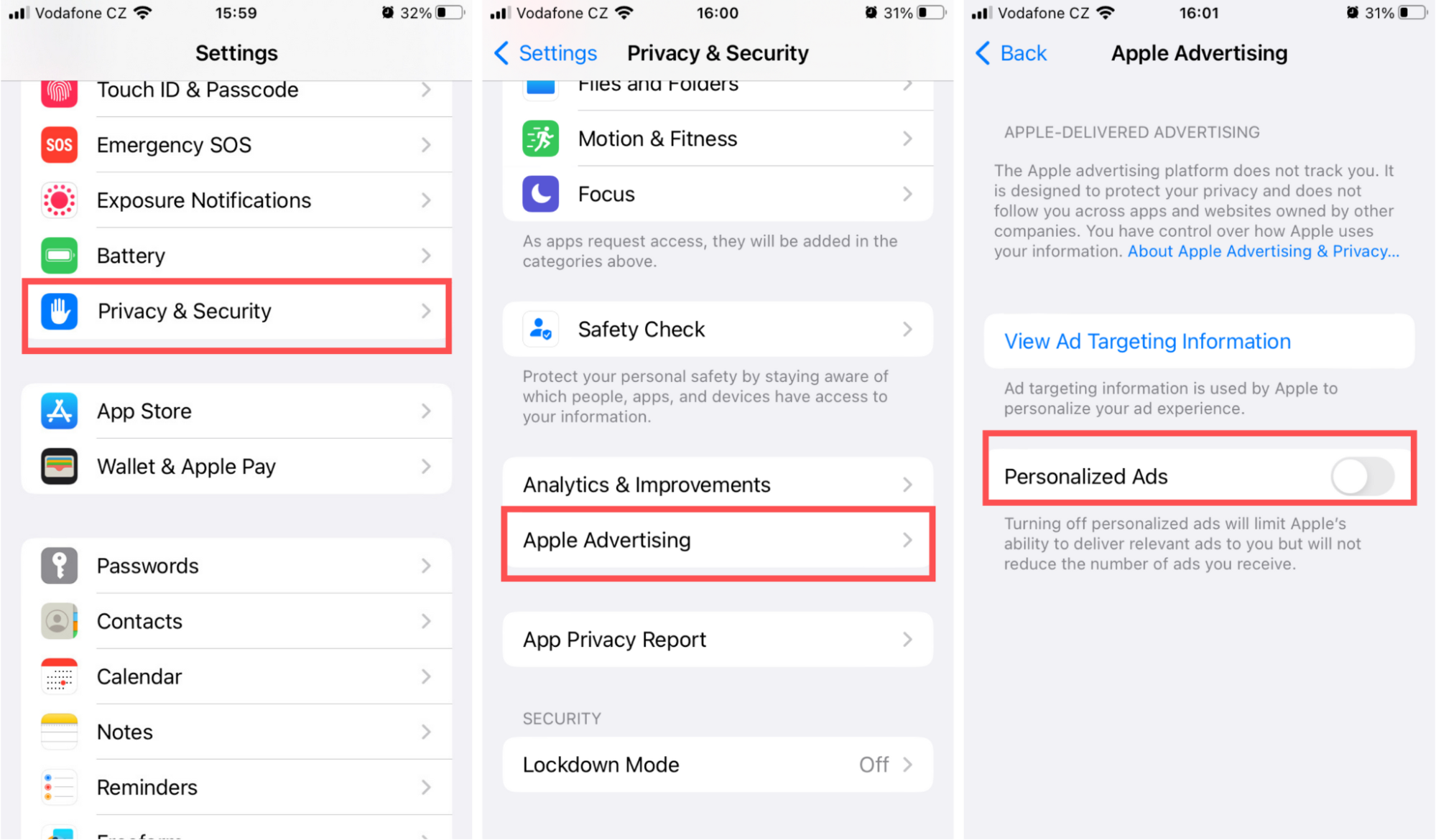
Limit ad personalization
- Tap Settings > Privacy & Security > Apple Advertising.
- Toggle Off Personalized Ads.
Windows and macOS
Below are ways to reduce Google data collection on Windows and macOS.
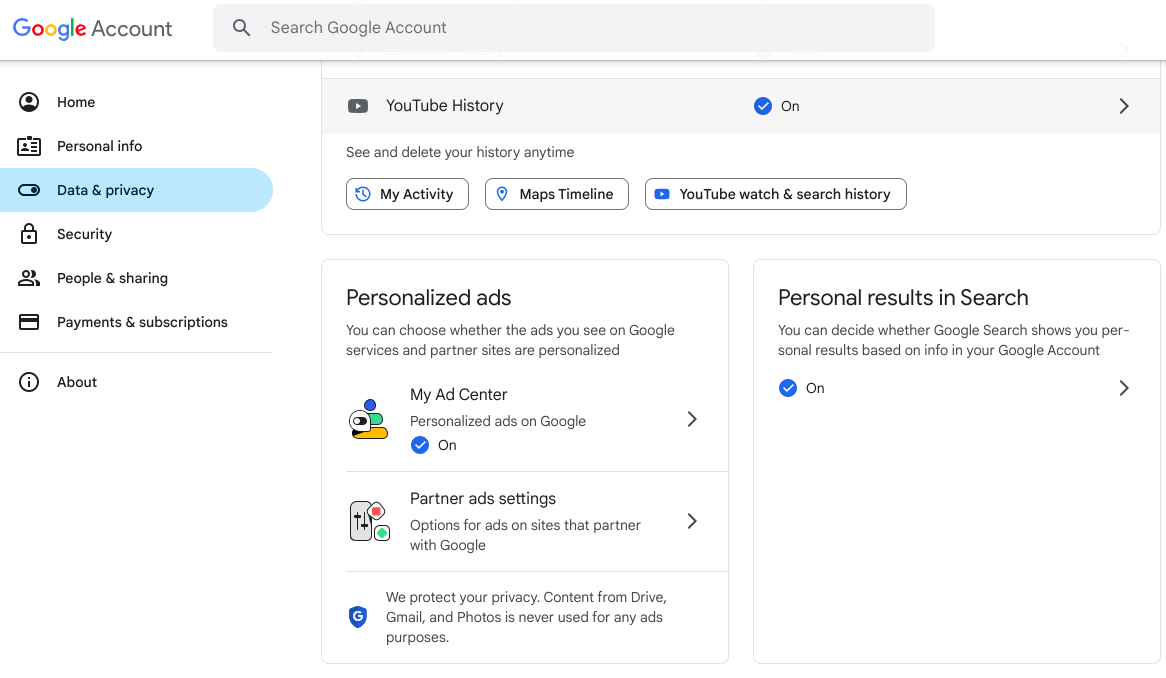
Google account settings
- Go to your Google account and review your stored information in various Google services.
- Under the Data & Privacy tab, you can review settings for activity controls, ad personalization, and location services.
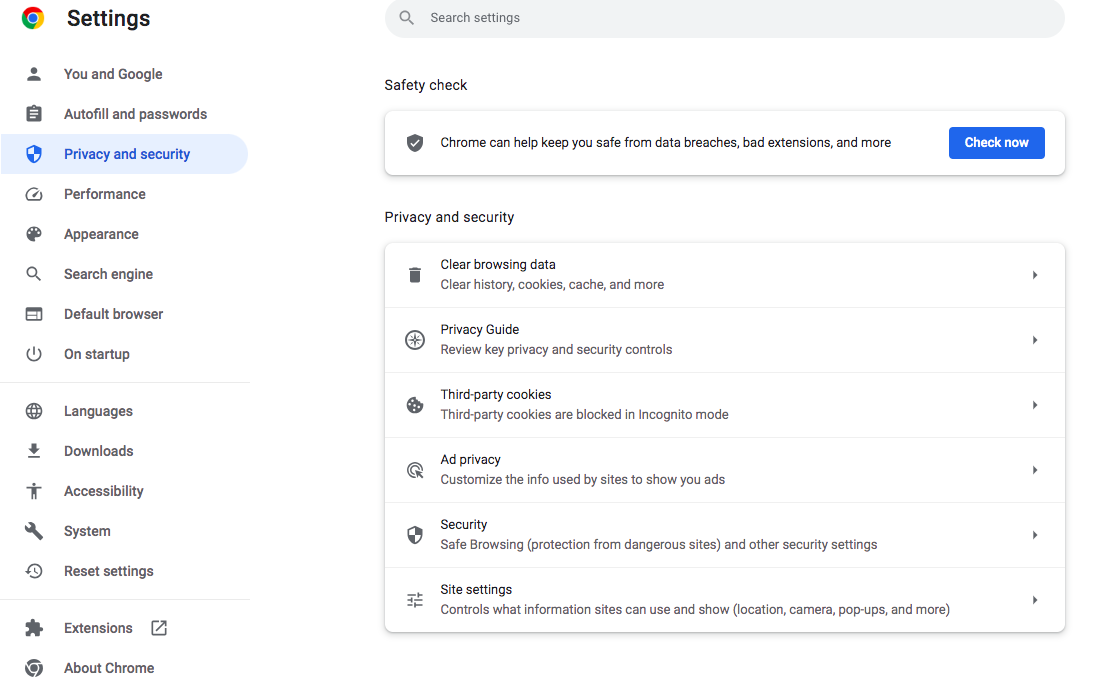
Google Chrome settings
- In Google Chrome, click the three-dots in the top-right corner, and select Settings.
- Under the Privacy & Security tab on the left, review your settings for Third-party cookies, Ad Privacy, and Security.
Final words
Though you can’t stop Google from “spying” on you through tracking your data, you can significantly reduce what they see. Be mindful of the information you reveal through Google services and adjust your settings for maximum privacy. And to stop other snoops from digging into your private data, use Clari Anti Spy.
Our tool can be your shield against spying, data breaches, and jailbreaks. The Device system feature checks if your iPhone device has been jailbroken and runs on the latest updates. The Spyware Scan feature conducts a thorough review of your Android device, digging for hidden spyware or suspicious app permissions, and empowers you to take necessary action to remove them.


