Table of contents
- Is digital footprint real
- How does digital footprint work
- Examples of digital footprints
- Types of digital footprints
- 1. Active internet footprint
- 2. Passive online footprint
- What are consequences of digital footprint
- 1. Personal privacy and security
- 2. Reputation and social media presence
- 3. Impact on job prospects and online identity
- How to check digital footprint
- How to reduce your digital footprint
- Why is protecting your digital footprint important and how to do it
- Conclusion
Is digital footprint real
A digital footprint might sound fancy, but it's very real. Everything you do online—no matter how trivial it seems—is constantly monitored by web trackers, data analytics companies, and even your ISP (internet service provider). When combined, these records paint a detailed picture of your preferences and habits.
Internet footprints exist because of:
- Tracking technology: Technologies like browser cookies, web beacons, and pixel trackers collect data about the websites you visit, the ads you click, and the items you purchase.
- Metadata: The emails, messages, and photos you send contain hidden details like timestamps, location data, and device information.
- Data collection by platforms: Social media, search engines, and e-commerce sites gather personal information to deliver targeted ads and personalized experiences.
Common misconceptions about digital footprints include:
- Deleting something means it's gone forever: Deleted posts, messages, or accounts may still be stored on backup servers, cached by search engines, or archived by third parties (like the Wayback Machine).
- Private browsing ensures complete anonymity: Private browsing only prevents cookies from being stored locally on your device. Websites, ISPs, and tracking scripts can still collect your data.
- Trackers only target specific individuals: Companies and advertisers track nearly everyone to build profiles, target ads, and analyze behavioral patterns regardless of social status.
- Only major activities contribute to a digital footprint: Even small actions, such as liking a post or clicking a link, are logged and contribute to your online footprint.
- Using a VPN completely hides activity: VPNs improve privacy but don't prevent all tracking forms, especially by apps or services that collect information directly from their users.
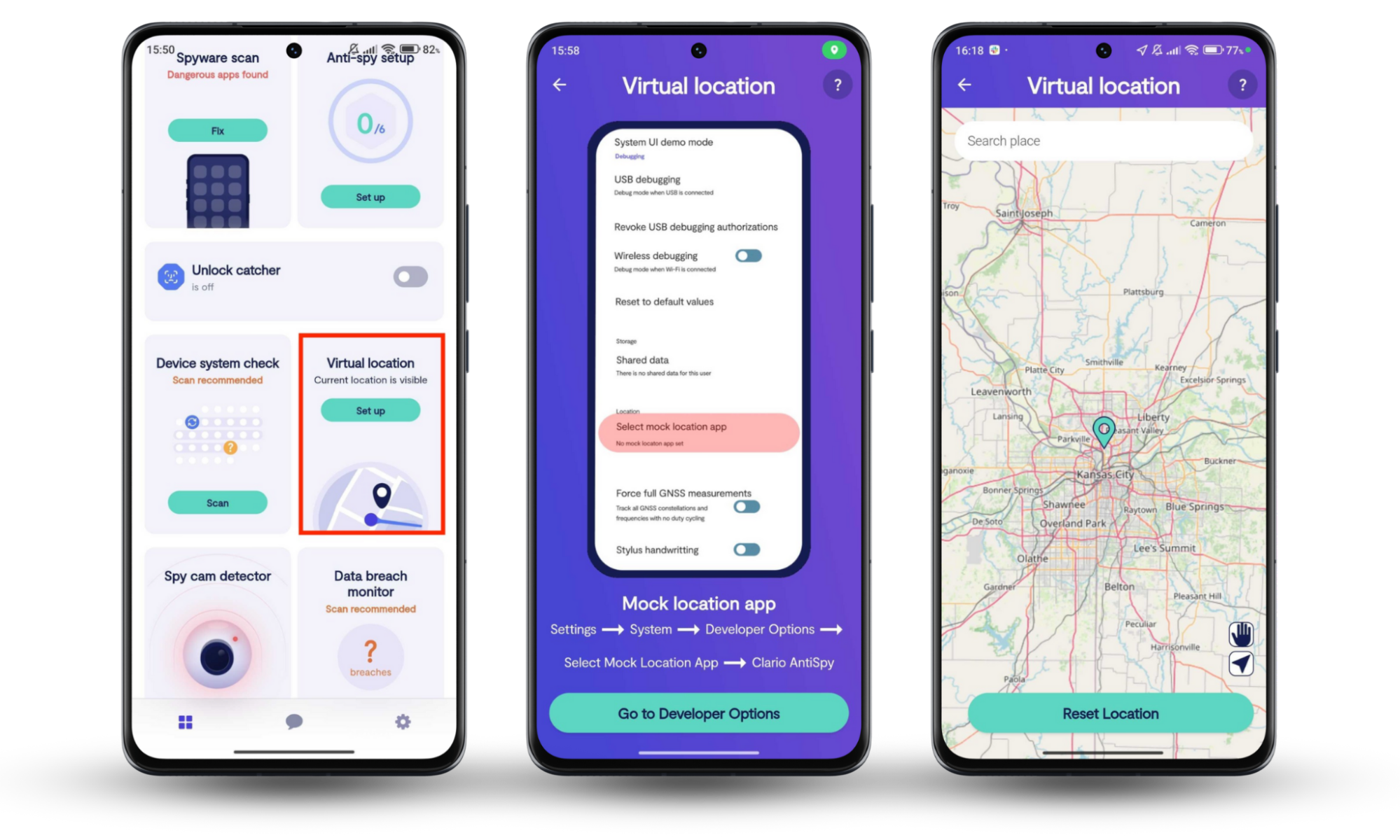
Clario Anti Spy is a robust anti-spyware solution designed by cybersecurity experts for mobile devices. In addition to checking your iPhone or Android for privacy risks like jailbreaks, it features an Anti-spy setup that guides you through the basics of protecting your device from spyware and stalking. On Android devices, it also offers the ability to hide your real location with a virtual one, which helps you cut down on your digital footprint.
Here's how to hide your location on Android with Clario Anti Spy:
- Download Clario Anti Spy and subscribe to create an account.
- Tap Set up under Virtual location.
- Follow the on-screen steps to hide your location.
- Tap Messages at the bottom of the screen to connect with a security expert if you need assistance.
How does digital footprint work
Your digital footprint is created through various data collection mechanisms—such as cookies, tracking pixels, and browser fingerprinting—and the metadata in emails, photos, and documents. Information you willingly submit online—e.g., on social media platforms—and the data you store on cloud servers also add to this online trail.
Data collection techniques used by websites include:
- Cookies: Small files downloaded to your device by websites. They remember your preferences, login status, and browsing activity—e.g., what you added to your shopping cart.
- Tracking pixels: Tiny images embedded in emails or webpages. They tell if you opened an email or clicked on a link.
- Browser fingerprinting: A method that collects information about your device, such as the browser type, system software version, and settings.
Metadata's role in your footprint includes:
- Emails: The time you sent each message, the routing information, and your IP address.
- Photos: The location you took your photos, their timestamps, and camera details.
- Documents: When your files were created and when they were modified.
Social media and search engines profile you based on:
- Interests: Your likes, follows, and clicks.
- Habits: How you perform searches, how long you engage with content, and when and where you buy stuff.
- Connections: How you interact with friends, followers, and groups.
All this information can be processed by data analytics companies to identify patterns and build detailed profiles about you. These profiles are then bought and sold by firms to influence your decisions online—e.g., through target ads, content recommendations, or other strategies. For more information, check our data protection vs data privacy guide.
Examples of digital footprints
Your online footprint is made up of both intentional and unintentional actions you take online. Examples include:
- Browsing and search histories: Websites you visit are recorded and can be tracked by third-party cookies, while search engines like Google keep records of your search queries.
- Social media activity: Posting updates, sharing photos, commenting, and liking posts on platforms like Facebook, X, or Instagram.
- Online shopping: Creating accounts on e-commerce sites, purchasing items, and leaving reviews.
- Blogging and content creation: Writing articles, uploading videos, or sharing music on platforms like Medium, YouTube, or SoundCloud.
- Online forms: Filling out surveys, registering for events, or signing up for newsletters.
- IP address tracking: Your IP address can reveal your approximate location and is logged by websites and services—learn the difference between public IP and private IP.
- Location data: With your permission (and sometimes not), apps and websites can have access to your physical location through GPS or Wi-Fi.
Types of digital footprints
There are two types of digital footprints—active internet footprint and passive online footprint.
1. Active internet footprint
Your active digital footprint is the data you knowingly share online. This could be the information you submit while creating accounts on apps and websites, your posts, comments, and likes on social media, reviews about the purchases you make, etc.
2. Passive online footprint
Your passive digital footprint is the trail of data that you leave just by interacting with the internet in general. Websites, apps, and services collect information like browsing history, search queries, and location data, usually through cookies and trackers. Metadata also adds to your passive footprint.
What are consequences of digital footprint
Your cyber footprint can reflect on you both positively and negatively. On the good side, it can bring personalized experiences, professional opportunities, and useful connections. But on the bad side, it can lead to risks like identity theft, privacy issues, or harm to your reputation.
1. Personal privacy and security
Your virtual footprint can lead to data breaches, identity theft, and phishing attacks. To protect yourself:
- Use privacy tools like VPNs, anti-spyware apps, and content-blocking extensions.
- Create strong, unique passwords for your accounts.
- Avoid oversharing sensitive information online.
- Tighten privacy settings on social media to limit data exposure.
2. Reputation and social media presence
Social media can be a double-edged sword. Old, embarrassing posts or comments might resurface and cause issues in your personal or professional life. However, using it thoughtfully can help you build a positive personal brand.
3. Impact on job prospects and online identity
Your digital footprint can make or break career opportunities. Unprofessional posts or comments could hurt your chances with potential employers, while a polished online presence—like a strong LinkedIn profile—can improve them.
How to check digital footprint
Ever wonder who is tracking you? Pretty much every website, social media platform, and app. Here's how to check your digital footprint:
- Search your name online: Use search engines like Google to check what's publicly visible. Just type in your name and review the results.
- Review your accounts: Audit your online accounts to see which ones are active. Use tools, such as BackgroundChecks.org, JustDeleteMe.xyz, or HaveIBeenPwned, to identify inactive, forgotten, or compromised accounts that might still hold your data.
- Review social media profiles: Review the privacy settings on your social media accounts. Ensure you understand who can view your posts and what information is publicly visible.
- Monitor with tools: Services like Google Alerts can notify you whenever your name, email address or other personal information appears online. This can help you stay updated about your online presence.
How to reduce your digital footprint
Our internet safety tips guide can help you reduce your digital footprint. Here's a quick summary:
- Delete unused accounts: Close old accounts that you no longer use. Again, tools like BackgroundChecks.org and JustDeleteMe.xyz can make the process faster.
- Limit social media sharing: Share only necessary information and adjust your privacy settings to minimize publicly visible data.
- Use private browsing: Your browser's private browsing mode reduces tracking by third-party cookies during sessions.
- Clear cookies and history: If you browse in normal mode, regularly delete cookies and browsing data to minimize tracking.
- Use a VPN: A VPN masks your IP address and prevents websites from pinpointing your location.
Why is protecting your digital footprint important and how to do it
Your digital footprint shapes your online identity. Neglecting to manage it can lead to risks like identity theft, data breaches, or even harm you professionally. Here's how to protect your digital footprint:
- Strengthen your privacy settings: Lock down your social media and online account to limit who can see your personal details.
- Practice mindful sharing: Think twice before posting or sharing sensitive information online.
- Clear your digital traces: Regularly delete cookies, browsing history, and unused accounts to reduce data exposure.
- Invest in privacy tools: Use a VPN to mask your IP address, and consider tools like Clario Anti Spy to hide your location on Android devices.
- Stay proactive: Keep up with the latest privacy tools and best practices for better control of your online presence—check our complete guide to protect your digital footprint for more information.
Your digital footprint has consequences
Your footprint on the internet can have serious repercussions if you fail to protect it. From identify theft and financial fraud to data breaches, there are countless horror stories about what happens when things go wrong.
Conclusion
You now understand what a digital footprint is and why managing it is so important. While it's impossible to control every aspect of your footprint online, taking actions like deleting unused accounts, tightening social media privacy settings, and being mindful of what you share can go a long way toward preserving your privacy. Installing Clario Anti Spy on your mobile devices and running an Anti-spy setup can also help address privacy and security issues you might otherwise overlook.


