What Is Spoofing? Definition, Types, and Security Tips
Table of contents
- What is a spoofing attack?
- How does spoofing work?
- Types of spoofing
- Domain spoofing
- Email spoofing
- Website spoofing
- IP address spoofing
- SMS number spoofing
- Caller ID spoofing
- GPS spoofing and GNSS spoofing
- MAC spoofing
- ARP spoofing
- How to detect spoofing?
- How to prevent spoofing?
Spoofing is a type of cybercrime committed through the use of false identities.
By pretending to be a trustworthy individual or company, cybercriminals gain a victim’s confidence to either steal their data or access their device.
Recent years have seen a significant rise in spoofing. In 2020 alone, thousands of people were targeted by personalized spoofing attacks.
Pro tip: What will be the next email in your inbox? A legit message or a spoofing attempt? Why not get Clario so there’s no need to guess? The security solution features 24/7 data breach monitoring, powerful antivirus and real-time anti-phishing protection — all you need to begin securing your digital life.
With countless people falling victim to cybercrime, you need to learn what spoofing is and how to protect yourself from it. Our article is a great place to start. Read it in its entirety or jump straight to the most relevant section:
- What is a spoofing attack?
- How does spoofing work?
- What are the types of spoofing?
- How to detect spoofing?
- How to prevent spoofing?
What is a spoofing attack?
Spoofing is a cyberattack aimed at tricking a victim into revealing sensitive information or allowing access to their device. To carry out the attack, cybercriminals impersonate an individual or a company their victim can trust.
To better understand what is a spoof, let’s look at one of its multiple types called a replay attack. When performing this highly coordinated attack, cybercriminals access the victim’s communication channels to intercept, delay or resend their messages. This type of spoofing most commonly occurs when people transfer money or share valuable information.
How does spoofing work?
Spoofing works by tricking a victim into revealing their own information or accepting false information as real. To this end, cybercriminals change their caller ID or email address. For some forms of spoofing, cybercriminals create copies of legit websites, hide their IPs and even broadcast fake GPS signals.
Clearly, in the vicious world of cybercrime, nothing is off limits. Let’s zoom in on the most common examples of spoofing to get a better picture of this cybersecurity threat.
Types of spoofing
There are different types of spoofing, each with its own method and target.
- Domain spoofing
- Email spoofing
- Website spoofing
- IP address spoofing
- SMS number spoofing
- Caller ID spoofing
- GPS spoofing and GNSS spoofing
- MAC spoofing
- ARP spoofing
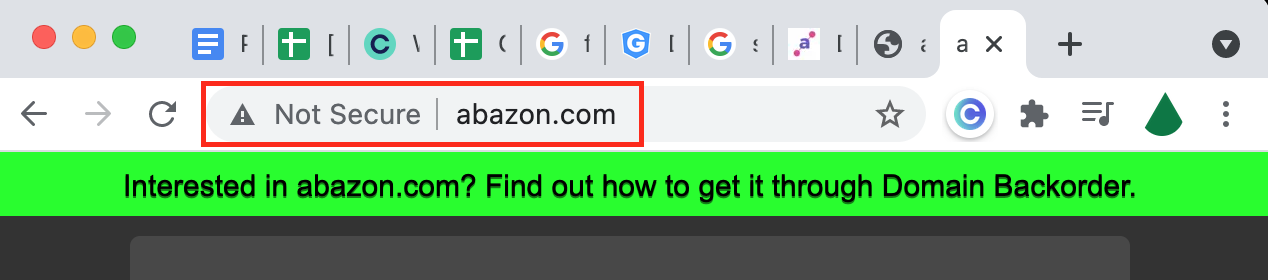
Domain spoofing
This type of spoofing involves the impersonation of a known website’s domain. Sadly, many organizations don’t even realize it is something to watch out for, let alone know when it happens. Though the rate of domain spoofing appears to be dropping, there is no guarantee that domain spoofing attacks will ever disappear.
So what happens when cybercriminals spoof a company’s domain? In this case, the company’s customers are fooled into submitting their personal information on a false website, thereby compromising their digital privacy and security.
Email spoofing
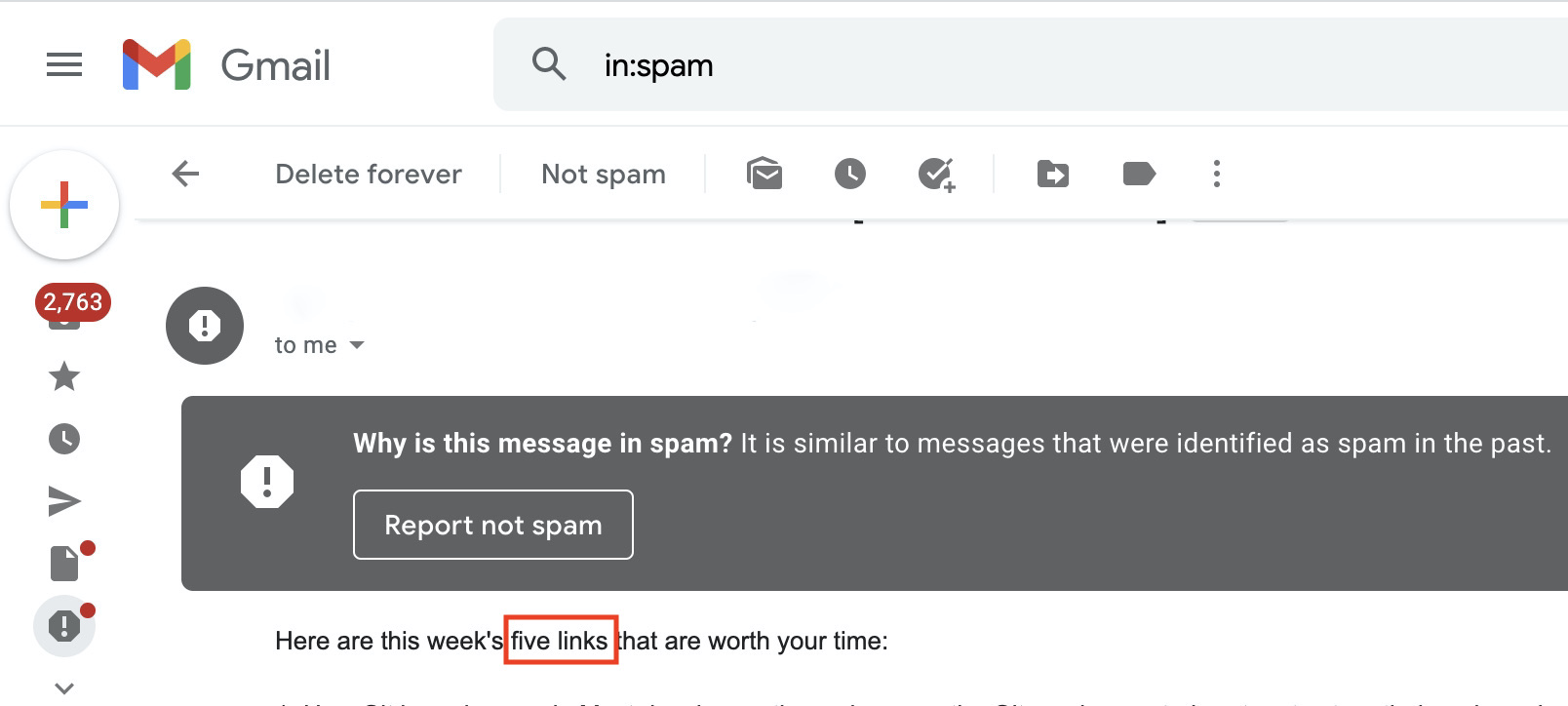
Email spoofing is the act of falsifying an email address. The purpose of email spoofing is to trick the recipient of a message into revealing valuable information.
Phishing is similar to email spoofing in its use of email. However, while the spoofing email senders usually impersonate a well-known brand or person, it’s not necessarily the case with phishing emails.
Website spoofing
Website spoofing refers to the crime of mimicking a well-known website to collect the personal information of its visitors. This cybercrime is usually combined with domain or DNS spoofing to create a false sense of security for website users.
After seeing a seemingly legitimate domain name, a victim clicks a spoofed URL without any concerns. Once on the website, they enter their login details or financial information into the fake submission forms, allowing cybercriminals to later misuse them.

IP address spoofing
IP spoofing or IP address spoofing is the creation or modification of Internet Protocol (IP) packets to hide the digital identity of cybercriminals. It is regularly used when launching DDOS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks to undermine a hosting server. The targeted server, and websites it hosts, slow down, as they are unable to handle a traffic spike.
Learn more about IP address spoofing to reduce your exposure to this cyber threat. And the best way to start is by subscribing to our cybersecurity blog where we regularly cover the latest digital threats and effective methods of countering them.
SMS number spoofing
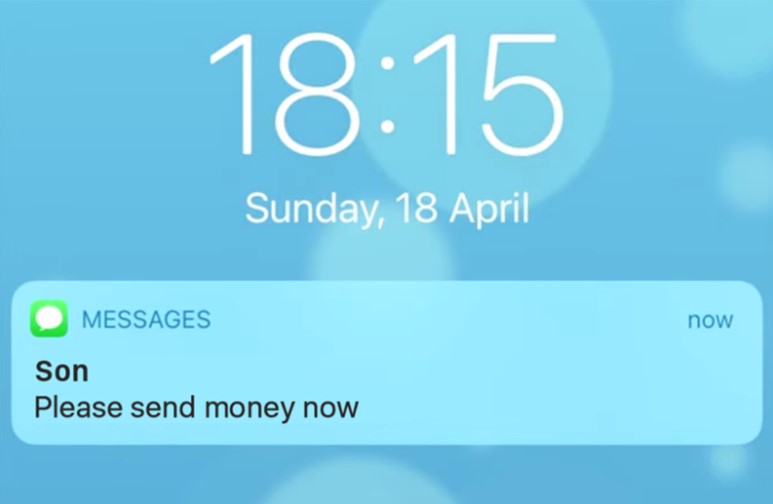
SMS spoofing is the imitation of a legit SMS number accompanied by a deceitful message. The targets of SMS number spoofing are usually the clients of well-known companies or brands.
Here’s an example of SMS spoofing: Your favorite clothing shop may send you a text message to let you know they’re having a sale! However, there’s more to SMS spoofing than meets the eye… or text, in this case. You may get a text from a scammer pretending to be a brand to get your private information or a friend or relative in trouble.
Due to the lack of awareness about SMS spoofing, cybercriminals can use it all the time without restraint. Be wary of any messages asking you for personal information or money.
To prevent SMS spoofing, refrain from giving your number to untrusted sources. You can also minimize the chances of malicious number spoofing by leaving your phone number off your social media accounts.
Caller ID spoofing
Caller ID spoofing is a criminal practice of masking a real phone number. A victim of caller ID spoofing mistakenly believes that the call originates from a trustworthy individual or company. This deceit offers cybercriminals plenty of opportunities to fish for their victim’s sensitive information or to trick them into doing whatever a spoofer wants, playing on their desires or fears.
The US Congress has passed the Truth in Caller ID Act, prohibiting malicious caller ID spoofing. Nevertheless, the crime is too profitable to disappear anytime soon.
GPS spoofing and GNSS spoofing
Is Global Positioning System (GPS) spoofing real? Is it really possible to trick GPS? Unfortunately, the answer is yes, especially if there is a radio transmitter nearby capable of interfering with legitimate GPS signals.
Apps relying heavily on location data are the most affected by GPS spoofing. This cybercrime can even have lethal consequences when targeting boats and planes, which cannot navigate without accurate GPS data.
GPS spoofing is closely linked to Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) spoofing, which also messes up the accurate time of systems. Though there are instances when the spoofing of GNSS signals is completely harmless (some use them to trick games like Pokemon Go!) there are legitimate reasons to be concerned about GNSS spoofing. For example, hackers and terrorists have been known to mess with the navigation of civilian vessels.
MAC spoofing
MAC spoofing doesn’t refer to the much-loved Apple device. Rather, it’s the spoofing of Media Access Control (MAC) or the identification numbers of devices.
Though there is a legitimate use of MAC spoofing in the context of privacy, the practice has become a cause of concern as it’s used to carry out cybercrime.
ARP spoofing
To conduct MAC spoofing, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) spoofing is required. ARP spoofing is the act of linking a MAC address with the IP address of another user.
Unfortunately, people cannot willingly opt out of ARP spoofing. If a hacker decides to link with your IP address, there’s nothing you can do about it.
How to detect spoofing?
To understand how to stop spoofing, you have to first learn the best methods to detect it. The following signs may indicate you are being spoofed:
Signs of email spoofing
- An email address is misspelled
- An email address doesn’t match a display name
- An email has an unusual request
- An email has grammar errors or typos
- An email features an embedded link with a suspicious domain
- An email has an attached file with an unfamiliar extension
Signs of website spoofing
- A misspelled URL
- Lack of a lock icon in the browser address bar
- HTTP URL in the browser address bar rather than a secure HTTPS URL
- A browser password manager does not recognize a website
- Logos, visuals, or fonts on a familiar website suddenly seem unusual
- Website content has poor spelling and grammar
Signs of caller ID spoofing
- An unknown phone number
- A request to press a number to stop getting calls
- A request to provide account login details, account PINs, Social Security numbers, or other sensitive information
- A caller sounds nervous or struggles to answer your questions
- A caller brings news or makes an offer that is too good to be true
- A caller demands an immediate action
How to prevent spoofing?
Follow these tips to stop spoofers in their tracks:
- Don’t give out your email to anyone outside your immediate social circle of trusted friends and family. Also, don’t post it on public forums or social media pages.
- Be wary of connecting to public networks. This may expose details about your identity or device.
- Don’t answer calls or emails from people or organizations you don’t know, especially if they’re soliciting money.
- Check email addresses every time you receive messages from a legitimate company. If it’s a new address, verify it on the company’s social media accounts.
- Double-check a website address before clicking a link. Sometimes, cybercriminals change one letter or symbol in the website address to make their spoofed website look legitimate.
- Avoid visiting websites without security features. Don’t trust any websites where the URL address starts with HTTP rather than HTTPS. Browsers like Google Chrome also warn you whenever you’re trying to enter an unsafe website.
- Partner with a trusted cybersecurity firm to secure your company’s devices and deflect the threat of spoofing.
- Always run a security scan on your devices to make sure you are protected from spoofing and other digital risks. To this end, use Clario — a comprehensive cybersecurity solution featuring real-time safe browsing, anti-malware, anti-phishing protection, and 24/7 data breach monitoring.
Read more:


