Table of contents
- Can Wi-Fi be hacked?
- What are the signs of a hacked router?
- 1. Unknown devices connected to your network
- 2. You can’t log in or there are unauthorized changes in router settings
- 3. Drop in internet speed
- 4. Unexpected redirects, pop-ups, and network traffic
- 5. Unknown software downloads
- 6. Internet provider alerts
- 7. Fake virus warning
- 8. Ransomware emails
- 9. Session hijacking
- 10. Increase in pop-up advertisements
- Possible causes of a compromised router
- How to remove hackers from your network
- How to fix your hacked router
- 1. Disconnect router from internet
- 2. Perform a hard reset
- 3. Change your account's password
- 4. Update the router's firmware
- How to secure Wi-Fi router
- 1. Regularly update the firmware
- 2. Change default admin credentials
- 3. Enable strong encryption
- 4. Use a firewall
- 5. Create a guest network
- 6. Schedule routine reboots
- 7. Disable remote access
- 8. Create a unique SSID
- 9. Turn off WPS
- 10. Install a VPN
- 11. Avoid suspicious links and attachments
- 12. Download antivirus software
- Conclusion
Can Wi-Fi be hacked?
Yes—malicious actors can hack your router, access your Wi-Fi network, and spy on you through Wi-Fi. Usually, they’ll get access through weak or compromised passwords. This is because many people never change their default router password, making it easy for hackers to brute force their way in.
However, hackers can also gain unauthorized access to your Wi-Fi network through firmware vulnerabilities and targeted hacks like cross-site scripting (XSS), WEP/WPA key cracking, Domain Name Setting (DNS) spoofing, and rogue access points.
What are the signs of a hacked router?
There can be several signs that a router has been hacked. Here’s how to tell if someone’s hacked your router:
- Unknown devices connected to your network
- You can’t log in or there are unauthorized changes in router settings
- Drop in internet speed
- Unexpected redirects
- Unknown software downloads
- Internet provider alerts
- Fake virus warning
- Ransomware emails
- Session hijacking
- Increases in pop-up advertisements
Below, we’ll explain in more detail how to know if your Wi-Fi is hacked and what to do about it.
1. Unknown devices connected to your network
If you have unknown devices on your network, it means that someone’s gained unauthorized access.
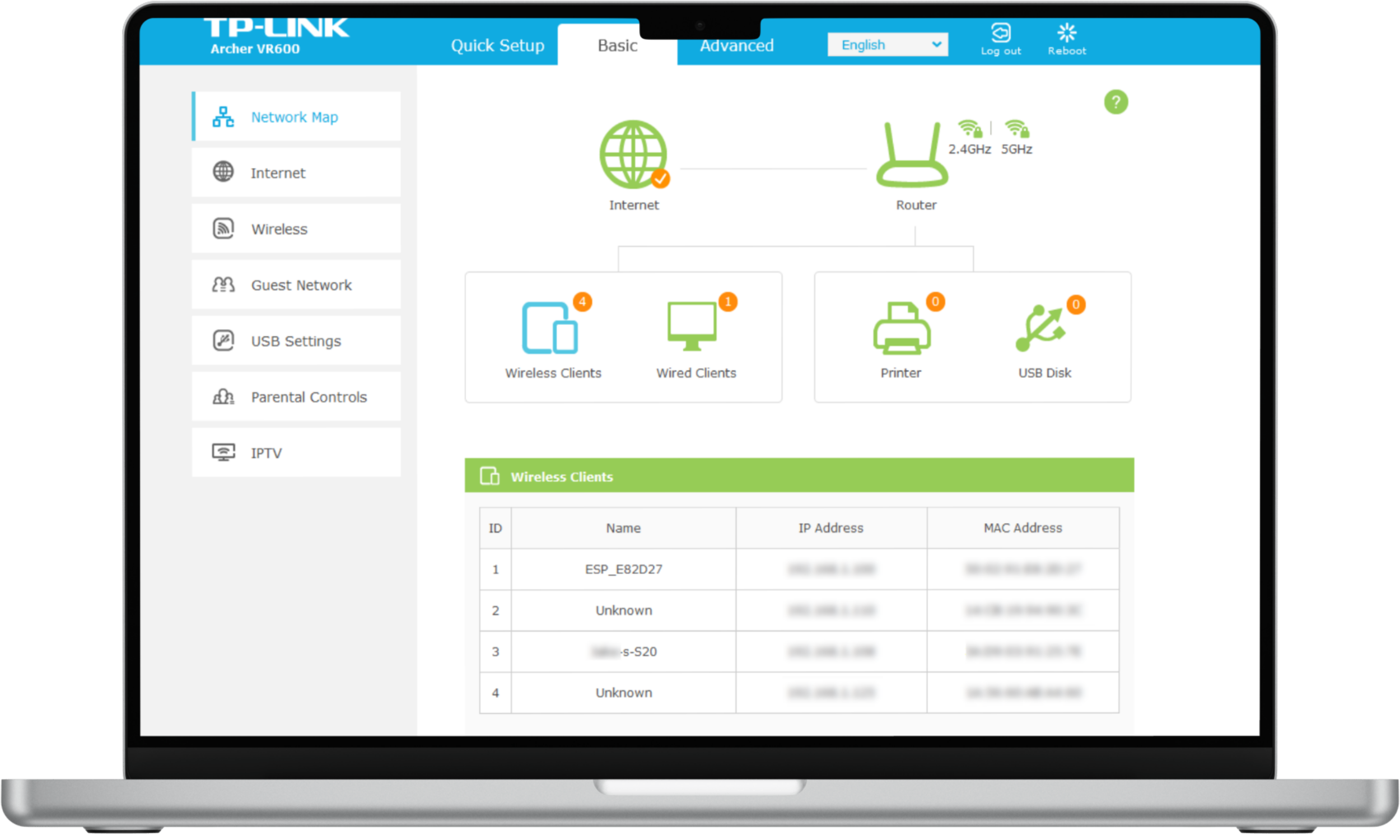
To identify devices on your Wi-Fi network, you need to access the router’s administration interface. Open your web browser and enter the router’s IP address in the address bar. This is usually found on the router itself and is something like 192.168.0.1.
In the admin interface, navigate to the connected devices page under a heading like “Status” or “Network.” Here, you’ll see the list of devices connected to your router. If there’s any you don’t recognize, you need to secure your network immediately.
2. You can’t log in or there are unauthorized changes in router settings
Cyber attackers will often change your router’s login settings so that you can’t protect yourself. If you can no longer log in to your router, it’s a sign that someone has hacked your router.
If you notice that there are other router configuration changes, including your Wi-Fi name or DNS settings, it might’ve been a hacker.
3. Drop in internet speed
If your internet suddenly slows down or you experience random drops in speed throughout the day, it’s a sign that your router’s compromised.
The more devices connected to your Wi-Fi network, the slower it’ll be. And, hackers will often use compromised networks to run malicious software like cryptocurrency miners that use device and network resources.
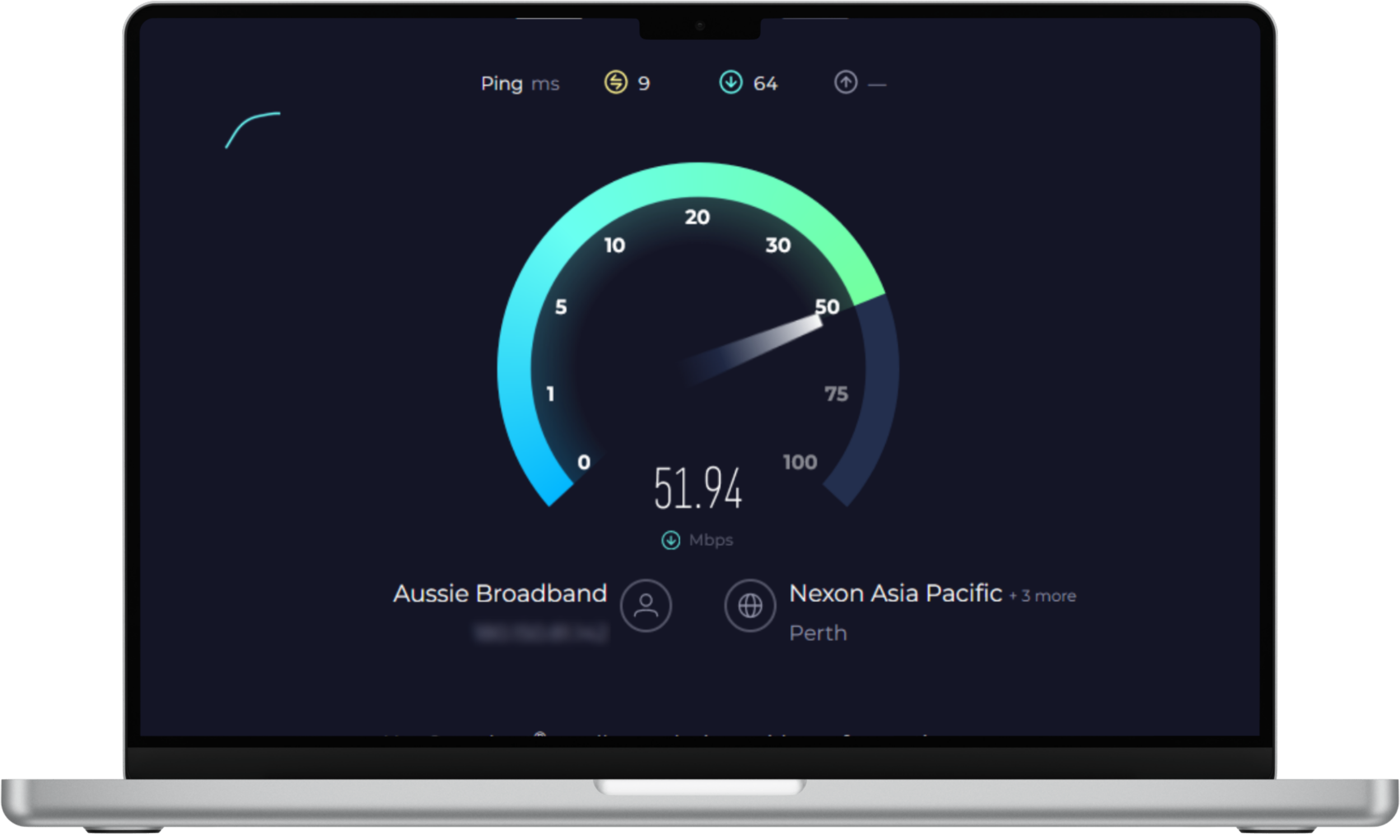
To check your internet speed, you can use a service like Speedtest by Ookla.
4. Unexpected redirects, pop-ups, and network traffic
If you notice unusual or excessive data usage on your network that you can’t account for, there might be unauthorized devices on your network.
Likewise, if you experience random pop-ups and web browser redirects (when you’re trying to access a website and it automatically loads a different one), your router might’ve been compromised by a hacker.
This is because hackers often change your DNS settings so that you can only access specific websites that try to steal your personal information or download malware to your devices.
5. Unknown software downloads
Hacked routers can lead to hacked devices. This is another way to check if your router is hacked. If your devices start working strangely, freezing a lot, or showing strange behaviors like randomly opening apps, you might have a hacked router.
The worst sign of this is if you suddenly have unknown software or app downloads on your mobile device, laptop, or PC. This can mean that your devices and your router are infected.
6. Internet provider alerts
If your network starts behaving strangely out of nowhere, you might receive a warning from your internet service provider (ISP). They might’ve noticed that your internet usage has skyrocketed or that there’s unusual activity over your network, and they’ll send you a notification.
If you receive an alert from your internet provider, you should act immediately to prevent further damage.
7. Fake virus warning
If a hacker has successfully infiltrated your network, they might try to install malicious software on your router or connected devices. One type of software often installed is called “Scareware” which causes fake antivirus notifications to appear, pressuring you to download an antivirus.
However, these are false advertisements, and the “antivirus” download link will install malware or other viruses and further compromise your network.
8. Ransomware emails
Ransomware is another type of malicious software that threatens to destroy or lock your device if you don’t pay the hacker a fee. If you start receiving warnings that you have a virus or that your device will be encrypted if you don’t pay up, it means that your device has been hacked.
Never respond to ransom demands. Although it can be daunting, there’s no guarantee that a hacker will restore access to your devices after you pay. Instead, they’re likely to keep asking for more money.
9. Session hijacking
A hacked Wi-Fi network can also lead to session hijacking. This is when an attacker takes control of your active browsing session. Instead of stealing your bandwidth, they grab cookies and login tokens to impersonate you online. That also gives them access to your email, online banking, or social accounts that you're signed in to.
Your Wi-Fi may be compromised if you notice strange login attempts or suddenly get locked out of your accounts. To stay safe, log out after visiting sensitive sites and turn on two-factor authentication for extra protection.
10. Increase in pop-up advertisements
Another way that you can rely on how to tell if your Wi-Fi is hacked is by watching out for pop-up ads. If you're suddenly flooded with them—even on sites that don't usually have them—it could mean your router has been compromised.
Hackers may inject malicious code into your network traffic, making regular web pages ad-filled traps. These ads can trick you into downloading fake software or giving away personal information.
If this happens, avoid clicking suspicious ads and check your router's logs or connected devices list to confirm if your Wi-Fi has been hacked.
Possible causes of a compromised router
There are several ways a router can be hacked, including:
- Weak or default passwords. Using weak passwords or never changing your default password can make it easier for a hacker to gain access. Default passwords are often publicly available, meaning hackers can just brute force their way in.
- Outdated firmware. New firmware updates often include security patches. If you don’t update your router, you leave it susceptible to exploitation.
- Phishing attacks. Attackers can trick you into providing your router login credentials through phishing emails and malicious websites. Always know the signs of a phishing attack to prevent this from happening.
- Wi-Fi encryption weaknesses. If your router is using weak encryption protocols like WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) it can be easier to hack.
- Physical access. If a hacker can get physical access to your router, they can easily manipulate its settings, gain access, and install malicious firmware.
- Insecure network configuration. If you use insecure network settings like open ports or enabled remote management, you’re providing an easy access point for hackers. They can easily exploit these features to get control of your router.
- Attacks on connected devices. If one of the devices connected to your router becomes compromised, it can be used to target the router with malicious software. From there, they can change your router’s configuration or attack other connected devices.
On mobile devices, Clario Anti Spy can enhance the security of both your phone and online accounts, helping protect your privacy if you ever connect to a compromised network. All you need to do is work through its Anti-spy setup.
Here's how to use Clario Anti Spy to stay secure:
- Download Clario Anti Spy and subscribe to create an account.
- Tap Setup under Anti-spy setup.
- Pick a category—e.g., Secure device—and work through the on-screen instructions.
- Repeat for all other categories within the Anti-spy setup screen.
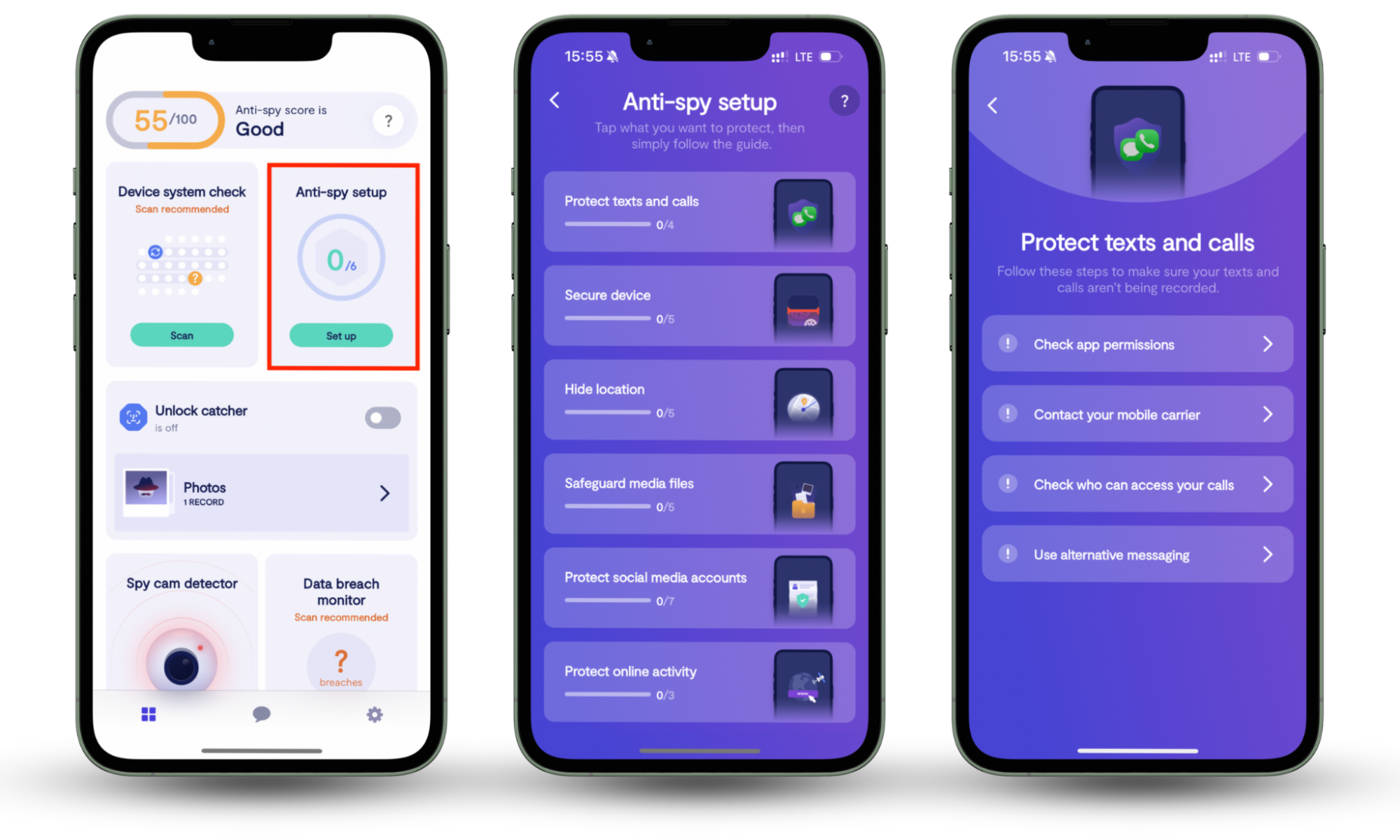
Clario Anti Spy also includes a Spy cam detector, which scans for suspicious devices connected to your Wi-Fi. This is another way that can help clue you in if your network is hacked. Tap Scan under Spy cam detector to initiate a scan.
If you're ever unsure, you can tap the Messages icon to access live tech support. A Clario agent who recently helped a customer search for suspicious devices had this to say:
"A client contacted us feeling uneasy because he suspected that something in his garage might be watching him, but didn’t know how to check for spying devices or secure his Wi-Fi network. We introduced him to the Spy Cam Detector feature, explaining how it works to scan for any devices connected to his Wi-Fi hotspot that could be secretly recording or transmitting data.
We took time to walk him through the scan results, helping him understand the difference between Trusted and Suspicious devices so he could easily identify potential threats. We also emphasized the importance of securing his Wi-Fi network to prevent unauthorized access and keep his data safe.
After using the feature, the client found a suspicious device connected to his network. Thanks to the guidance, he was able to remove the threat and felt much more confident about safeguarding his privacy and security going forward."
How to remove hackers from your network
If you suspect that your Wi-Fi network has been compromised by hackers, you should take immediate action to secure it and block Wi-Fi hackers.
The first step is to disconnect your router. Unplug the internet cable (and any cables connecting it to your devices) from the router to prevent the hacker from accessing your network.
Next, scan your devices for malware infections. Run your antivirus or antimalware software on all connected devices to remove any malware.
Finally, secure your devices and accounts. Change the passwords for your devices, online accounts, and services that were connected to the compromised network. Use strong, unique passwords and consider enabling two-factor authentication for added security.
In the meantime, use your cellular network to access the internet. If you’re wondering, “is 4G secure?”, yes—it’s usually more secure than a home Wi-Fi network.
How to fix your hacked router
You now know how to check if your Wi-Fi is hacked. But what can you do to fix it? That involves several important steps.
Start by disconnecting your router from the internet. Then perform a hard reset and change the admin and Wi-Fi passwords. Finally, check for and install the latest firmware updates to patch any security vulnerabilities.
Let's check out what to do if your wifi is hacked in more detail.
1. Disconnect router from internet
If you suspect your router has been hacked, your first move should be to disconnect it from the internet. This instantly cuts off the hacker's access and stops any active attacks. Simply unplug the Ethernet cable or switch off your modem.
While offline, jot down any unusual behavior you notice. This could be unknown devices, strange redirects, or login problems. Acting fast helps protect your data and makes it easier to troubleshoot the issue later.
2. Perform a hard reset
After disconnecting the router, the next step is to perform a hard reset. This restores the device to its factory defaults and wipes out any malicious changes a hacker may have made.
Find the reset button, which is usually a small recessed hole on the back, and press it with a paperclip. Hold it for about 10-15 seconds until the lights flash.
This clears out unauthorized settings and gives you a clean slate to rebuild your network security.
Note
Contact your ISP if your router fails to connect to the internet after a hard reset.
3. Change your account's password
Once the reset is complete, log into your router's admin panel and change the default login credentials immediately. Many people leave these settings untouched, making it easy for hackers to slip in.
Here's how to change your router's admin password:
- Log into your router's admin panel.
- Look for a Password option—it should be listed under a section like Security or Maintenance.
- Enter the new password and select Save.
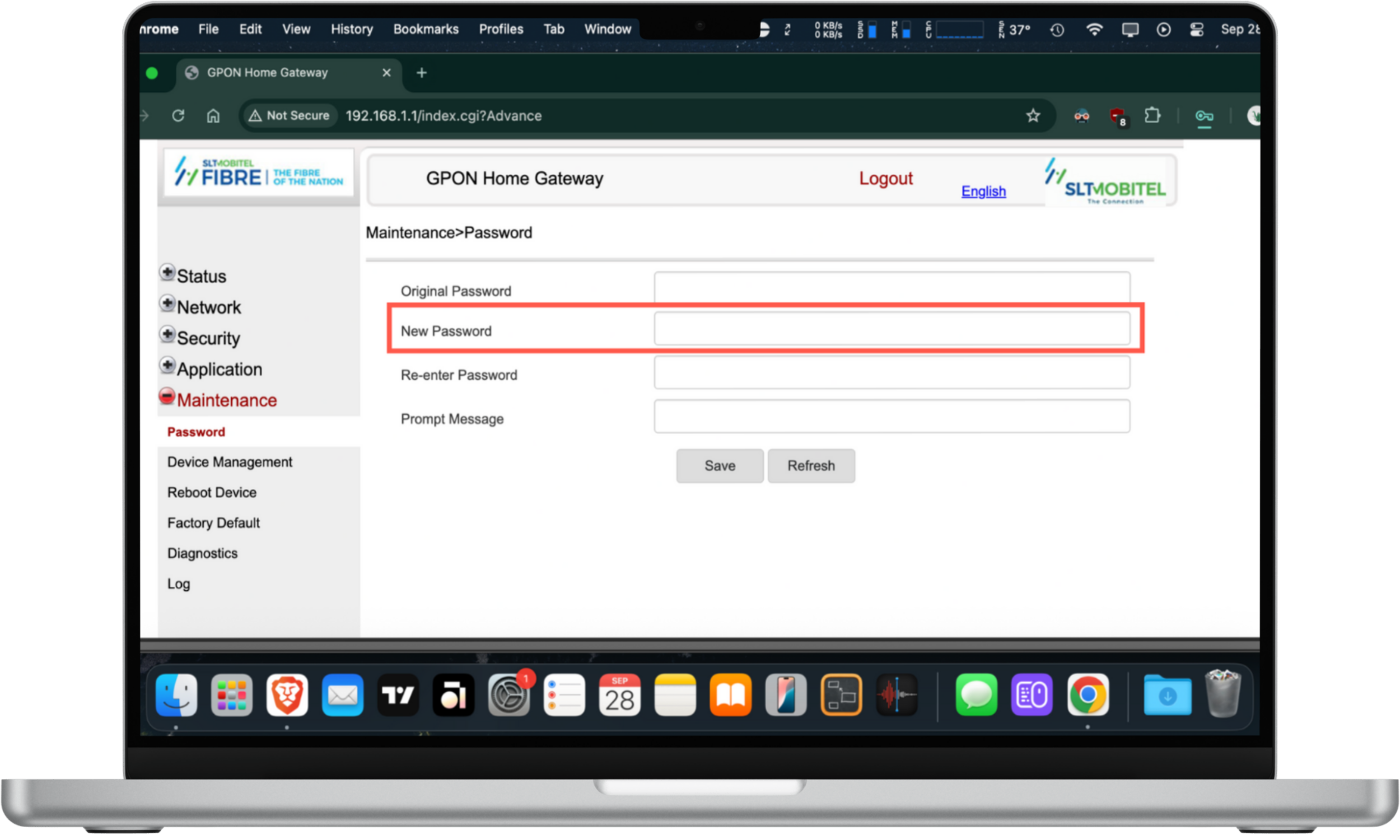
Set a strong, unique password using a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Don't forget to update your Wi-Fi password too, ensuring unwanted devices are kicked off and can't reconnect.
4. Update the router's firmware
After securing your router, make sure it's running the latest firmware. Outdated software often has security flaws that hackers can exploit. Keeping the firmware up-to-date patches any security vulnerabilities and strengthens your router's defenses against future attacks.
Check your router's admin panel or manufacturer's website for updates, then install them right away.
How to secure Wi-Fi router
Once you’ve fixed your router and removed the hackers, the next step is securing your network. That means enabling strong encryption, disable risky features like remote access, and scheduling routing reboots. The steps below walk you through how to secure Wi-Fi in detail.
1. Regularly update the firmware
Keeping your router's firmware up to date is one of the simplest ways to protect against hackers. Updates patch known security flaws that attackers might exploit.
If you're worried your Wi-Fi might be compromised, the first thing to check is whether your router is running the latest firmware. That's because many breaches happen on outdated devices.
2. Change default admin credentials
Default usernames and passwords are widely shared online, making them an easy target for hackers. Changing them to something strong and unique prevents anyone from logging into your router using generic credentials.
3. Enable strong encryption
Make sure your router is using WPA2 or WPA3 encryption. Older protocols like WEP are outdated and can be cracked in minutes. With strong encryption, hackers can't easily intercept your traffic or steal sensitive data while you're online.
Here's how to check your router's encryption level:
- Log into your router's admin panel.
- Navigate to the Security section.
- Look around for an option like Encryption Mode and make sure it's set to WPA2 or WPA3.
4. Use a firewall
A firewall acts as a shield between your devices and the internet. It filters out suspicious traffic and blocks many common hacking attempts before they reach your network.
Most modern routers come with a basic built-in firewall, so visit the router admin page and make sure it's active.
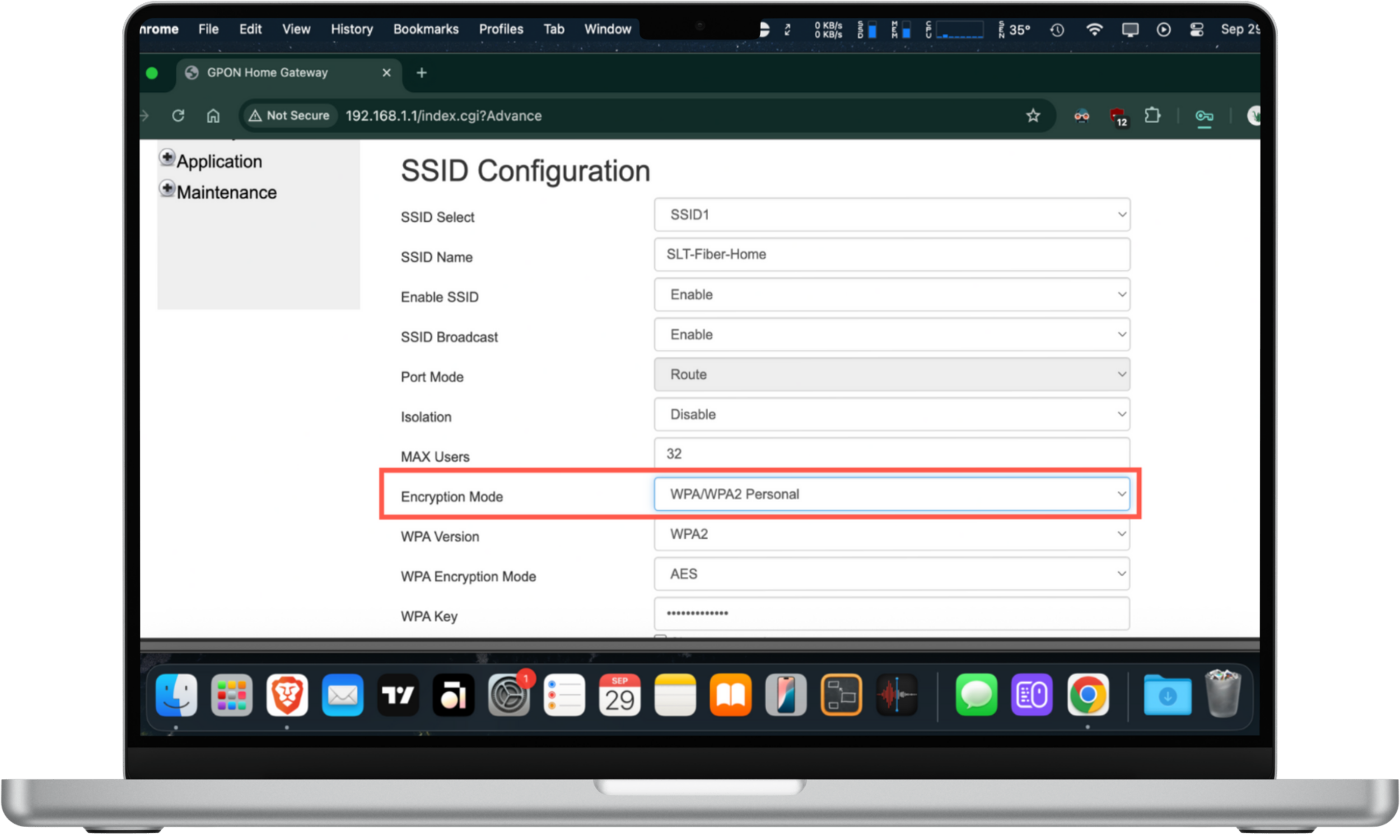
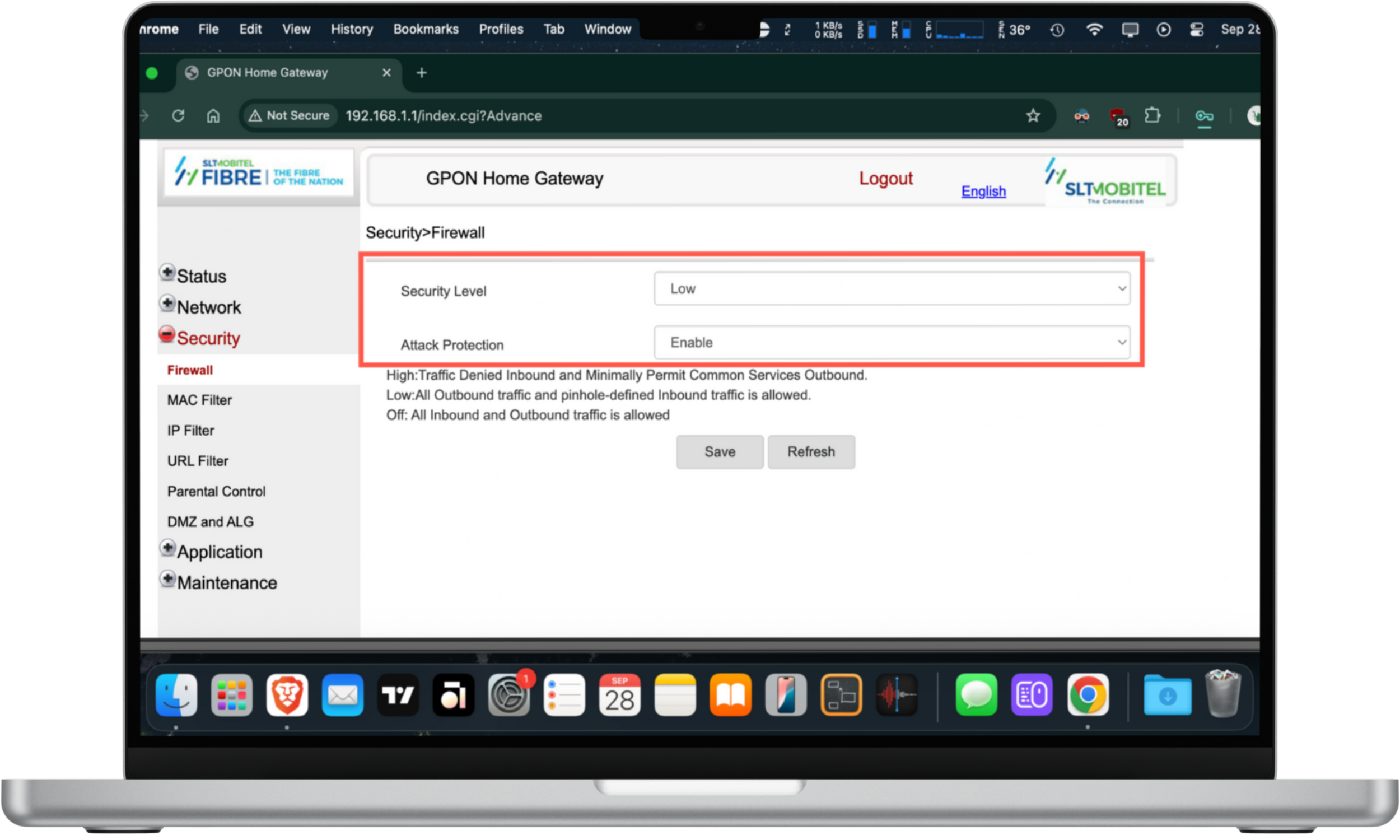
Here's how to check your router's firewall settings:
- Log into your router's admin panel.
- Look around for a Firewall option.
- Check if the firewall is active and any important security features listed within—like Attack Protection—are enabled.
5. Create a guest network
If visitors use your Wi-Fi, set up a separate guest network if your router allows you to. This keeps your main devices isolated and secure, even if a guest's phone or laptop is carrying malware. It's a simple way to share your connection without putting your personal data at risk.
6. Schedule routine reboots
Hackers often depend on keeping long-running sessions active. By rebooting your router on a regular schedule, say once a week, you can disrupt those connections and lower the risk of intrusion.
7. Disable remote access
Turn off your router's remote management feature via the admin panel unless you really need it. Leaving it enabled gives attackers a way to log in from outside your home network. By disabling remote access, only devices connected to your Wi-Fi can reach the admin panel.
Note
If you use an ISP-issued router, you may not have seen an option to disable remote access on the admin panel. Your best option in this case is to contact your ISP.
8. Create a unique SSID
Don't leave your Wi-Fi name on the default. Instead, set a unique SSID that doesn't reveal your router brand or model. This makes it harder for hackers to know which exploits might work against your network.
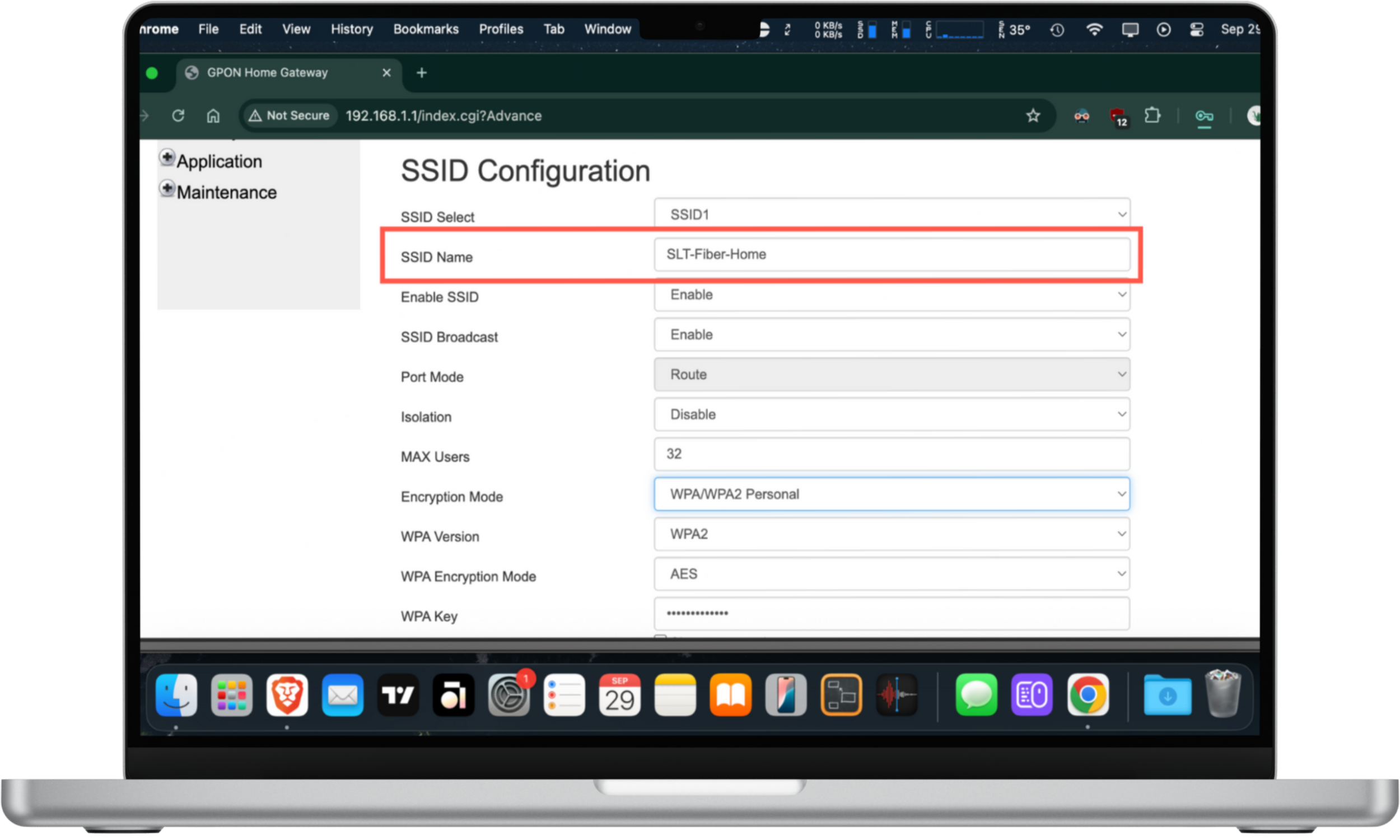
Here's how to create a unique SSID:
- Log into your router's admin panel.
- Locate the SSID Configuration settings.
- Replace the exciting SSID Name with something unique and select Save.
9. Turn off WPS
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) might seem convenient, but it's notoriously insecure. Hackers can easily crack WPS PINs, giving them full access to your Wi-Fi. For long-term protection, it's best to keep WPS turned off.
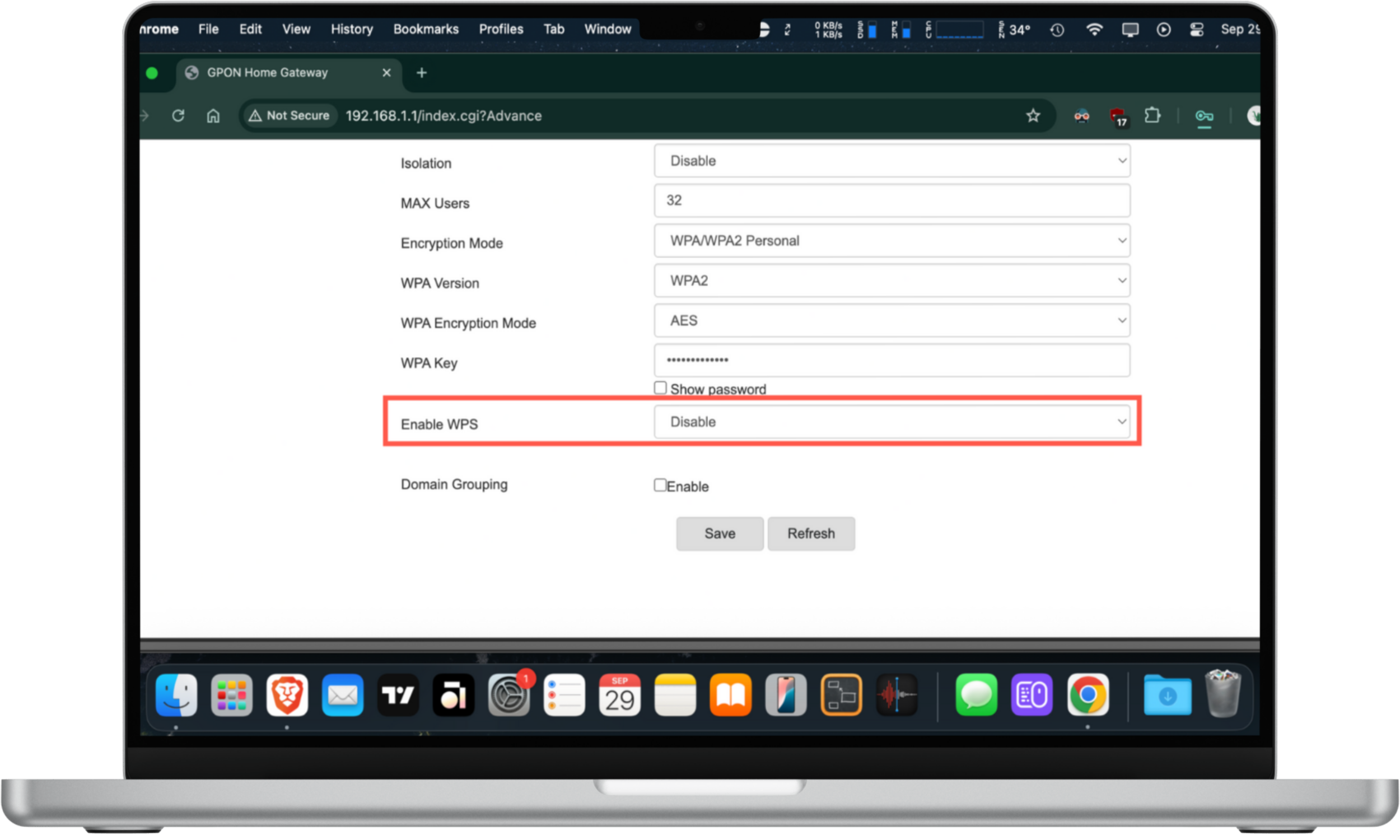
Here's how to turn off WPS:
- Log into your router's admin panel.
- Go to SSID Configuration.
- Set Enable WPS to Disable.
10. Install a VPN
A VPN (virtual private network) encrypts your internet traffic, making it unreadable to hackers even if they've hijacked your router.
VPNs are especially useful on public Wi-Fi, but they also add an extra layer of protection at home by shielding your data from prying eyes.
11. Avoid suspicious links and attachments
Hackers often break into routers by first compromising a connected device. To reduce the risk, don't click on suspicious links, download unknown attachments, or install untrusted apps. Safe browsing habits go a long way in keeping your devices and your Wi-Fi secure.
12. Download antivirus software
Protect every desktop device on your network with reputable antivirus software. These programs can detect and remove malware if your Wi-Fi has already been hacked, while also acting as a safety net against future threats. Choose a solution that offers real-time protection and automatic updates to stay secure.
On mobile, a cybersecurity solution with 24/7 live tech support like Clario Anti Spy is the best way to protect your phone and online accounts.
Conclusion
The last thing you want is for a hacker to gain access to your router and hold your network for ransom. To protect your network from hackers, make sure your router settings are secure, use unique passwords, and be on the lookout for suspicious activity.
And don’t forget—Clario Anti Spy features like the Anti-spy setup can help secure your devices and prevent cybercriminals from spying on your online activity.


