Table of contents
- What is a router in a computer network
- Difference between a router and a modem
- Differences between a wired and wireless router
- Routers and security
- Change default passwords
- Turn on Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
- Set up a guest Wi-Fi network
- Update the router’s firmware regularly
- Use a reliable VPN
- Conclusion
What is a router in a computer network
Before we go into the details of how they work, let’s explain what they are with a simple router definition.
Router definition
A router in a computer network is a hardware device that acts as a communication gateway between two or more packet-switch networks or subnetworks within a local area network (LAN).
The router allows multiple devices to send and receive data packets within a LAN and from the devices to the internet.
A LAN is a group of connected devices within a small geographic location, like a residential home or a small commercial building—for example, a school.
Routers in networking coordinate data flow between connected devices on a network by assigning a unique local IP address to each device. During data exchange on a network, the assigned IP addresses allow the router to send each data packet to the designated receiving address quickly and efficiently. Similarly, when a host network sends data packets to external networks, the router uses IP routing to determine the designated external networks.
IP routing is a router function whereby a series of internet routers help forward data across multiple networks until it reaches the designated external network.
Difference between a router and a modem
People often use internet routers and modems interchangeably because of their similarities and perhaps because Internet Service Providers (ISPs) now provide 2-in-1 router/modem devices. However, modems and routers have different functions.
The modem, which stands for modulator and demodulator, is a device that converts computing and internet signals to the required formats. While the internet uses analog signals, computing devices like smartphones use digital signals, thus making it impossible for them to communicate directly. The modem is the technology that converts analog signals to digital signals and vice versa to enable smooth communication between connected devices and the internet.
You can connect multiple devices to a modem and use it without a router, but the connected devices will not form a LAN because it’s a router function. Without a modem, a router can only create a LAN that enables connected devices to transfer data between themselves without internet access. While routers enable multiple devices within a small geographic location to form a network, modems provide internet connection, hence why routers and modems are often used together.
Another router function that differentiates it from a modem is the layer in which it works. A router in networking works in the network layer, while modems work in the data link layer.
Differences between a wired and wireless router
According to our router definition, routers can create LANs in two different ways, which is why there are two main types of routers—wired and wireless.
A wired router uses cable ports to create a connection with the devices on its network, thus generating a LAN. Wired routers connect to modems through an Ethernet cable and distribute the internet connection from the modem to the connected devices on its network. Although wired routers are tagged old-school, they provide top internet speed because of the direct cable connection to each device.
A wireless router also connects to a modem through an Ethernet cable. However, instead of LANs, wireless routers create wireless local area networks (WLANs) and use an antenna to broadcast the internet connection to the devices on its network. Most modern routers and modems have built-in antennas and LAN ports, thus giving users multiple connection options.
Routers and security
In addition to seamless connectivity between devices, one of the reasons people install home routers is to enjoy browsing the internet with additional security against cyber threats. Internet routers often come with a built-in network-level firewall that acts as a barrier between the internet and the devices within its network. This enables routers to vet each incoming data packet from external networks to determine whether to forward them to the destination or block them.
That said, using a router with default settings doesn’t necessarily prevent hackers from hijacking the devices on the network and eavesdropping—or worse, infecting them with malware. Additionally, people often keep using their routers without updating the firmware regularly, thus exposing their network to cyber threats. Hence, it is vital that you learn how to secure your home network to ensure safe browsing with your Wi-Fi router.
Yes, public Wi-Fi connections are unsafe, but people have been asking for ages what is more secure, home Wi-Fi or cellular data? To hit the nail on the head, cellular data is more secure than home Wi-Fi. Although you can improve data encryption functionality in your home Wi-Fi, cellular data is still more secure because it automatically encrypts the data it sends to the internet.
Here are simple best practices to improve your router security:
- Change default passwords
- Turn on Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
- Set up a guest Wi-Fi network
- Update the router’s firmware regularly
- Use a reliable VPN
Change default passwords
Ensure to change all default passwords after installing your router. Hackers know the default passwords and admin credentials that routers and modem manufacturers provide, so it will be unwise not to change them. Use a complex, unique password or passphrase to protect your home network against brute-force attacks.
Turn on Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
Always turn on the WPA on your router. The WPA on routers is a security protocol that provides data encryption for wireless devices. There are currently three types, WPA, the widely used WPA2, and the more recent WPA3, which is compatible with Wi-FI 6.
Before the introduction of WPA3 in 2018, there has been an ongoing WPA vs. WPA2 debate. To clarify, the WPA2 is more secure than the classic WPA for many reasons, one of them being that it allows users to create longer passwords. While this feature allows users to create complex passwords that can’t be guessed easily, the WPA3 is more secure than the WPA2. However, regardless of the WPA type on your router, we recommend turning it on to enjoy more protection against hackers.
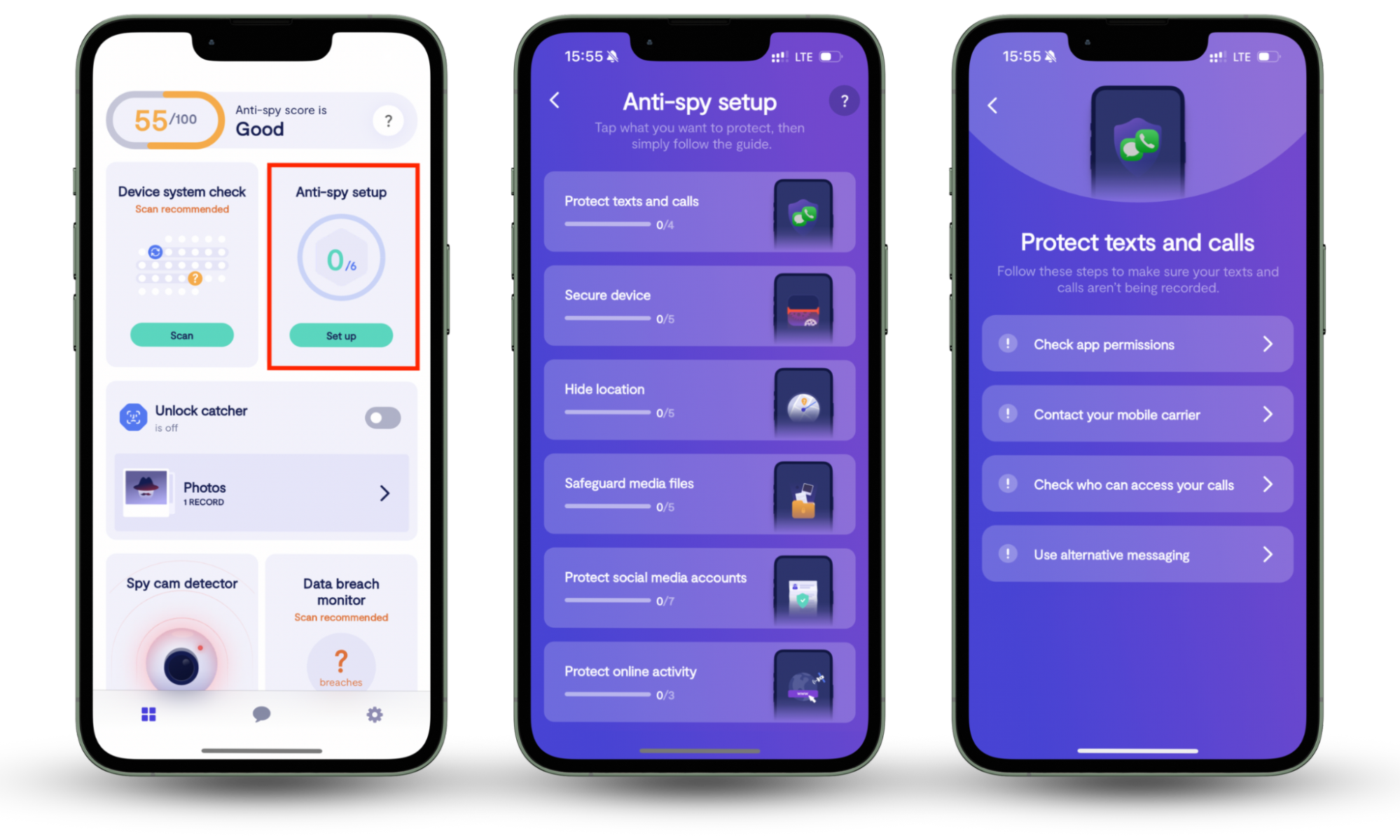
Router security is important, but so is device security. That's where Clario Anti Spy comes in. Developed by cybersecurity experts, this anti-spyware solution can check the integrity of your smartphone for jailbreaks, rooting, data breaches, and offline tampering. It also features an Anti-spy setup to guide you through the basics of protecting yourself against spying and stalking.
Here's how to run an Anti-spy setup in Clario Anti-Spy:
- Download Clario Anti Spy and subscribe to create an account.
- Tap Setup under Anti-spy setup.
- Tap on a category—such as Protect texts and calls—to improve your phone's security.
- Work through the remaining categories in the Anti-spy setup to enhance your device's overall protection.
- Tap the Messages icon at the bottom of the screen for 24/7 assistance if you encounter any issues.
Set up a guest Wi-Fi network
Instead of sharing your Wi-Fi password with visitors, set up a guest network. This reduces the risk of hackers breaking into the devices on your primary network and discovering sensitive information that can expose you to cyberattacks. We have written extensively about how to set up a guest Wi-Fi network including best practices for securing your guest network. Be sure to peruse it to learn lifesaving router security measures.
Update the router’s firmware regularly
Enable automatic firmware updates on your router to get the latest bug fixes and security patches as they are released. Now, if your router doesn’t have a feature for automatic firmware updates, check regularly and install new updates to fortify your network against security vulnerabilities.
Use a reliable VPN
Virtual private networks (VPNs) are particularly useful when connected to public Wi-Fi because of their vulnerabilities and threat actors lurking on these networks looking for victims. However, threat actors are also lurking in private networks with the intention of discovering and taking advantage of security loopholes. Use a VPN to hide your IP addresses, Wi-Fi activity, and browsing data across all connected devices.
Now, if you can avoid using public Wi-Fi connections entirely, do so. Otherwise, always use a reliable VPN to reduce security risks. What is the danger of using public Wi-Fi connections, you might ask? Some vulnerabilities you will be exposed to when using public Wi-Fi include identity theft, malware infection, data breach, and eavesdropping.
Once you have added an additional layer of protection to your home router, mobile phone, or laptop, you can be sure no cybercriminal will steal your valuable data by exploiting your IP address. However, if they really want to steal your ID or reach your personal data by installing a malicious file on your device, they can most definitely do it even if you are VPN-protected.
Conclusion
Cellular data is superb, and free public Wi-Fi connections are enticing, but personal home Wi-Fi will give you peace of mind. You can’t trade that, especially if you have a home office with a need to prioritize seamless interaction between devices like printers, PCs, phones, tablets, and more.
Practice the router security measures discussed in this article to protect your home network from threat actors. Since device-specific vulnerabilities can still play a factor, don't forget to install Clario Anti Spy to tighten the privacy and security of your iPhone or Android.


