Table of contents
- Hacking Definition
- Types of Hackers
- Black Hat Hackers
- White Hat Hackers
- Grey Hat Hackers
- Other Types of Hackers
- Why Do Hackers Hack?
- How Does a Hacker Hack?
- How Did Hacking Come About?
- Is Hacking Illegal?
- How Do I Know If My Device Has Been Hacked?
- Hacking Prevention: 5 Expert Tips
- 1. Upgrade Your Password Safety
- 2. Keep Your Devices Up to Date
- 3. Know the Warning Signs of a Scam
- 4. Reduce Your Digital Footprint
- 5. Use a High-Quality Digital Security App
- Protect Yourself From Hacking
Hacking Definition
Many people think of hacking as when their family members start sending random messages all of a sudden. And while that can be the result of a hack, it isn’t always. So, what is hacking? And what is a hacker?
The usual definition of hacking is the act of exploiting flaws in a computer or network to gain unauthorized access to data. A person who is involved in the process of discovering and exploiting system weaknesses is known as a hacker.
Hackers use many tools and techniques to gain access to computer systems. And while hackers have a bad reputation for cybercrime, hacking isn’t always a malicious or illegal activity. For example, it can also be used to discover security flaws so that they can be fixed.
Types of Hackers
There are three main types of hackers: black hat, white hat, and gray hat hackers. Let’s take a look at how they differ from each other.
Black Hat Hackers
Black hat hackers are cybercriminals that use hacking to break into other people’s computer systems for nefarious reasons. Black hat hackers make illegal and unauthorized attempts to gain access to systems in order to damage files, hold the computer for a ransom, or steal important data.
Many black hat hackers work out of self-motivated reasoning. For example, they might target an organization or individual because they disagree with their business practices or ideology.
White Hat Hackers
White hat hackers are the opposite of black hat hackers. They are ethical agents who use hacking as a tool for good, helping to improve cybersecurity and combat the tools of black hat hackers, like malware.
White hat hackers are often hired by companies to uncover weaknesses in their computer networks to help strengthen the system’s security.
Grey Hat Hackers
Gray hat hackers are those who sit somewhere in the middle of black and white hat hackers. They don’t have the malicious intent of black hat hackers, but they also don’t have permission from organizations to gain access to their systems.
Often gray hat hackers will uncover weaknesses in a system without consent and then sell that information back to the organization. While technically performing a good deed, they do it under the demand of payment and without permission.
Other Types of Hackers
Most hackers are either black, white, or gray hat hackers. However, there are a few other subcategories:
- Green hat hackers. These are inexperienced or new hackers who use less technical methods and tools to access people’s data.
- Blue hat hackers. These are hackers who are employed by companies to improve their system security.
- Red hat hackers. Red hat hackers are vigilante hackers who combat black hat hackers directly by launching attacks against their devices and networks on the dark web.
Why Do Hackers Hack?
There’s a variety of reasons why hackers would want to gain access to computer systems, but the main reasons include:
- Financial gain. Hackers use various techniques to steal people’s data (like credit card information), hold computers for ransom, or steal money directly. This is the most common motivation for illegal hacking by far.
- Espionage. Many companies and countries employ hackers to steal information from their competitors or rival states in order to maintain a competitive advantage.
- State-sponsored hacking. During times of war, countries will use hackers to temporarily damage key networks in other countries. Since most vital infrastructure is now heavily digitized and connected to the internet, this can have a devastating effect.
- Hacktivism. This is when hackers use their skills to promote or fight for a political agenda or social movement. For example, environmentalist hackers might try to crash an oil company’s website.
- Notoriety. Many hackers are competitive and try to outdo each other. This is why hackers often target famous and more robust security systems of companies (like NASA or the FBI). With a successful hack, they gain fame in the hacker community.
How Does a Hacker Hack?
Hackers use many different tools and techniques depending on what they want to achieve. Here are some of the most common types of hacking:
- Social engineering attacks. Social engineering techniques use manipulation to get people to hand over access to their personal information. Usually, they deceive people using tricks like phishing scams so that people disclose their sensitive data. This data is then used to take their identity, gain access to their accounts, or steal their money.
- Infecting devices with malicious software. By targeting people with emails, messages, or websites with downloadable content (usually in the form of a link), hackers can easily install malware, spyware, adware, or ransomware on a victim’s computer.
- Discovering passwords. Hackers use several automated methods to guess or steal people’s passwords so that they can gain access to their accounts. For example, the brute force method involves using programs to guess every possible combination until the successful password is found.
- Logging people’s keystrokes. Different types of malicious software can be installed on a victim’s computer. Keyloggers are one of the most common programs a hacker will use. These log every keystroke made on a computer, sending it straight to the hacker. They then have all of the information they need to access the system.
How Did Hacking Come About?
Hacking hasn’t always had the cybercrime connotations that it has today. In fact, the term ‘hacking’ was invented in the 1960s by members of the MIT Tech Model Railroad Club who were trying to modify their train sets.
Early hackers focused on improving and testing programs with the goal of developing better software. However, as the world became more digitized, cybercrime increased in popularity.
As soon as personal computers became more widely available in the 1980s, there was a significant rise in black hat hacking. Hackers now tried to infiltrate systems for personal gain, inventing pirating software and viruses along the way.
This led to today, where we see a constant battle between hackers and cybersecurity experts, with ordinary people often caught in the middle. Nowadays, security breaches, hacks, and cybercrime are nearly unavoidable, and knowing how to spot and avoid cybercrime has become a household necessity.
Is Hacking Illegal?
While the specifics differ depending on your country, it’s usually illegal to try to gain access to, manipulate, or prevent the operation of a computer system that you don’t own and don’t have permission to interfere with.
In the U.S., it is illegal to gain access to a government, business, or personal computer with the goal of causing damage, obtaining something of value, or committing fraud.
How Do I Know If My Device Has Been Hacked?
If your device has been hacked, there may be several obvious red flags (or there may be none). Here are some things to keep your eye out for:
- There’s strange activity on your accounts. If you’ve been hacked, the hacker may have already discovered your login information and signed into one or multiple of your accounts. In this case, you’ll have to do a password reset to reclaim your accounts before more damage is done.
- Your device is running slower, hotter, or losing charge quicker than usual. Often, hackers will install malicious software that runs in the background on your device. This uses many hardware resources, causes the phone to slow down, and drains the battery much faster than usual.
- You’re seeing adverts in strange places. If you’re suddenly getting random pop-up advertisements or banner ads in places you’ve never seen, you’ve likely been infected with adware.
- Random apps appear. If you notice that you suddenly have apps or programs that you never installed on your device, malware is probably to blame. Malware will often authorize your device to install further malicious software in order to steal your data.
- Your friends and family receive messages or emails from you. Malware can cause your phone or computer to send spam messages to your contacts. The goal is to infect more people with the same malware that you’ve got. If someone tells you they received a strange message from you, there’s a good chance your device has been infected.
If you notice these symptoms, you need a way to confirm whether hidden malware is behind them.
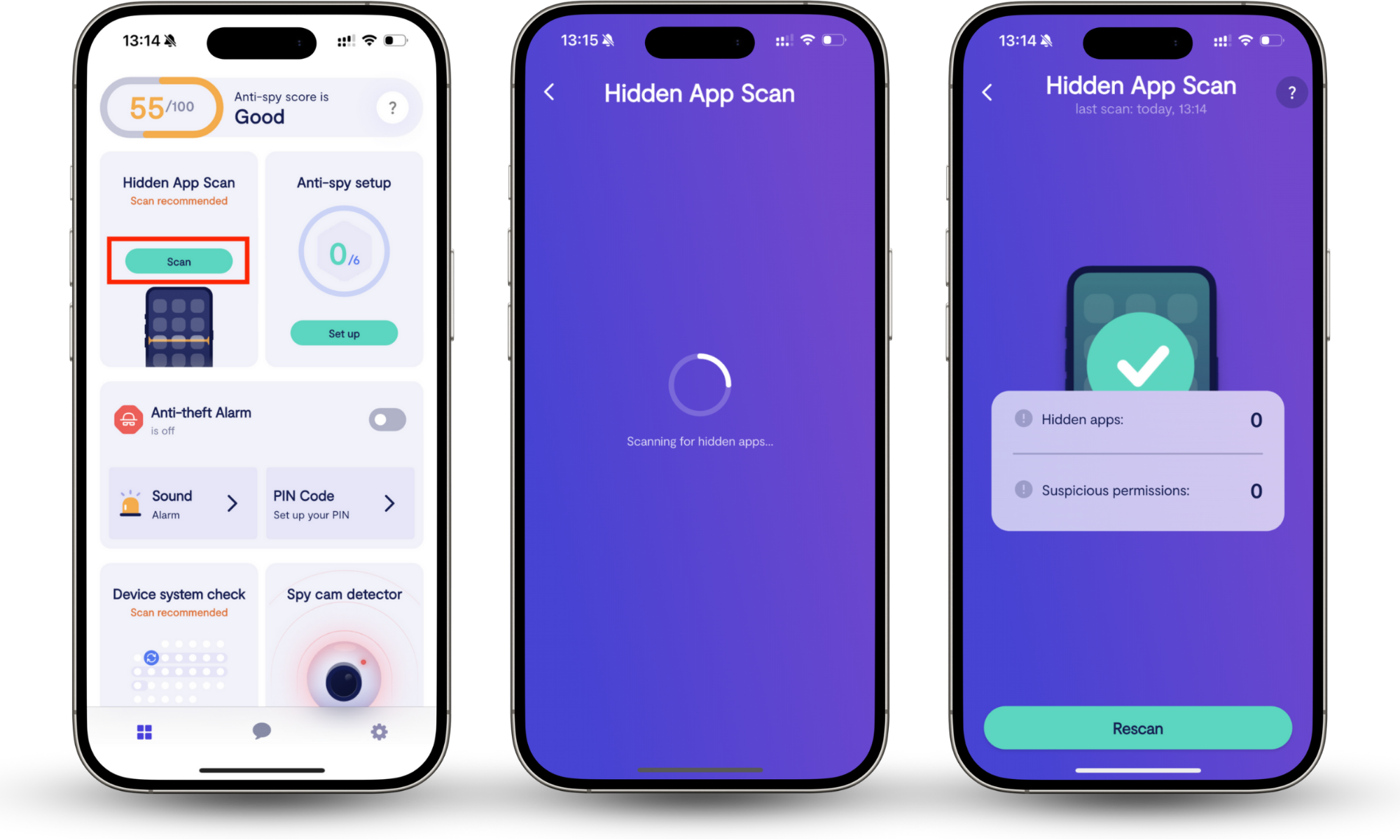
Hidden app scan helps by checking your phone for apps you never installed, reviewing their permissions, and flagging the ones that put your data at risk.
Follow these steps to run Clario Anti Spy’s Hidden app scan on your device:
- Download Clario Anti Spy and create an account.
- Select Hidden App Scan.
- Tap Scan to check your phone.
- Review suspicious apps and permissions.
- Follow the recommendations to remove threats.
Hacking Prevention: 5 Expert Tips
If your computer or phone has already been hacked, it’s often too late – the hacker has access to all of your data and personal information. That’s why when it comes to cybersecurity, being proactive is vital.
Here are 5 tips to help you prevent hacking:
1. Upgrade Your Password Safety
One of the main things hackers target is your passwords. With your passwords, they can access your accounts, impersonate you, and steal your hard-earned money. Here are some ways to improve your password security:
- Use strong passwords. Strong passwords have between 12-15 characters and are made up of a mix of upper- and lower-case letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Use unique passwords. If you use the same password for every account, as soon as a hacker gets a hold of it, you’re in trouble. Using unique passwords means that even if a hacker finds one password, they can only access the account associated with it. This lets you isolate the damage and quickly regain control of your account.
- Use a password manager. It can be hard to keep track of multiple passwords. A password manager helps by storing your passwords in a secure location for easy access.
- Use two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA). By using 2FA or MFA on your accounts, you make it much harder for a hacker to steal your identity – even if they have all of your personal information and passwords.
2. Keep Your Devices Up to Date
Device updates can be frustrating (especially when they’re coming in every day). However, they often provide you with additional security measures. New malware is released every day, and device manufacturers work hard to introduce countermeasures as quickly as possible to protect their user’s devices.
Whenever you receive a notification to update your device, whether it’s your Android, iPhone, Mac, or Windows PC, you should update it as quickly as possible. And this goes for apps too – updates for software often fix bugs and flaws that hackers can exploit. So, make sure these stay up to date as well.
3. Know the Warning Signs of a Scam
Many hackers will use deceptive tactics to try to get you to hand over your personal information or login credentials. To avoid this, you need to be up to speed with current internet safety tips and know what scams to be on the lookout for while using the internet.
- Be careful browsing. Before entering a website, you need to make sure it’s safe. Only ever visit websites with up-to-date security certificates. These are websites for which their URL begins with HTTPS rather than HTTP. They should also have a padlock icon next to the address bar.
- Be careful with apps. Don’t download apps from untrustworthy third-party sources. Stick to apps on the Apple App Store and Google Play Store which have good reviews. Likewise, carefully research any software you download to your personal computer (especially if it’s free).
- Be vigilant against phishing attacks. Phishing has become incredibly common in recent years. To avoid falling victim, you should only ever open emails from senders who you know and trust. Also, never click a link inside a text or email. Instead, load the website manually. And remember the golden rule – if it looks too good to be true, it is.
4. Reduce Your Digital Footprint
Your digital footprint is the amount of information and data you leave behind you online. This information remains on the internet forever and can be collected by malicious actors to steal your identity or personally identifiable information (PII).
To reduce your digital footprint:
- Delete any accounts (including email and social media accounts) that you no longer use. When you delete them, send an email to the company and request that your data be removed as soon as possible.
- Review your privacy settings on social media and ensure that they are as strict as possible.
- Avoid sharing personal information online, whether it’s on social media or elsewhere. Even information as seemingly harmless as your birthday can be used against you.
- Use privacy-enhancing tools like Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), anonymous browsers, and anti-tracking software.
5. Use a High-Quality Digital Security App
Hackers break in through weak points you rarely think about. An outdated system. A Wi-Fi network that feels safe but is not. A moment of panic when you do not know what step to take. That is why protection today means relying on more than one tool on your side.
With Clario Anti Spy, you get a full set of protections in one app. Clario Anti Spy helps you block hackers, catch threats early, and know exactly what to do when something feels wrong.
Here are some of Clario Anti Spy features you can use right away:
- Device System Check
Hackers love outdated systems because they are full of flaws. Clario Anti Spy’s Device System Check scans your operating system, points out jailbreaks or missed updates, and gives you clear steps to fix them.
- Spy Cam Detector
If hackers sneak onto your Wi-Fi, they can watch traffic and target your devices. Clario Anti Spy’s Spy Cam Detector scans your network, shows every connected device, and helps you kick out strangers before they do damage.
- Data Breach Monitor
Hackers often use leaked emails and passwords as keys to your accounts. Clario Anti Spy’s Data Breach Monitor alerts you if your details appear in a breach so you can act before they are misused.
- 24/7 Expert Help
When you suspect you’ve been hacked, the hardest part is not knowing what comes next. Clario Anti Spy’s Expert Help connects you with real specialists at any time of day, so you are never left guessing.
Protect Yourself From Hacking
Staying safe online is harder than ever, with hackers always looking for new ways in. It can feel overwhelming to keep up, but you don’t have to do it alone. Clario Anti Spy gives you the tools to protect your phone, watch for breaches, and get expert help any time you need it. Take control of your security today and keep your data safe.


