Table of contents
- How does Bluetooth get hacked
- 1. Bluejacking
- 2. Bluesnarfing
- 3. Bluebugging
- 4. Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks
- 5. Bluesmacking
- 6. Bluetooth spoofing
- 7. Blueborne
- 8. Car whispering
- How to know if your Bluetooth is hacked
- 1. Unfamiliar paired devices
- 2. Unexpected battery drain
- 3. Unexpected or strange notifications
- 4. Increased mobile data usage
- 5. Unrecognized apps
- 6. Slow performance
- 7. Strange interference during calls
- 8. High battery temperature
- 9. Bluetooth settings changes
- How to protect yourself from Bluetooth hacking
- 1. Turn off Bluetooth when not in use
- 2. Avoid sharing or sending sensitive information via Bluetooth
- 3. Keep your operating system and software up to date
- 4. Don’t pair Bluetooth in public places
- 5. Turn off Bluetooth for specific apps
- 6. Delete unused or old Bluetooth connections
- 7. Decline all unknown Bluetooth pairing requests
- 8. Be careful with Bluetooth accessories
- 9. Update your devices
- 10. Use antivirus software
- Conclusion
How does Bluetooth get hacked
Bluetooth hacking usually happens when attackers take advantage of weak security, outdated software, or unsafe pairing methods. Some attacks are harmless and only send spam messages. However, someone can spy through Bluetooth, steal personal data, or even take control of a device using more advanced methods. Using Bluetooth in public places, keeping old phones or devices, or connecting to unknown accessories increases the risk.
1. Bluejacking
Bluejacking is when someone sends unsolicited messages to nearby devices using Bluetooth. It doesn't steal data or infect your phone, but scammers sometimes use it for phishing. This could be fake "security alerts" or promotional messages in places like malls, airports, or trains. Devices with Bluetooth set to discoverable are the easiest targets. It's mostly annoying rather than dangerous, but it can still be a privacy concern.
2. Bluesnarfing
What is Bluesnarfing? It's another Bluetooth-based attack method that quietly steals data like contacts, messages, photos, and sometimes calendar entries. It mostly affects older phones, outdated Android devices, and unpatched laptops with known security flaws. Attackers use specialized tools, often in public places, to access vulnerable devices. Because the attack happens silently, most victims don't notice anything unusual at all.
3. Bluebugging
Bluebugging is a serious form of Bluetooth hacking that gives bad actors remote control over a device. It lets them listen to phone calls, read and send text messages, access contacts, and even view calendar events. This happens when a device has security vulnerabilities or the user unknowingly approves a malicious connection.
4. Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks
In a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack, a hacker secretly intercepts the Bluetooth connection between two devices—e.g., your phone and wireless earbuds. This lets them listen in, steal data, or even alter what's being sent. These attacks usually occur during pairing in public places.
5. Bluesmacking
Bluesmacking is a Bluetooth-based denial-of-service (DoS) attack. Instead of stealing data, it floods a device with connection requests or data packets until the software freezes, crashes, or restarts. This can temporarily make phones, laptops, and even smart home devices unusable. It's more disruptive than dangerous, but it can still be a frustrating experience.
6. Bluetooth spoofing
Bluetooth spoofing is when attackers create fake devices that look legit, like "AirPods" or "Car Audio." If you connect to one, they may be able to steal data, track your device, or try to push harmful content. Smartphones and laptops are the most common targets, especially in public places where people are more likely to connect quickly without double-checking.
7. Blueborne
Blueborne is a serious Bluetooth vulnerability that surfaced in 2017. It didn't require any pairing at all, and attackers could exploit it as long as Bluetooth was enabled. The flaw affected Android phones, iPhones, PCs, and even smart TVs. At the time, millions of devices were at risk, and this pushed a lot of companies to release emergency security patches. This is a huge reason why keeping your devices up-to-date really matters.
8. Car whispering
Car whispering targets older Bluetooth-enabled car systems with weak security. Attackers can inject audio into the car's speakers and listen in through the built-in microphone. This was first demonstrated in 2005 as a proof of concept and works by scanning for vulnerable systems and connecting without proper authentication. Newer vehicles are much more secure, but older models can still be at risk.
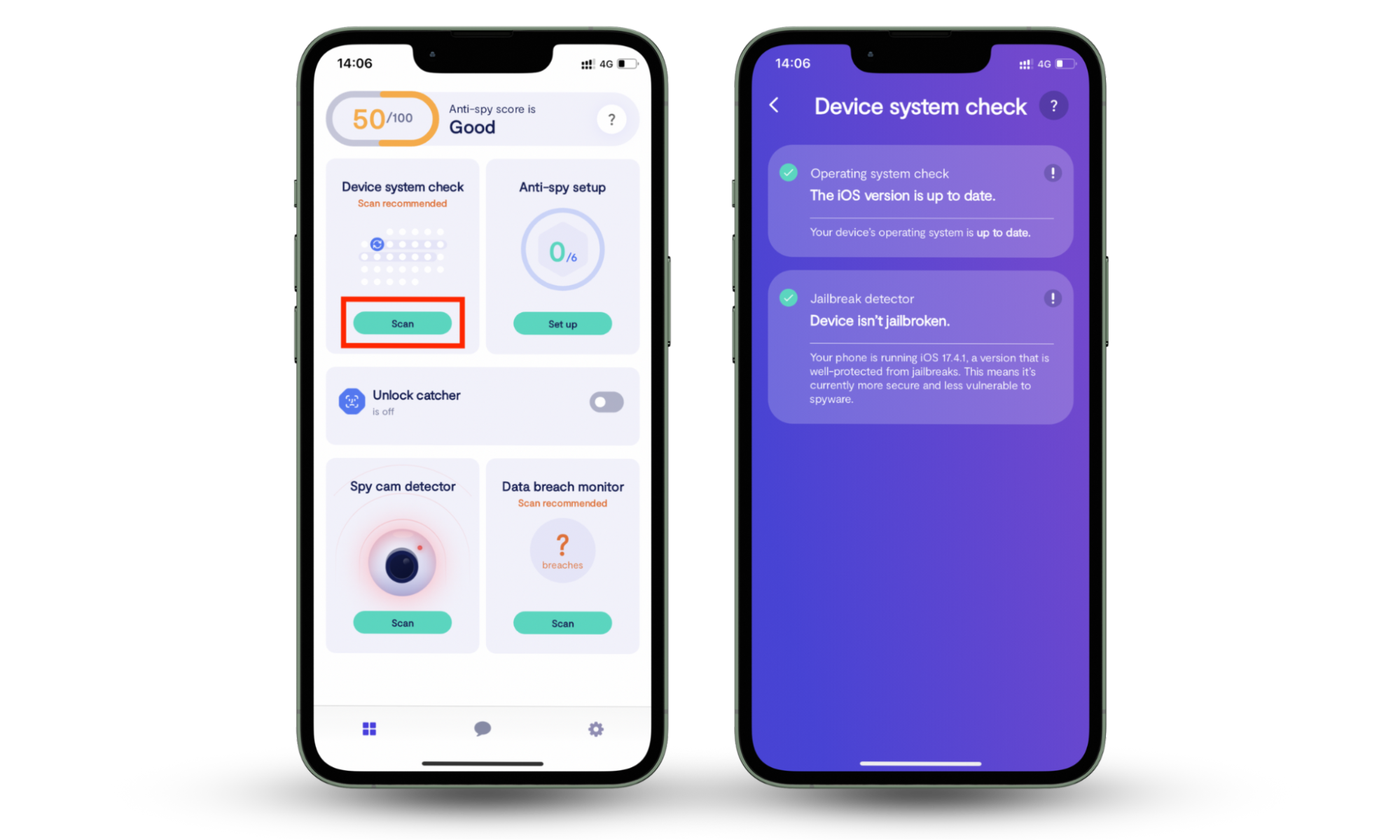
On mobile devices, Bluetooth attacks are easy to avoid as long as you keep your system software up to date. Clario Anti Spy helps with this by running a quick Device system check to make sure your phone has the latest updates. It also makes sure the device isn't jailbroken or rooted and that the device isn't wide open to spyware and hacking.
Here's how to run a Device system check with Clario Anti Spy:
- Download Clario Anti Spy and subscribe to create an account.
- Tap Scan under Device system check.
- Wait for the scan to finish and follow the on-screen steps to fix any issues.
Clario Anti Spy also offers 24/7 live tech support if you ever need extra help. Just tap the Messages icon to chat with a Clario expert.
One customer reached out after noticing unusual behavior on their phone and worrying it might be hacked. Here's what the expert who helped them had to say:
"The client contacted us with concerns that a potentially malicious application may have been installed on his phone, citing unusual behavior and performance issues that raised suspicions of unauthorized surveillance. Seeking reassurance that no spyware or harmful software was operating in the background, the client requested our assistance in verifying the integrity of his device.
As a first step, we recommended running a comprehensive scan using the Device System Check feature to assess the phone's overall security status. Once the scan results indicated that the device was most likely secure, we proceeded to a more in-depth review, examining all installed applications and their associated permissions, and scanning for any hidden or unauthorized apps that might be operating covertly.
Additionally, we advised the client to restart the device and ensure that all available system updates were installed, as keeping the operating system up to date is a key factor in maintaining device security and performance.
After implementing our recommendations, the client reported a noticeable improvement in the phone’s responsiveness and functionality, and expressed relief and satisfaction upon confirming that no malicious software capable of spying was present on the device."
How to know if your Bluetooth is hacked
You can know if Bluetooth is hacked by checking for common warning signs associated with spying and hacking. These include unknown paired devices, sudden battery drain, strange notifications, and unusually high data usage. Because Bluetooth attacks happen quietly, it's a good idea to regularly check your Bluetooth settings and watch for any unusual device behavior.
1. Unfamiliar paired devices
If you see random phones, headsets, or car systems in your Bluetooth settings, it could mean an unsafe connection. There's a chance you were targeted by Bluetooth spoofing. Since it's best not to take any chances, make sure to unpair any devices you don't recognize.
2. Unexpected battery drain
Some Bluetooth-based threats can stay active in the background, constantly searching for connections or sending data. This uses extra power, even when you're not actively using Bluetooth. If your battery is draining much faster than usual, especially on your phone or wireless accessories, it could be a warning sign.
3. Unexpected or strange notifications
Random pairing requests, message alerts you didn't send, or Bluetooth pop-ups you didn't trigger are all red flags. These usually happen when someone nearby is trying to connect to your device or imitate a trusted accessory.
4. Increased mobile data usage
Some Bluetooth-related threats use the internet to continuously upload your personal information. If your mobile data usage suddenly spikes for no clear reason, it could be a sign that a malicious app or background process is sending data from your phone.
5. Unrecognized apps
If you notice apps you don't remember installing, such as ones with access to Bluetooth, your microphone, or files, your device could be compromised. Some forms of spyware appear as system tools or utility apps to avoid being noticed, so it's a good idea to closely monitor your app list regularly.
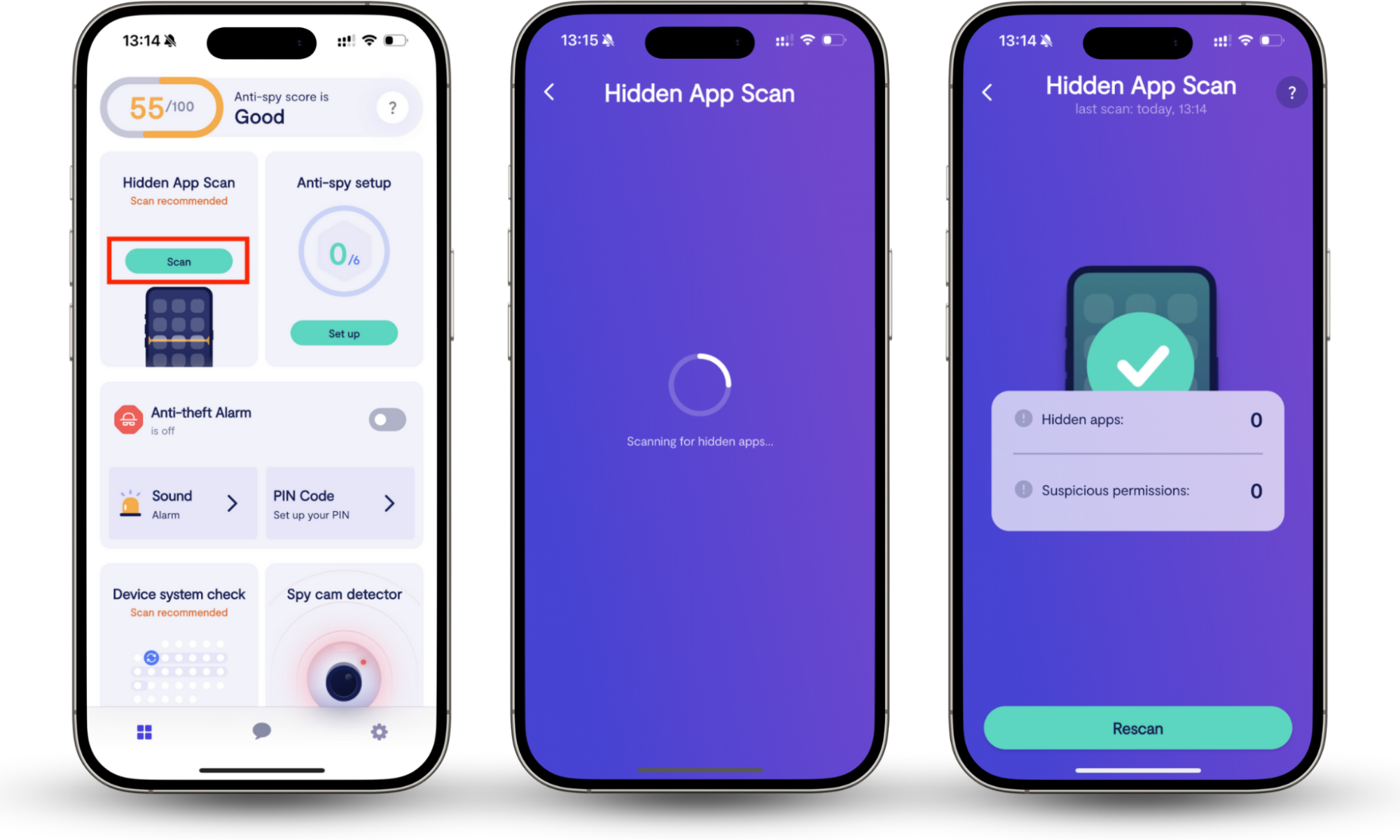
Clario Anti Spy can help you here as well. Its Hidden app scan feature makes it easy to quickly scan your Android or iPhone for hidden apps and spyware.
Here's how to run a Hidden app scan with Clario Anti Spy:
- Open Clario Anti Spy and tap Scan under Hidden app scan.
- Wait for the scan to finish.
- Review the results and remove any apps you don't recognize.
6. Slow performance
If your device starts lagging, freezing, crashing, or overheating, it could be a sign that hidden processes are running in the background. Some Bluetooth-based malware uses up memory and processing power, making your phone or laptop feel slow or unstable.
7. Strange interference during calls
If you hear static, echo, dropped audio, or sudden call interruptions, it could be a sign that your Bluetooth connection is being interfered with. This is more likely to happen with wireless headsets, car systems, or Bluetooth calling features on smartphones.
8. High battery temperature
If your phone feels hot even when you're not using it, background Bluetooth activity could be the reason. Constant scanning, data transfers, or unauthorized connections can put extra strain on your battery and processor, making the device heat up more than usual.
9. Bluetooth settings changes
Another way to know if Bluetooth is hacked is to check for automatic settings changes. For instance, if your device becomes "discoverable" without your input, or your pairing settings suddenly change, it's a strong warning sign. Some forms of spyware can hijack these settings to allow outside devices to connect to yours without you noticing
How to protect yourself from Bluetooth hacking
There are several ways to protect yourself from Bluetooth hacking. These include turning off Bluetooth when you're not using it, keeping your device updated, and only connecting to trusted accessories to reduce the risk of wireless attacks.
1. Turn off Bluetooth when not in use
Leaving Bluetooth on all the time makes your device visible to nearby attackers. Turning it off when you're not using headphones, speakers, or your car system helps reduce your exposure. However, you don't need to always do this. For example, on both Android and iOS, your phone only becomes discoverable while the Bluetooth settings screen is open.
Good to know
Can a phone be hacked if it is turned off? No. Turning your phone off cuts power to all parts of the device, including Bluetooth. This closes off all attack routes, but it's something you'd only need to do if you have a strong reason to believe you're being targeted.
2. Avoid sharing or sending sensitive information via Bluetooth
Bluetooth isn't designed for secure data transfers, so it's best to avoid sending passwords, financial details, or personal files this way. Hackers can sometimes intercept Bluetooth connections, especially on older phones or devices that use outdated Bluetooth protocols.
3. Keep your operating system and software up to date
Security updates often fix Bluetooth vulnerabilities. When major flaws like BlueBorne were discovered, updates were the main way people stayed protected. Phones, laptops, smart TVs, and other smart devices all need regular updates to stay secure. Consider enabling automatic updates so your devices stay protected at all times.
4. Don’t pair Bluetooth in public places
Crowded places like airports, malls, and cafes make it easier for attackers to set up fake Bluetooth devices. It's safer to pair your devices in private, trusted environments so you don't accidentally connect to spoofed or malicious accessories.
5. Turn off Bluetooth for specific apps
Some apps ask for Bluetooth access even when they don't really need it. Limiting these permissions helps reduce the risk of background tracking or unauthorized connections. On both desktop and mobile devices, you can manage Bluetooth access for apps through your privacy settings.
6. Delete unused or old Bluetooth connections
Old or unused Bluetooth pairings can become security risks over time, especially if the devices are no longer in your control. Removing these connections helps reduce the chances of unauthorized access and keeps your Bluetooth list clean and secure.
7. Decline all unknown Bluetooth pairing requests
If a random device tries to connect, it's best to ignore it. Attackers often disguise their devices with names like "Headphones" or "Car Audio" to trick users into accepting the connection.
8. Be careful with Bluetooth accessories
Cheap or knockoff Bluetooth accessories may lack proper security. These devices usually don't receive regular updates (if they get any at all) and tend to use weaker protocols, making them more vulnerable to Bluetooth exploits. To stay safe, it's best to stick with trusted brands and buy from verified sellers whenever possible.
9. Update your devices
Firmware updates for earbuds, smartwatches, cars, and speakers are the best ways to fix Bluetooth security flaws. It's not just phones and computers that need updates—Bluetooth accessories can be vulnerable, too, so keeping everything up to date, wherever possible, helps reduce your risk.
10. Use antivirus software
A good antivirus app can help spot suspicious Bluetooth-based malware, hidden apps, and unauthorized activity. This adds an extra layer of protection, especially on laptops and Android devices. An anti-spyware tool like Clario Anti Spy can also help keep your phone up to date and free from spyware.
If you'd like more ways to stay safe, check out our guide on how to secure Bluetooth.
Conclusion
Bluetooth hacking is rare, but it can happen. The good news is that it's also easy to prevent. Most attacks succeed because of habits like leaving Bluetooth on, using outdated software, or pairing in public places. By staying alert, checking your settings, and following a few basic safety steps, you can use Bluetooth without putting your privacy at risk. Knowing how to tell if your Bluetooth is hacked can also help you take safety precautions early.
On Android and iPhone, you can install Clario Anti Spy and run a Device system check to make sure your system software is fully up to date with the latest security patches.


