Table of contents
- What is ransomware?
- How does ransomware work?
- Ransomware impact on businesses
- The most common types of ransomware
- Crypto ransomware
- Doxware
- Scareware
- Locker ransomware
- How to prevent a ransomware attack?
- Conclusion
Picture this. You just got an email from a mysterious sender with “Unable to deliver your package” or “New voicemail message from [your mom’s phone number]” in the subject line. You open it, and it says a courier was unable to deliver a parcel to you. Logically, this prompts you to click on the attachment to find out more and see what went wrong.
A ransomware virus often hides in attachments like this. If you open it, then it may cause you far more severe problems than an undelivered parcel.
Pro tip
You won’t need to deal with the consequences of a ransomware attack if you don’t allow it to happen. Clario Anti Spy has your back by checking links for safety and providing you with real-time protection from viruses. Download Clario Anti Spy now and stay safe whenever you need to surf the web.
In this article, we’ll touch upon the basics of ransomware, so you know what to do to prevent the attack.
What is ransomware?
Ransomware is malware that silently blocks victims from accessing their own data or locks them out of their devices.
According to recent reports, the number of ransomware attacks increased by 73% in the past year alone. In 2023, there were over 6,600 incidents globally, causing an estimated $1.1 billion in ransom payments.
An attacker holds the data hostage, threatening to expose or destroy it. The attackers’ main aim is to demand payment (or ransom) from a victim in exchange for unlocking their device or data. Not only can the ransomware perpetrators exhort hard-earned bitcoins from regular users like you and I, but they can stir up trouble at a national level too — like in the recent Colonial Pipeline attack.
What’s even worse, cybercriminals sometimes offer a specific window of time during which victims should pay the ransom. If they miss the deadline, the ransom can increase.
CryptoWall, Maze, and WannaCry are only a few ransomware names that you might have heard of that can infiltrate your device looking for vulnerabilities. Unfortunately, cyberattacks are neither new nor rare. The first ransomware virus, AIDS Trojan, was distributed on floppy disks more than 30 years ago. Back then, cyber actors were asking for a ransom of $189.
Now the techniques that cybercriminals use are much more advanced and can break down the barriers of even the most sophisticated defense systems. For instance, Cognizant, one of the largest Fortune 500 tech and consulting companies, was attacked by Maze ransomware in 2020. Reportedly, they lost between $50m and $70m in the immediate aftermath.
How does ransomware work?
Ransomware uses various ways to access your device, be it a computer or a smartphone. Its main aim is to infiltrate your network, encrypt your data, and extort a ransom from you. And, of course, to replicate itself and spread across the internet.
Let’s take a closer look at the steps this type of malware takes to attack your device.
- Stage 1. Infection.
Ransomware threats may be waiting for you at malicious or compromised websites or hiding behind malvertisements. The most frequent way ransomware gets into victims’ devices is by sending them phishing emails with malicious attachments.
- Stage 2. Security key exchange
Once you download it, malware establishes its presence on your device and encrypts the data it stores.
- Stage 3. Compromising a system
You think your device has just started lagging, but this could be an indicator that ransomware is taking control of your computer or phone. Apart from encrypting the data, it can also delete any backups or even look for Bitcoin wallets to steal.
- Stage 4. Extortion
This is the stage when ransomware reveals itself. The victim usually receives a note from attackers together with a payment request. But, in practice, attackers rarely deliver the decryption keys, even when a victim pays the ransom. Removing ransomware from Mac, Windows PC, smartphone, or any other device is never as easy as sending an attacker some money.
Pro tip
Businesses should implement a Zero Trust security model, which assumes no device or user is trustworthy until verified. This method minimizes the chances of ransomware spreading within an organization, even if one device is compromised. By verifying every access attempt, Zero Trust reduces the risk of lateral movement within a network, ensuring attackers don’t have free reign even after infiltrating one device.
Ransomware impact on businesses
Ransomware is not only a threat to individual users but also a major risk to businesses and organizations. In 2023, a large-scale attack on a healthcare provider resulted in data breaches, operational disruption, and a hefty financial loss of over $12 million. This attack led to a massive recovery effort that took over 6 months, showing the profound impact ransomware can have on business continuity and customer trust. Businesses that suffer from ransomware often experience a decline in reputation, loss of intellectual property, and sometimes irreparable damage to customer relations.
The most common types of ransomware
Ransomware covers several different types of malware. They all include a ransom that attackers demand from victims. Here’s a list of the most widespread ransomware that can threaten your device and put your data at risk.
Crypto ransomware
This type of ransomware is exceptionally savvy. First, it encrypts all valuable data such as your files, folders, and hard drives. Then, it reveals itself and demands a ransom to be paid within a specific time slot, usually 24 to 48 hours. Of course, paying the ransom won’t guarantee that your files will be decrypted.
Doxware
Also known as extortionware or leakware, dox ransomware not only encrypts your data but also steals it and sends copies back to the attacker. After that, it extorts victims by threatening to publicly expose their sensitive information. For businesses and organizations, a doxware attack could mean compromising their entire systems, including customer records, confidential files, or intellectual property. This can lead to financial, reputational, and legal problems.
Scareware
As the name implies, scareware itself doesn’t cause any harm. Instead, it sends alerts and pop-ups falsely claiming your computer is in danger. It usually behaves like antivirus software, notifying you that your files have been infected and tricks you into visiting malware-infested websites. When you do, you may be prompted to purchase software that is supposed to “fix” the so-called problem. But, like any other kind of ransomware, it will encrypt or steal your data instead.
Locker ransomware
Lockers shut down computers and mobile devices, allowing only limited access, so the victim can respond to the ransomware demands. But unlike other types of ransomware, it doesn’t encrypt the files and doesn’t fully infiltrate your device. So you can identify it and then remove it from your PC or smartphone without paying anything.
| Ransomware | Type encryption | Method impact | Example attacks |
| Crypto ransomware | Encrypts files/folders | Loss of access to important data | WannaCry, CryptoLocker |
| Doxware | Encrypts files + steals data | Leaks sensitive data publicly | Data leak via email threats |
| Scareware | Simulates a threat | Trick users into buying fake software | Fake antivirus software |
| Locker ransomware | Locks device without encryption | Limits access to device | SynAck ransomware |
How to prevent a ransomware attack?
Ransomware allows hackers to hijack your sensitive data and turn your life upside down.
Here are a few tips on preventing ransomware attacks to help you avoid falling into the hackers’ trap. Following our tips on how to avoid ransomware is only the first step in securing your digital life. You need to be vigilant to stay protected. But even the most cautious internet surfer can sometimes end up catching computer viruses or ransomware.
- Enable Multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all critical accounts. MFA adds an extra layer of security, making it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Regularly back up your data and store backups offline or in secure cloud storage. This ensures your data remains safe even if your system is compromised.
- Update your software to ensure any known vulnerabilities are patched. Keeping your software up to date reduces the chances of exploitation by ransomware
- Be Wary of phishing and verify any suspicious emails before opening attachments. Ransomware is often spread via phishing emails, so it's important to double-check the sender and message authenticity.
- Only install software from trusted resources. Ransomware file extensions often have the same format as regular files (.exe, .txt, or .zip). To be sure the software is safe, only download files from trusted websites and stores.
- Turn on your spam filter. Phishing emails are often disguised as notifications from a delivery service, e-commerce store, financial institution, or even a law enforcement agency. An effective spam filter can prevent about 99% of these emails from ever reaching your inbox.
- Secure your backups. Frequent and automatic backups are a must. But, today’s ransomware is wily enough to encrypt or delete them. The best option is to use backup systems that either do not allow direct access to the backup files or keep these files offline.
- Think twice before clicking. Danger may sometimes hide behind a shared link from someone you trust. Often, cybercriminals use compromised accounts to distribute malicious links to their contact lists. So if the link you received looks suspicious, don’t click on it. Even when it comes from your mom. It’s better to check if she sent you anything instead of risking being compromised by ransomware.
- Use secure networks. Public Wi-Fi networks aren’t safe, so cybercriminals use them to snoop on your internet surfing. If you absolutely need to connect using public Wi-Fi, consider installing a VPN to ensure a secure connection.
- Keep your software updated. Cybercriminals often obtain access to old software versions since they are full of security loopholes. Timely software updates can keep you out of trouble and ensure you get the most from the software you’re using.
- Use mobile protection. Mobile ransomware is a rising threat, particularly as smartphones hold vast amounts of personal data. To protect your phone from ransomware, ensure that you only install apps from trusted sources, keep your phone’s operating system updated, and avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading files from unverified sources. Consider using mobile-specific anti-malware apps for added protection.
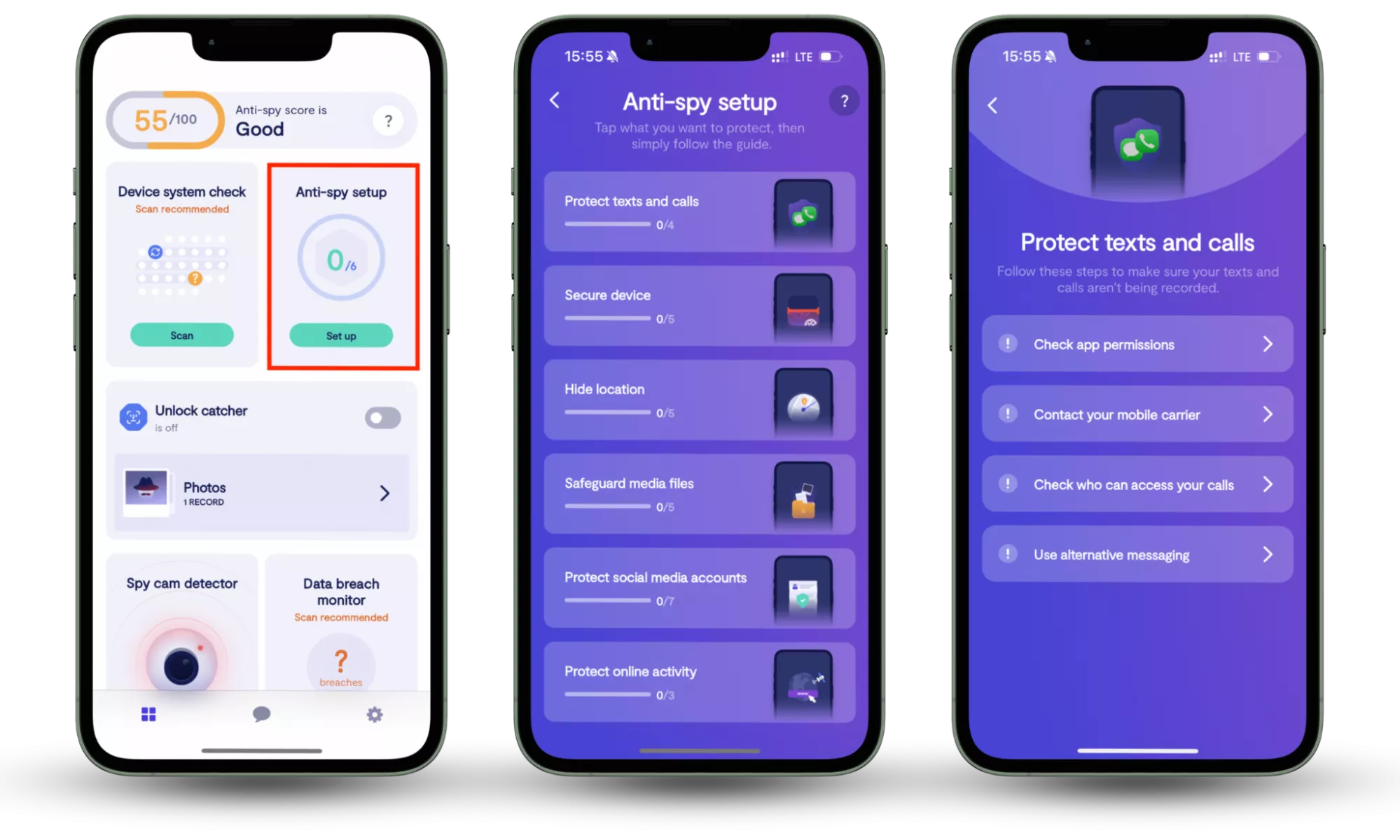
The Anti-spy setup feature in Clario Anti Spy is designed to help guide you through a comprehensive checklist of essential privacy settings, significantly reducing your exposure to spyware. Spyware is often the gateway for ransomware attacks, typically delivered via phishing emails or malicious attachments. By compromising your system, spyware can silently track and steal sensitive data, making it easier for cybercriminals to launch a ransomware attack.
With the Anti-spy setup, you can take proactive steps to secure your device. It walks you through the process of enabling vital security settings, such as turning off unnecessary permissions for apps, blocking trackers, and adjusting your system’s privacy preferences. By securing these areas, you lower the risk of inadvertently allowing spyware to gain access to your device, which could lead to a ransomware infection.
Here is how to use Clario Anti Spy’s Anti-spy setup feature:
- Download Clario Anti Spy, create an account, and sign in.
- Under the Anti-Spy setup section, select Set up.
- Follow the step-by-step guide to secure your devices and reduce the risk of malware and ransomware infections.
To keep your data safe, install anti-malware software like Clario Anti Spy. With Clario Anti Spy’s all-round protection, and 24/7 real human support, you can sleep soundly knowing that your digital security is in good hands.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ransomware attacks are a growing threat, but by taking proactive steps, you can protect your devices and data. With Clario Anti Spy’s Anti-spy setup, securing your privacy and reducing exposure to spyware has never been easier. Follow the step-by-step guide to strengthen your defenses against ransomware and other digital threats, ensuring your peace of mind while navigating the online world. Stay safe with Clario.
Read more:


